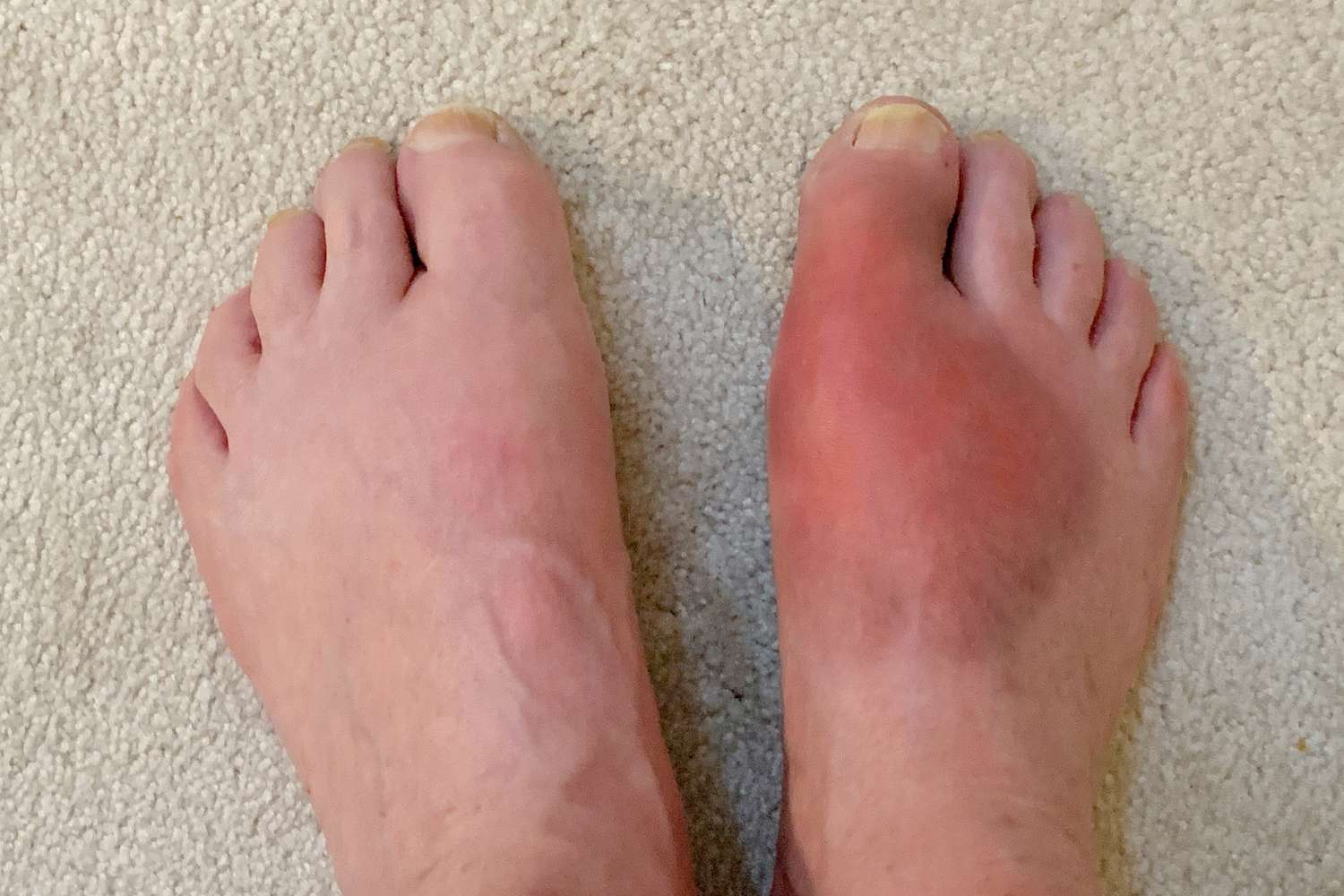
Gout, a type of arthritis, can be a real pain—literally! It's caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, leading to sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling in the joints. But what exactly causes this painful condition? Uric acid builds up when the body breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks. When kidneys can't eliminate enough uric acid, crystals form in the joints, causing inflammation. While anyone can get gout, it's more common in men and those with a family history. Lifestyle choices like diet and alcohol consumption play a big role too. Managing gout involves medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes avoiding certain foods. Understanding gout helps in managing symptoms and preventing future flare-ups. Stay informed and take control of your health!
Key Takeaways:
- Gout is a painful type of arthritis caused by high uric acid levels. It can be managed with lifestyle changes and medication, and it's not just a "rich man's disease."
- Understanding gout symptoms, triggers, and treatment options can help people manage the condition effectively and lead healthy, active lives.
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe pain, redness, and swelling in the joints. It often affects the big toe but can occur in other joints too. Understanding gout can help manage its symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Gout is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. When uric acid builds up, it forms sharp crystals in the joints, leading to pain and inflammation.
-
The condition is more common in men than women. Men are more likely to develop gout, especially between the ages of 30 and 50.
-
Women are at higher risk after menopause. Post-menopausal women have a higher chance of developing gout due to changes in hormone levels.
-
Gout attacks often occur at night. The body's temperature drops during sleep, which can trigger the formation of uric acid crystals.
-
The big toe is the most commonly affected joint. Known as podagra, this is a classic symptom of gout.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gout. Knowing these can help in taking preventive measures.
-
Diet plays a significant role in gout development. Foods high in purines, like red meat and seafood, can raise uric acid levels.
-
Alcohol consumption is a known trigger. Beer and spirits, in particular, can increase uric acid production.
-
Obesity increases the risk of gout. Excess body weight can lead to higher uric acid levels and increased stress on joints.
-
Certain medications can contribute to gout. Diuretics and some blood pressure medications may raise uric acid levels.
-
Family history can influence gout risk. If a family member has gout, the likelihood of developing it increases.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of gout is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
-
Gout attacks are sudden and intense. They often start with a burning sensation in the affected joint.
-
Swelling and redness are common symptoms. The affected area may become tender and warm to the touch.
-
Limited joint movement can occur. Severe pain and swelling can restrict movement in the affected joint.
-
Diagnosis often involves a joint fluid test. Doctors may extract fluid from the joint to check for uric acid crystals.
-
Blood tests can measure uric acid levels. High levels may indicate gout, but not everyone with high uric acid develops the condition.
Treatment and Management
Managing gout involves lifestyle changes and medication to reduce symptoms and prevent future attacks.
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used. These medications help reduce pain and swelling during gout attacks.
-
Colchicine is another treatment option. This medication can relieve gout symptoms if taken soon after an attack begins.
-
Corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe cases. These drugs can quickly reduce inflammation and pain.
-
Allopurinol helps lower uric acid levels. This medication is used for long-term management to prevent future attacks.
-
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact gout management. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, and avoiding trigger foods can help.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
Preventing gout involves making smart lifestyle choices and being mindful of potential triggers.
-
Staying hydrated is essential. Drinking plenty of water helps flush uric acid from the body.
-
Limiting alcohol intake can reduce risk. Cutting back on beer and spirits can help prevent gout attacks.
-
Eating a balanced diet is crucial. Focus on low-purine foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
-
Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight. Physical activity reduces stress on joints and lowers uric acid levels.
-
Monitoring uric acid levels is important. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help manage gout effectively.
Interesting Facts About Gout
Gout has a long history and some surprising facts that might intrigue you.
-
Gout was once known as the "disease of kings." Historically, it was associated with wealthy individuals who indulged in rich foods and alcohol.
-
Famous figures like Benjamin Franklin and Leonardo da Vinci had gout. These historical personalities are believed to have suffered from the condition.
-
Gout is one of the oldest recorded diseases. Ancient Egyptians documented symptoms similar to gout over 4,000 years ago.
-
The term "gout" comes from the Latin word "gutta," meaning drop. It refers to the belief that gout was caused by drops of bad humors.
-
Gout can affect any joint in the body. While the big toe is most common, it can also impact knees, ankles, and wrists.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths surrounding gout that can lead to misunderstandings about the condition.
-
Gout is not just a "rich man's disease." While diet plays a role, genetics and other factors contribute to its development.
-
Only older adults get gout. Although more common in older adults, younger people can also develop the condition.
-
Gout is not always caused by poor diet. Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to high uric acid levels.
-
All joint pain is not gout. Other forms of arthritis and conditions can cause similar symptoms.
-
Gout is not always a lifelong condition. With proper management, many people can control their symptoms and prevent future attacks.
Gout in Modern Times
Today, gout remains a common condition, but advances in medicine have improved its management.
-
Gout affects millions worldwide. It's estimated that over 8 million people in the United States alone have gout.
-
Telemedicine is making gout management more accessible. Virtual consultations allow patients to receive care without leaving home.
-
Research is ongoing to find new treatments. Scientists are exploring new medications and therapies to improve gout management.
-
Public awareness campaigns are helping educate people about gout. These initiatives aim to reduce stigma and promote understanding of the condition.
-
Support groups provide valuable resources for those with gout. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can offer support and advice.
Fun Facts About Gout
Some lighthearted facts about gout can add a bit of humor to an otherwise serious topic.
-
Gout has been featured in literature and art. Writers and artists have depicted gout in various works throughout history.
-
Some animals can get gout too. Birds and reptiles are known to develop gout due to high uric acid levels.
-
Gout was once treated with leeches. In the past, doctors believed that removing blood could cure the condition.
-
The "gout diet" has become a popular trend. Some people follow a low-purine diet to prevent gout, even if they don't have the condition.
-
Gout has inspired creative nicknames. Terms like "the unwalkable disease" and "the patrician malady" have been used to describe it.
Final Thoughts on Gout
Gout is a complex condition with a rich history and many facets. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition effectively.
-
Gout awareness is increasing. More people are learning about the condition and how to manage it.
-
Advancements in medicine are improving gout treatment. New medications and therapies offer hope for better management.
-
Lifestyle changes can make a big difference. Simple adjustments can help prevent gout attacks and improve quality of life.
-
Education is key to managing gout. Understanding the condition empowers individuals to take control of their health.
-
Gout is a manageable condition. With the right approach, many people can lead healthy, active lives despite having gout.
Gout: A Glimpse into the Past and Present
Gout, often called the "disease of kings," has a rich history and remains relevant today. This painful form of arthritis results from excess uric acid in the blood, leading to joint inflammation. Historically, it was associated with indulgence in rich foods and alcohol, but modern research shows genetics and lifestyle play significant roles.
Managing gout involves a combination of dietary changes, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. Reducing intake of purine-rich foods like red meat and shellfish can help, as can staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy weight. Medications like allopurinol and colchicine are often prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Understanding gout's causes and treatments empowers individuals to take control of their health. By staying informed and proactive, those affected can lead more comfortable lives, minimizing the impact of this ancient yet persistent ailment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
