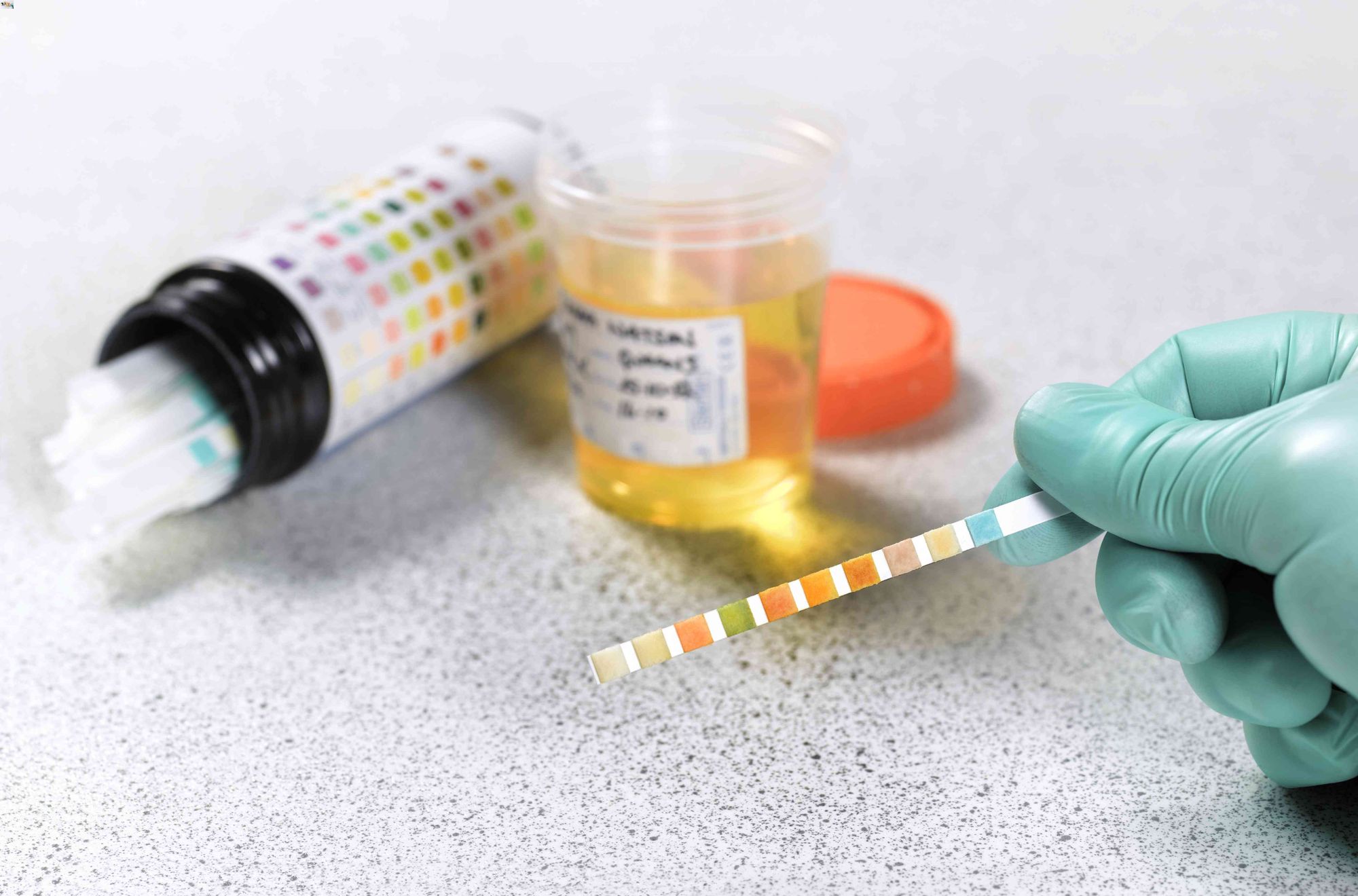
Glycosuria is a condition where glucose spills into the urine. This happens when blood sugar levels exceed the kidneys' ability to reabsorb glucose. Common causes include diabetes, kidney issues, and certain medications. Symptoms might be subtle, like frequent urination or thirst. Diagnosis often involves urine tests. Treatment focuses on managing the underlying cause. Prevention includes regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle. Interesting fact: Glycosuria can sometimes occur during pregnancy. Want to know more? Keep reading to uncover 50 fascinating facts about this condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Glycosuria is when sugar ends up in your pee, and it can happen to anyone, not just people with diabetes. It's important to watch for symptoms like frequent peeing and thirst.
- To prevent glycosuria, it's essential to keep your blood sugar levels in check by exercising, eating healthy, and staying hydrated. Regular check-ups and lifestyle changes can make a big difference.
What is Glycosuria?
Glycosuria is a condition where glucose is present in the urine. This happens when the kidneys fail to reabsorb glucose back into the bloodstream. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
- Glycosuria occurs when blood glucose levels exceed the renal threshold.
- The renal threshold for glucose is typically around 180 mg/dL.
- Glycosuria can be a sign of diabetes mellitus.
- It can also occur in pregnancy, known as gestational glycosuria.
- Not all glycosuria cases indicate diabetes; some are benign.
Causes of Glycosuria
Understanding what causes glycosuria can help in managing and preventing it. Here are some common causes.
- High blood sugar levels due to diabetes.
- Genetic mutations affecting kidney function.
- Certain medications like diuretics.
- Hormonal disorders such as Cushing's syndrome.
- Kidney diseases that impair glucose reabsorption.
Symptoms of Glycosuria
Recognizing the symptoms can lead to early diagnosis and treatment. Here are some signs to watch for.
- Frequent urination.
- Increased thirst.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Sweet-smelling urine.
Diagnosis of Glycosuria
Diagnosing glycosuria involves several tests and procedures. Here’s what you need to know.
- Urine dipstick test is a common initial test.
- Blood glucose tests help confirm the diagnosis.
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) can be used.
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test measures long-term glucose levels.
- Kidney function tests may be conducted.
Treatment Options for Glycosuria
Managing glycosuria often involves treating the underlying cause. Here are some treatment options.
- Insulin therapy for diabetes.
- Oral hypoglycemic agents.
- Lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.
- Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly.
- Treating any underlying kidney conditions.
Complications of Glycosuria
If left untreated, glycosuria can lead to several complications. Here are some potential risks.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
- Increased risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Dehydration due to frequent urination.
- Electrolyte imbalances.
- Kidney damage over time.
Prevention of Glycosuria
Preventing glycosuria involves maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Here are some tips.
- Regular exercise helps regulate blood sugar.
- A balanced diet low in refined sugars.
- Regular medical check-ups.
- Staying hydrated.
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
Interesting Facts about Glycosuria
Here are some intriguing tidbits about glycosuria that you might not know.
- Glycosuria was first described in the 19th century.
- It was once diagnosed by tasting the urine for sweetness.
- Some people have a genetic predisposition to glycosuria.
- Glycosuria can occur temporarily after a high-carb meal.
- It is more common in older adults.
Glycosuria in Animals
Glycosuria isn't just a human condition; it can affect animals too. Here are some facts about glycosuria in pets.
- Dogs and cats can develop glycosuria.
- It is often a sign of diabetes in pets.
- Veterinary tests for glycosuria are similar to human tests.
- Treatment in animals also involves insulin and diet changes.
- Regular vet check-ups are crucial for managing the condition.
Myths about Glycosuria
There are many misconceptions about glycosuria. Let’s clear up some of these myths.
- Myth: Only diabetics get glycosuria. Fact: It can occur in non-diabetics too.
- Myth: Glycosuria always requires medication. Fact: Lifestyle changes can manage it.
- Myth: Sweet-smelling urine always means glycosuria. Fact: Other conditions can cause this too.
- Myth: Glycosuria is always permanent. Fact: It can be temporary.
- Myth: Only adults get glycosuria. Fact: Children can develop it as well.
Understanding Glycosuria
Glycosuria, the presence of glucose in urine, often signals underlying health issues like diabetes or kidney problems. Regular monitoring can help catch these conditions early. Symptoms might include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. If you notice these signs, consult a healthcare professional.
Managing glycosuria involves lifestyle changes like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and possibly medication. Staying informed about your health is crucial. Remember, early detection and proactive management can make a significant difference.
By understanding glycosuria, you can take steps to maintain better health. Keep an eye on symptoms, get regular check-ups, and follow medical advice. Knowledge is power when it comes to managing your well-being. Stay vigilant, stay healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
