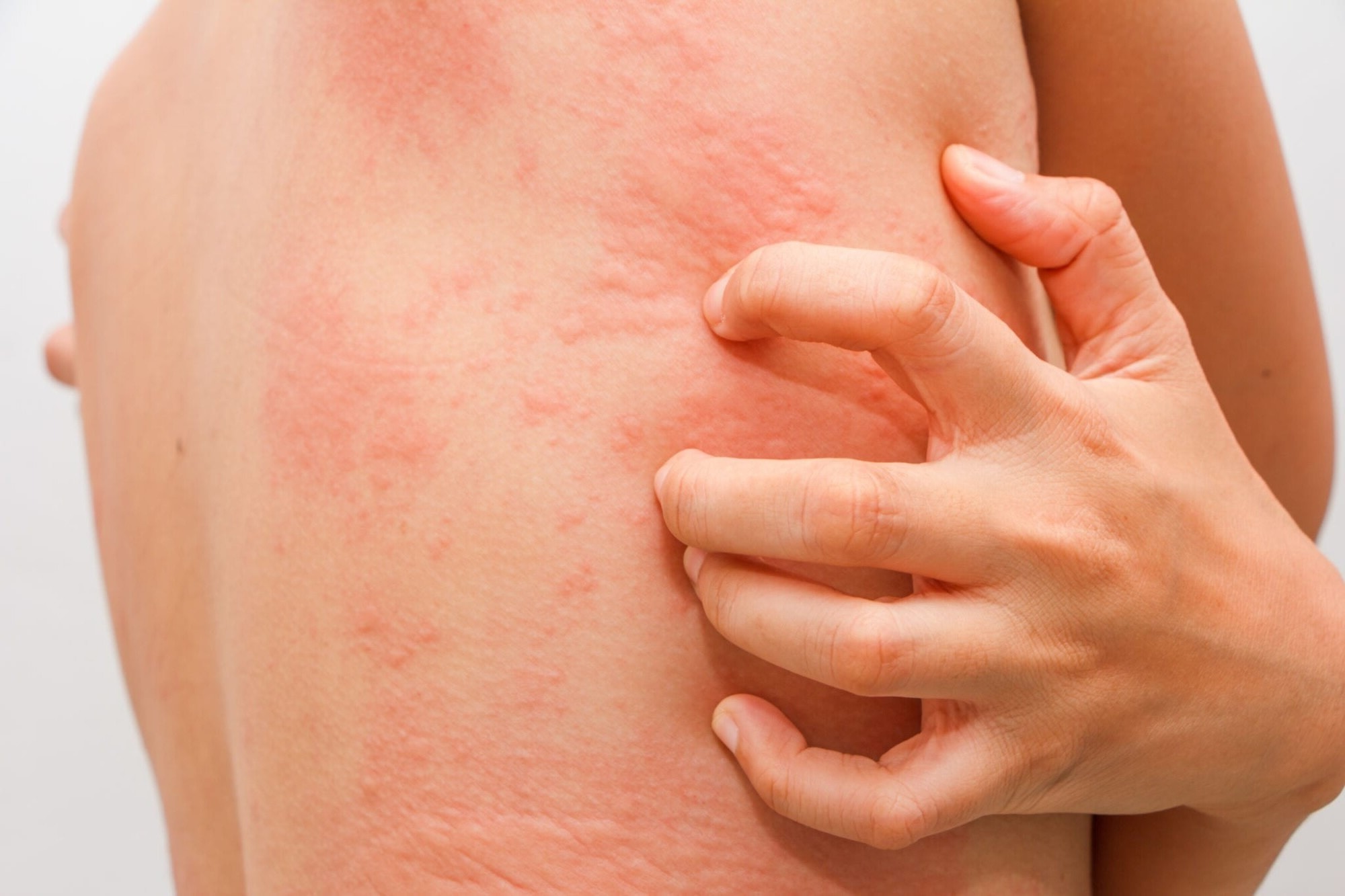
Mast Cell Disease is a rare condition that affects the body's mast cells, which play a crucial role in the immune system. These cells release chemicals like histamine during allergic reactions. When someone has this disease, their mast cells behave abnormally, leading to a range of symptoms from mild to severe. Common symptoms include itching, swelling, abdominal pain, and even anaphylaxis. Diagnosis often involves blood tests, skin biopsies, and bone marrow exams. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms through medications like antihistamines and mast cell stabilizers. Understanding this disease can help improve the quality of life for those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- Mast Cell Disease involves abnormal mast cell behavior, causing a range of symptoms. Proper diagnosis and management are crucial for improving quality of life.
- Understanding different types of Mast Cell Disease and their symptoms can aid in timely intervention and personalized treatment. Accessing support and resources is essential for coping with the impact on daily life.
What is Mast Cell Disease?
Mast Cell Disease (MCD) involves abnormal growth or activation of mast cells, which play a role in allergic reactions. Understanding this condition can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- MCD can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe.
- Mast cells release chemicals like histamine, leading to allergic reactions.
- Symptoms often mimic other conditions, making diagnosis tricky.
- MCD can affect multiple organs, including skin, gastrointestinal tract, and bones.
- The disease can be systemic or localized.
Types of Mast Cell Disease
There are several forms of MCD, each with unique characteristics. Knowing the differences can aid in proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Cutaneous Mastocytosis primarily affects the skin.
- Systemic Mastocytosis impacts internal organs.
- Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) involves abnormal mast cell activation without increased numbers.
- Mastocytoma is a benign tumor made of mast cells.
- Monoclonal Mast Cell Activation Syndrome is a rare form with genetic mutations.
Symptoms of Mast Cell Disease
Symptoms vary widely, making it essential to recognize the signs for timely intervention.
- Flushing and itching are common skin symptoms.
- Gastrointestinal issues include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Cardiovascular symptoms can involve low blood pressure and fainting.
- Respiratory problems may include wheezing and shortness of breath.
- Neurological symptoms like headaches and brain fog are also reported.
Diagnosing Mast Cell Disease
Accurate diagnosis requires a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests.
- Blood tests can measure tryptase levels, a marker of mast cell activation.
- Bone marrow biopsies help identify systemic involvement.
- Skin biopsies are used for diagnosing cutaneous forms.
- Genetic testing can detect mutations linked to MCD.
- Urine tests measure histamine and its metabolites.
Treatment Options for Mast Cell Disease
Managing MCD involves a multi-faceted approach to control symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Antihistamines are commonly used to reduce allergic reactions.
- Mast cell stabilizers help prevent mast cells from releasing chemicals.
- Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in severe cases.
- Epinephrine auto-injectors are essential for emergency situations.
- Immunotherapy may be considered for some patients.
Living with Mast Cell Disease
Daily life with MCD requires careful management and lifestyle adjustments.
- Avoiding known triggers is crucial for symptom control.
- Dietary changes can help manage gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Stress management techniques like yoga and meditation can be beneficial.
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential.
- Support groups offer emotional and practical support.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of MCD.
- New medications are being developed to target mast cell pathways.
- Clinical trials are exploring the efficacy of existing drugs for MCD.
- Genetic research may lead to personalized treatment options.
- Improved diagnostic tools are being investigated.
- Patient registries help track long-term outcomes and treatment effectiveness.
Myths and Misconceptions
Clearing up common myths can help patients and caregivers better understand MCD.
- MCD is not just an allergy; it involves abnormal mast cell behavior.
- Symptoms can occur without obvious triggers.
- MCD is not always visible; internal symptoms can be severe.
- It is not a psychological condition, though stress can worsen symptoms.
- Not all patients will have the same symptoms or severity.
Support and Resources
Access to resources and support networks can make a significant difference.
- Organizations like The Mastocytosis Society provide valuable information.
- Online forums offer a platform for sharing experiences and advice.
- Educational materials can help patients and caregivers stay informed.
- Advocacy groups work to raise awareness and funding for research.
- Healthcare providers specializing in MCD can offer expert care.
Impact on Daily Life
Understanding how MCD affects daily activities can help in planning and management.
- Work and school accommodations may be necessary.
- Travel requires careful planning to avoid triggers.
- Exercise should be tailored to individual tolerance levels.
- Social activities might need adjustments to manage symptoms.
- Mental health support is important for coping with chronic illness.
Final Thoughts on Mast Cell Disease
Mast Cell Disease, though rare, impacts many lives. Understanding its symptoms, triggers, and treatments can make a huge difference for those affected. From skin reactions to severe anaphylaxis, the range of symptoms is broad. Early diagnosis and proper management are key. Patients often need to avoid specific triggers and may rely on medications to control symptoms. Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends is crucial. Raising awareness about this condition can lead to better research, treatments, and support networks. If you or someone you know shows signs of Mast Cell Disease, seek medical advice. Knowledge is power, and staying informed helps manage this challenging condition. Remember, every small step in understanding and supporting those with Mast Cell Disease makes a big difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
