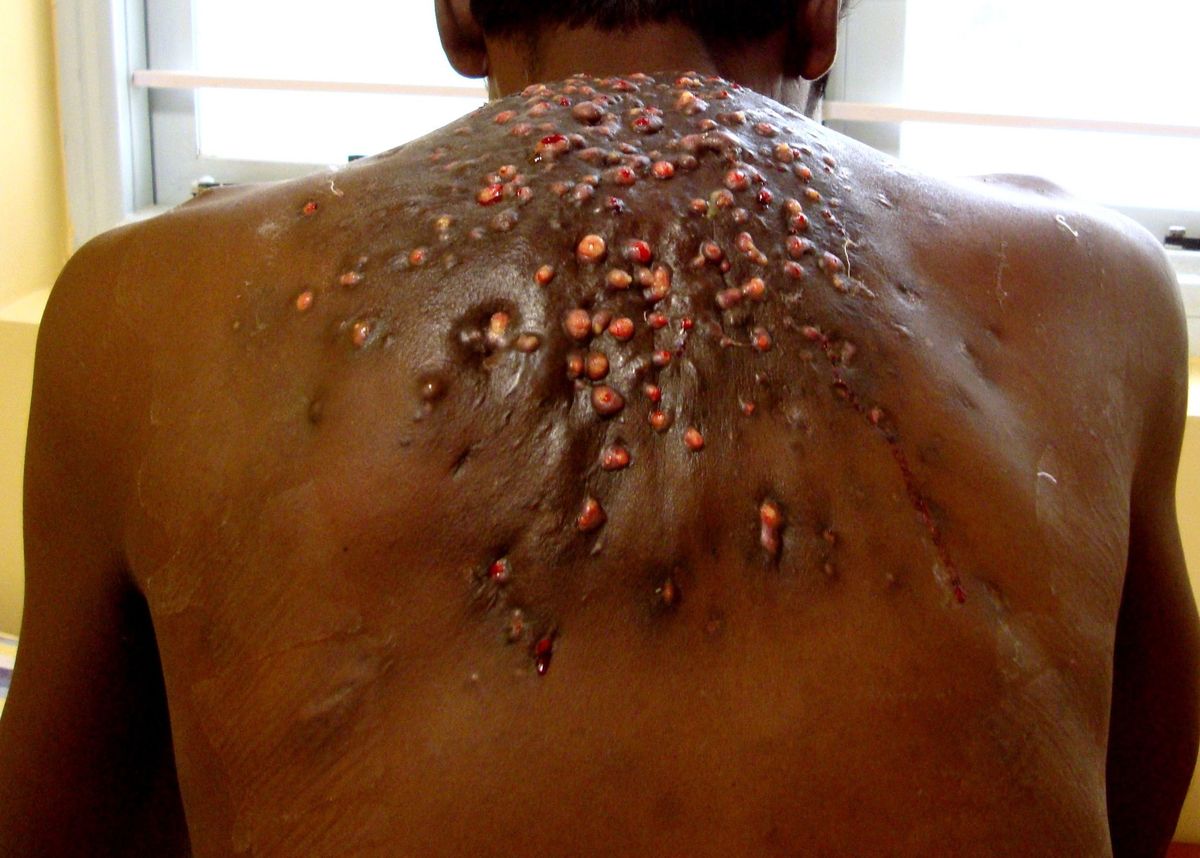
Nocardiosis is a rare but serious infection caused by bacteria from the genus Nocardia. Found in soil and water, these bacteria can enter the body through inhalation or skin wounds. Nocardiosis primarily affects the lungs, but it can spread to other parts of the body, including the brain and skin. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk. Symptoms can vary widely, making diagnosis tricky. Common signs include fever, cough, chest pain, and weight loss. Early detection and treatment with antibiotics are crucial for a better prognosis. Understanding nocardiosis can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely medical care.
Key Takeaways:
- Nocardiosis is a rare bacterial infection that primarily affects people with weakened immune systems. It can lead to serious complications if not diagnosed and treated early.
- Preventive measures, such as wearing protective gear and maintaining good hygiene, can help reduce the risk of contracting nocardiosis, especially for those with weakened immune systems.
What is Nocardiosis?
Nocardiosis is a rare but serious bacterial infection caused by Nocardia species. These bacteria are found in soil and water. The infection can affect the lungs, brain, and skin. Here are some interesting facts about this disease.
- Nocardiosis is caused by bacteria from the genus Nocardia, which are found in soil and water.
- The disease primarily affects people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy.
- Nocardia bacteria can enter the body through inhalation, skin wounds, or contaminated medical equipment.
- The infection can spread to various organs, including the lungs, brain, and skin.
- Symptoms of nocardiosis can vary depending on the affected organ but often include fever, weight loss, and night sweats.
Symptoms of Nocardiosis
Understanding the symptoms can help in early detection and treatment. Here are some common symptoms associated with nocardiosis.
- Pulmonary nocardiosis often presents with symptoms like cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
- Brain infections caused by Nocardia can lead to headaches, confusion, and seizures.
- Skin infections may result in abscesses, ulcers, or cellulitis.
- Fever is a common symptom across all types of nocardiosis.
- Weight loss and night sweats are also frequently reported by patients.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and treating nocardiosis can be challenging due to its rarity and varied symptoms. Here are some key points about its diagnosis and treatment.
- Diagnosis often involves imaging studies like X-rays or CT scans to identify affected areas.
- Laboratory tests, including cultures and biopsies, are used to confirm the presence of Nocardia bacteria.
- Treatment typically involves long-term antibiotic therapy, often lasting several months.
- Sulfonamides are the most commonly used antibiotics for treating nocardiosis.
- In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove infected tissue.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing nocardiosis. Knowing these can help in taking preventive measures.
- Immunocompromised individuals are at a higher risk of contracting nocardiosis.
- Chronic lung diseases like COPD or cystic fibrosis can also increase susceptibility.
- Long-term use of corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive drugs is a significant risk factor.
- Organ transplant recipients are particularly vulnerable to nocardiosis.
- People working in environments with high exposure to soil and dust, such as farmers, are at increased risk.
Prevention and Awareness
Preventive measures and awareness can go a long way in reducing the incidence of nocardiosis. Here are some tips and facts about prevention.
- Wearing protective gear like masks and gloves can reduce the risk of inhaling or coming into contact with Nocardia bacteria.
- Regular hand washing and maintaining good hygiene can help prevent skin infections.
- Immunocompromised individuals should avoid activities that involve close contact with soil or dust.
- Awareness campaigns can educate at-risk populations about the symptoms and risks associated with nocardiosis.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes and preventing complications.
Complications
Nocardiosis can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly. Here are some potential complications.
- Untreated pulmonary nocardiosis can lead to chronic lung disease or respiratory failure.
- Brain infections can result in long-term neurological deficits or even death.
- Skin infections may cause extensive tissue damage, requiring surgical intervention.
- The infection can spread to other organs, leading to multi-organ failure.
- Recurrence of the infection is possible, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known but fascinating facts about nocardiosis.
- Nocardiosis was first described by French veterinarian Edmond Nocard in 1888.
- The disease is more common in tropical and subtropical regions.
- Nocardia bacteria are known for their ability to form branching filaments, similar to fungi.
- There are over 80 species of Nocardia, but only a few are pathogenic to humans.
- Nocardiosis is considered an opportunistic infection, meaning it primarily affects those with weakened immune systems.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for better understanding and managing nocardiosis. Here are some current research trends and future directions.
- Researchers are exploring new antibiotics and treatment regimens to combat antibiotic-resistant strains of Nocardia.
- Studies are being conducted to understand the genetic factors that contribute to susceptibility and resistance.
- Advances in molecular diagnostics are improving the accuracy and speed of nocardiosis diagnosis.
- Vaccine development is in the early stages, aiming to provide protection for high-risk populations.
- Collaborative efforts between researchers, healthcare providers, and public health organizations are essential for advancing our knowledge and treatment of nocardiosis.
Final Thoughts on Nocardiosis
Nocardiosis, a rare but serious infection, primarily affects those with weakened immune systems. Understanding its symptoms, like persistent cough, fever, and weight loss, can lead to early diagnosis and better outcomes. Treatment usually involves antibiotics, sometimes for an extended period, to fully eradicate the bacteria. Prevention focuses on maintaining a strong immune system and avoiding exposure to soil and dust, where Nocardia bacteria thrive. Awareness of this condition is crucial for those at higher risk, such as individuals with chronic lung diseases or those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy. By staying informed and vigilant, you can protect yourself and loved ones from the potential dangers of nocardiosis. Remember, early detection and proper medical care are key to managing this infection effectively. Stay healthy and proactive in safeguarding your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
