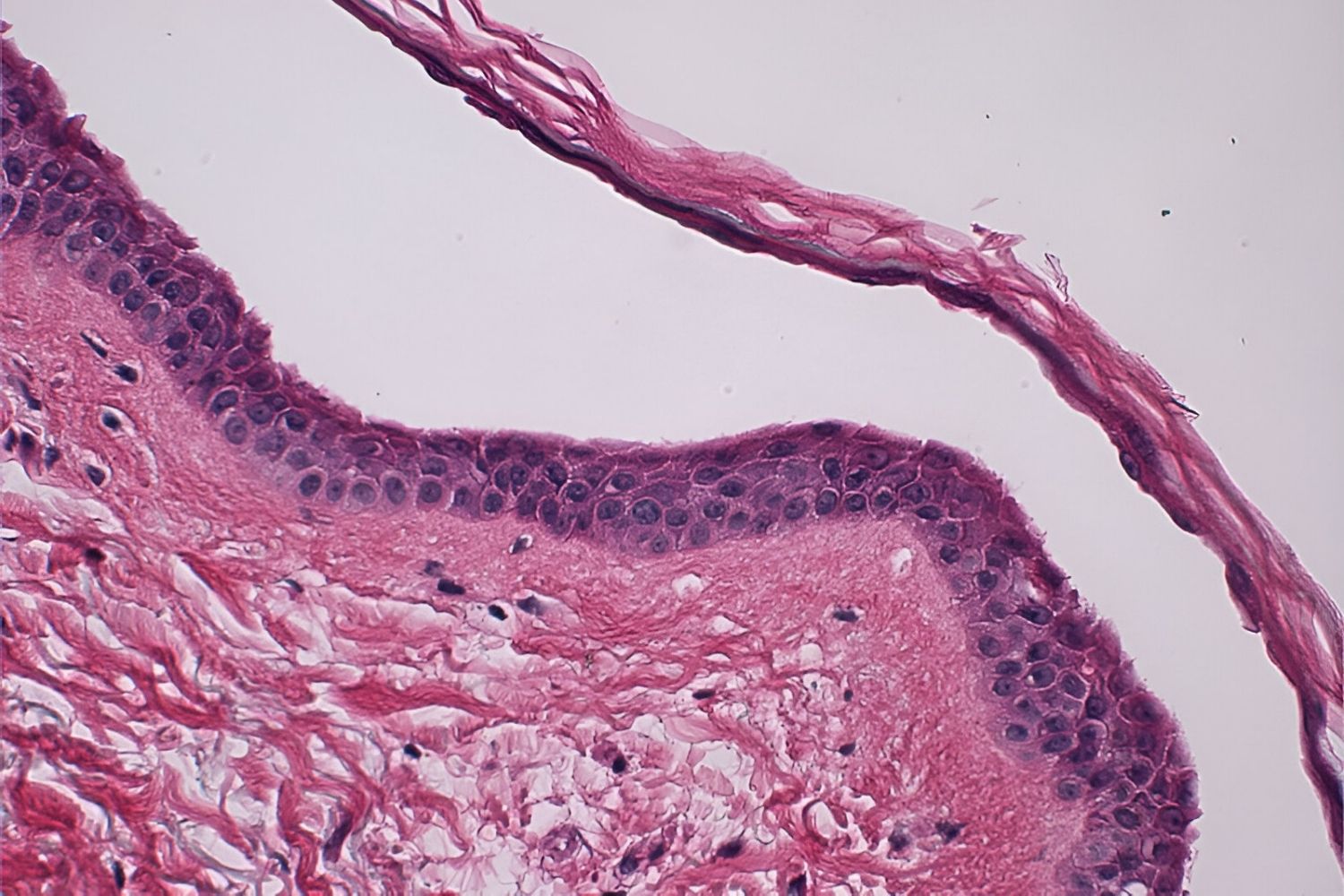
What is Pemphigus Foliaceus? Pemphigus Foliaceus is a rare skin disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This condition causes blisters and sores, primarily on the skin's surface. Unlike other forms of pemphigus, it doesn't affect the mouth. The blisters are fragile, often breaking easily, leaving raw, painful areas. This autoimmune disease can be challenging to diagnose due to its similarity to other skin conditions. Treatment usually involves medications to suppress the immune system, helping to reduce symptoms and prevent further skin damage. Understanding this condition is crucial for managing symptoms effectively and improving quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference in managing this condition. If you or someone you know is experiencing unexplained skin issues, consulting a healthcare professional is essential.
Key Takeaways:
- Pemphigus Foliaceus is a rare autoimmune disorder causing skin blisters. Treatment involves medication, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing research for better understanding and management.
- Living with Pemphigus Foliaceus requires a gentle skin care routine, sun protection, stress management, and support from healthcare providers and community. Ongoing research offers hope for better treatments.
Understanding Pemphigus Foliaceus
Pemphigus foliaceus is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the skin. It causes blisters and sores on the skin's surface, often leading to discomfort and complications. Let's explore some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Autoimmune Nature: Pemphigus foliaceus occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This results in the separation of skin layers, forming blisters.
-
Blister Formation: The blisters in pemphigus foliaceus are superficial, meaning they form on the outermost layer of the skin. They are fragile and can easily rupture.
-
Common Areas Affected: Blisters typically appear on the scalp, face, and trunk. However, they can also spread to other parts of the body.
-
No Mucous Membrane Involvement: Unlike other forms of pemphigus, pemphigus foliaceus does not usually affect mucous membranes such as those in the mouth.
-
Age of Onset: This condition can occur at any age, but it most commonly affects middle-aged individuals.
-
Gender Prevalence: Pemphigus foliaceus affects both men and women equally, showing no gender preference.
-
Genetic Factors: There is a genetic predisposition to pemphigus foliaceus, meaning it can run in families.
-
Environmental Triggers: Certain environmental factors, such as sun exposure, can exacerbate the symptoms of pemphigus foliaceus.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is typically made through a skin biopsy, where a small sample of skin is examined under a microscope.
-
Direct Immunofluorescence: This test is often used to confirm the diagnosis by detecting specific antibodies in the skin.
Treatment and Management
Managing pemphigus foliaceus involves a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some key points about treatment options.
-
Corticosteroids: These are the primary treatment for reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system.
-
Immunosuppressants: Drugs like azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil may be used to help control the immune response.
-
Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments can be applied directly to the skin to help heal blisters and reduce itching.
-
Antibiotics: These may be prescribed if there is a secondary bacterial infection due to open sores.
-
Avoiding Triggers: Patients are advised to avoid known triggers, such as excessive sun exposure, to prevent flare-ups.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
-
Dietary Considerations: Some patients find that certain foods can trigger symptoms, so dietary adjustments may be necessary.
-
Emotional Support: Living with a chronic condition can be challenging, so emotional and psychological support is important.
-
Patient Education: Understanding the condition and its management is key to improving quality of life.
-
Research and Advances: Ongoing research is focused on finding more effective treatments and understanding the underlying causes of pemphigus foliaceus.
Historical and Cultural Aspects
Pemphigus foliaceus has been recognized for centuries, with historical references and cultural implications.
-
Historical References: Ancient texts describe conditions similar to pemphigus foliaceus, indicating its long-standing presence.
-
Cultural Beliefs: In some cultures, skin conditions like pemphigus foliaceus were misunderstood and often associated with myths or superstitions.
-
Medical Advancements: Over time, advancements in medical science have improved the understanding and treatment of pemphigus foliaceus.
-
Famous Cases: Some historical figures are believed to have suffered from pemphigus foliaceus, though documentation is limited.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Modern awareness campaigns aim to educate the public and reduce stigma associated with skin conditions.
Living with Pemphigus Foliaceus
Living with pemphigus foliaceus requires adaptation and resilience. Here are some insights into daily life with this condition.
-
Skin Care Routine: A gentle skin care routine is essential to prevent irritation and manage symptoms.
-
Clothing Choices: Wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing can help reduce discomfort and prevent blistering.
-
Sun Protection: Sunscreen and protective clothing are important for minimizing sun exposure, a known trigger.
-
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated supports skin health and overall well-being.
-
Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation may be beneficial.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide a sense of community and shared experiences.
-
Communication with Healthcare Providers: Open communication with doctors ensures that treatment plans are effective and tailored to individual needs.
-
Adapting Activities: Some activities may need to be modified to prevent skin damage or discomfort.
-
Travel Considerations: Planning ahead for travel, including packing necessary medications and skin care products, is important.
-
Positive Outlook: Maintaining a positive outlook and focusing on what can be controlled can improve quality of life.
Research and Future Directions
Research continues to shed light on pemphigus foliaceus, offering hope for better treatments and understanding.
-
Genetic Research: Studies are exploring the genetic factors that contribute to pemphigus foliaceus.
-
New Therapies: Researchers are investigating new therapies that target specific immune pathways involved in the condition.
-
Biological Treatments: Biologics, a type of medication that targets specific parts of the immune system, are being studied for their potential benefits.
-
Clinical Trials: Ongoing clinical trials are testing the safety and efficacy of new treatments for pemphigus foliaceus.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries collect data to help researchers understand the condition better and develop targeted treatments.
-
International Collaboration: Researchers worldwide are collaborating to share knowledge and advance the understanding of pemphigus foliaceus.
-
Public Awareness: Increased public awareness can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes for patients.
-
Advocacy Efforts: Advocacy groups work to support patients and promote research funding for pemphigus foliaceus.
-
Technological Advances: Advances in technology, such as telemedicine, are improving access to care for patients with pemphigus foliaceus.
-
Future Prospects: The future holds promise for more effective treatments and a better quality of life for those affected by pemphigus foliaceus.
Miscellaneous Facts
A few more intriguing tidbits about pemphigus foliaceus that might surprise you.
-
Animal Cases: Pemphigus foliaceus can also occur in animals, including dogs and cats, though it is rare.
-
Geographical Variations: The prevalence of pemphigus foliaceus varies by region, with certain areas reporting higher rates.
-
Seasonal Patterns: Some patients notice seasonal patterns in their symptoms, with flare-ups occurring more frequently in certain weather conditions.
-
Rare Complications: In rare cases, pemphigus foliaceus can lead to complications such as secondary infections or scarring.
-
Community Support: Online communities and forums provide a platform for patients to share experiences and support each other.
Final Thoughts on Pemphigus Foliaceus
Pemphigus foliaceus, a rare autoimmune disorder, affects the skin, causing blisters and sores. Understanding this condition is crucial for those affected and their caregivers. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life. While the exact cause remains unknown, genetics and environmental factors play a role. Treatment often involves corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals ensure effective management of the disease. Support groups and online communities offer valuable resources and emotional support for patients and families. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Though challenging, living with pemphigus foliaceus is manageable with the right care and support. By raising awareness and fostering understanding, we can improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
