Hypogonadism is a condition where the body doesn't produce enough sex hormones. These hormones play a crucial role in growth, development, and overall health. Testosterone in men and estrogen in women are the primary hormones affected. Symptoms can vary widely, from fatigue and depression to reduced muscle mass and infertility. Understanding hypogonadism is essential for managing its effects and improving quality of life. This blog post will provide 50 facts about hypogonadism, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, treatments, and more. Whether you're personally affected or just curious, these facts will offer valuable insights into this often misunderstood condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Hypogonadism affects both men and women, impacting hormone levels and overall health. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life.
- Lifestyle changes, hormone therapy, and regular check-ups are crucial for managing hypogonadism and living a fulfilling life.
What is Hypogonadism?
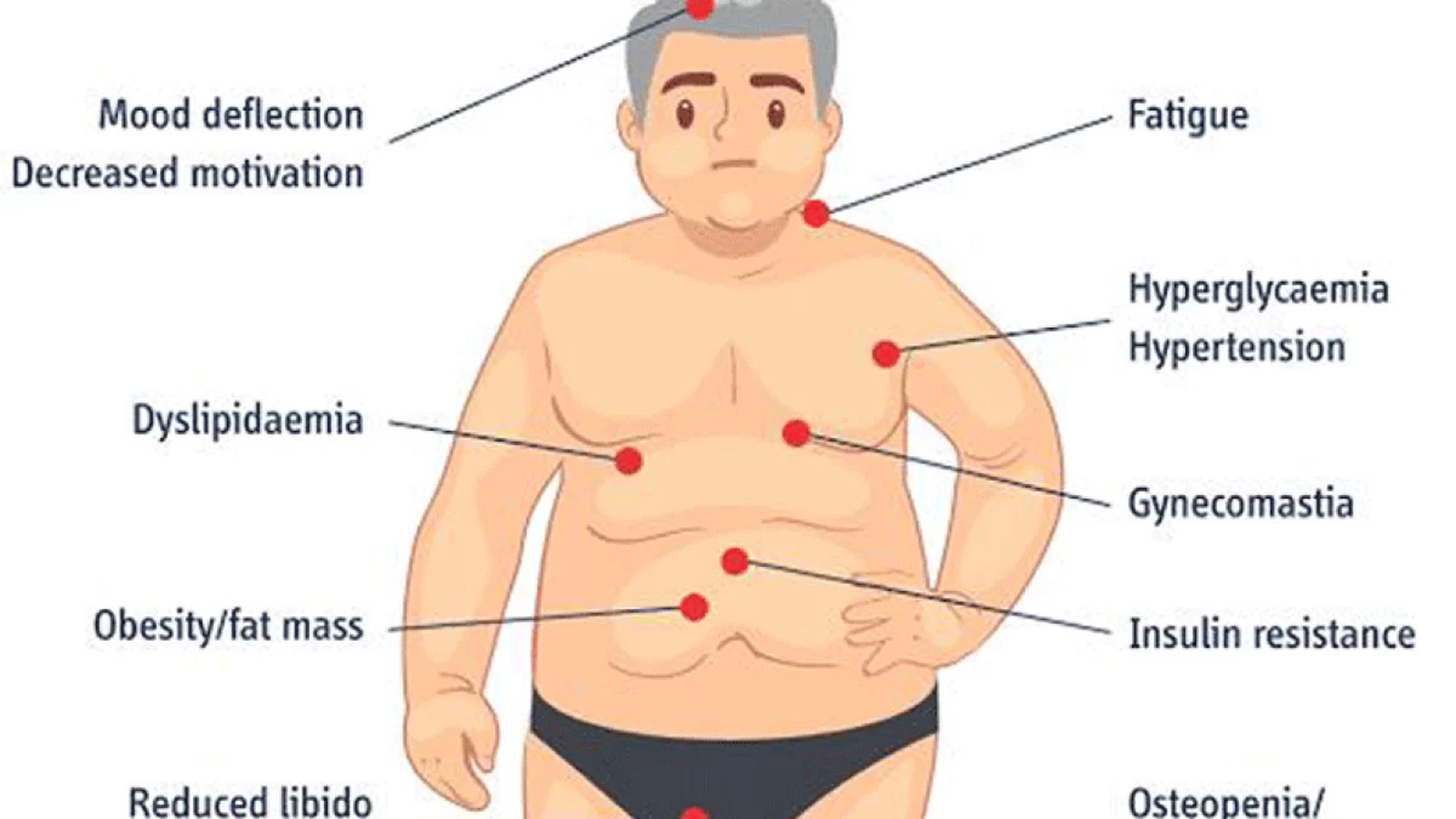
Hypogonadism is a medical condition where the body doesn't produce enough sex hormones. These hormones are crucial for various bodily functions and overall health. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about hypogonadism.
-
Hypogonadism can affect both men and women, though it manifests differently in each gender.
-
In men, it often results in low testosterone levels, impacting muscle mass, bone density, and mood.
-
Women with hypogonadism may experience irregular menstrual cycles or early menopause.
-
Primary hypogonadism originates from problems in the gonads (testes or ovaries).
-
Secondary hypogonadism is due to issues in the brain's hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
Causes of Hypogonadism
Understanding the causes can help in early diagnosis and treatment. Here are some common causes:
-
Genetic disorders like Klinefelter syndrome can lead to hypogonadism.
-
Autoimmune diseases may attack the gonads, reducing hormone production.
-
Severe infections, such as mumps, can damage the testes.
-
Radiation or chemotherapy treatments for cancer can impair hormone production.
-
Chronic illnesses like diabetes and obesity are linked to secondary hypogonadism.
Symptoms of Hypogonadism
Recognizing symptoms early can lead to better management. Here are some signs to watch out for:
-
In men, reduced libido and erectile dysfunction are common symptoms.
-
Women may experience hot flashes and night sweats.
-
Both genders might notice fatigue and decreased energy levels.
-
Mood swings and depression can also be indicators.
-
Loss of body hair and reduced muscle mass are physical signs in men.
Diagnosis of Hypogonadism
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here's how doctors diagnose hypogonadism:
-
Blood tests measure hormone levels to confirm the condition.
-
Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans check for abnormalities in the brain or gonads.
-
Genetic testing can identify inherited conditions causing hypogonadism.
-
Bone density tests might be conducted to assess the impact on bone health.
-
A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential parts of the diagnosis process.
Treatment Options for Hypogonadism
Various treatments can help manage hypogonadism. Here are some common options:
-
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a primary treatment for both men and women.
-
Testosterone replacement can be administered through gels, patches, or injections.
-
Women might receive estrogen or progesterone therapy.
-
Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and exercise, can improve symptoms.
-
Fertility treatments may be necessary for those wanting to conceive.
Impact on Quality of Life
Hypogonadism can significantly affect daily life. Understanding its impact can help in managing the condition better:
-
Reduced energy levels can make daily tasks challenging.
-
Emotional symptoms like depression can strain relationships.
-
Physical changes might affect self-esteem and body image.
-
Sexual dysfunction can impact intimate relationships.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life significantly.
Hypogonadism and Aging
Aging can influence the onset and progression of hypogonadism. Here's how:
-
Testosterone levels naturally decline with age in men.
-
Postmenopausal women are at higher risk due to decreased estrogen levels.
-
Age-related hypogonadism can exacerbate other health conditions like osteoporosis.
-
Regular health check-ups can help monitor hormone levels as one ages.
-
Healthy lifestyle choices can mitigate some age-related effects of hypogonadism.
Hypogonadism in Adolescents
Adolescents can also be affected by hypogonadism, impacting their development. Here are some key points:
-
Delayed puberty is a common sign in adolescents with hypogonadism.
-
Boys may experience slower growth of facial and body hair.
-
Girls might have delayed breast development and menstrual cycles.
-
Hormone therapy can help stimulate normal puberty in affected adolescents.
-
Early intervention is crucial for normal physical and emotional development.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths surrounding hypogonadism. Let's clear up some common misconceptions:
-
Hypogonadism is not just an "old man's disease"; it can affect people of all ages.
-
It's not always related to lifestyle choices; genetic factors play a significant role.
-
Hormone replacement therapy is safe when monitored by a healthcare professional.
-
Hypogonadism doesn't always lead to infertility; many affected individuals can still conceive with treatment.
-
It's not a sign of weakness or failure; it's a medical condition that requires proper management.
Living with Hypogonadism
Managing hypogonadism involves more than just medical treatment. Here are some tips for living with the condition:
-
Regular exercise can help maintain muscle mass and bone density.
-
A balanced diet supports overall health and hormone production.
-
Mental health support is crucial for managing emotional symptoms.
-
Joining support groups can provide a sense of community and shared experiences.
-
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure effective management of the condition.
Final Thoughts on Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism affects many people, but understanding it can lead to better management and treatment. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for anyone dealing with this condition. Whether it's primary hypogonadism or secondary hypogonadism, early diagnosis and proper medical care can make a significant difference.
Hormone replacement therapy and lifestyle changes often help manage symptoms effectively. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are essential. Don't ignore signs like fatigue, low libido, or mood changes.
Awareness and education about hypogonadism can empower individuals to seek help and improve their quality of life. Stay informed, stay proactive, and don't hesitate to reach out for support. Hypogonadism doesn't have to control your life; with the right approach, you can manage it successfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
