Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (GI NETs) might sound like a mouthful, but understanding them is crucial. These tumors are rare growths that originate in the hormone-producing cells of the digestive system. They can pop up anywhere from the stomach to the rectum. While some grow slowly and remain harmless for years, others can be aggressive and spread quickly. Symptoms often mimic other common digestive issues, making diagnosis tricky. Common signs include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and unexplained weight loss. Treatment varies based on the tumor's location and stage, ranging from surgery to medication. Early detection can significantly improve outcomes. Knowing the basics about GI NETs helps in recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely medical advice. Stay informed and proactive about your health!
Key Takeaways:
- Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (GI NETs) originate from specialized cells in the digestive system and can cause symptoms like flushing and abdominal pain. Early detection and treatment options offer hope for improved outcomes.
- Despite being rare, GI NETs can be effectively managed with treatments like surgery, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy. Ongoing research and support resources provide hope for patients and their families.
Understanding Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors
Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (GI NETs) are rare, but they can be quite complex. These tumors originate from neuroendocrine cells found in the gastrointestinal tract. Let's explore some intriguing facts about these unique tumors.
-
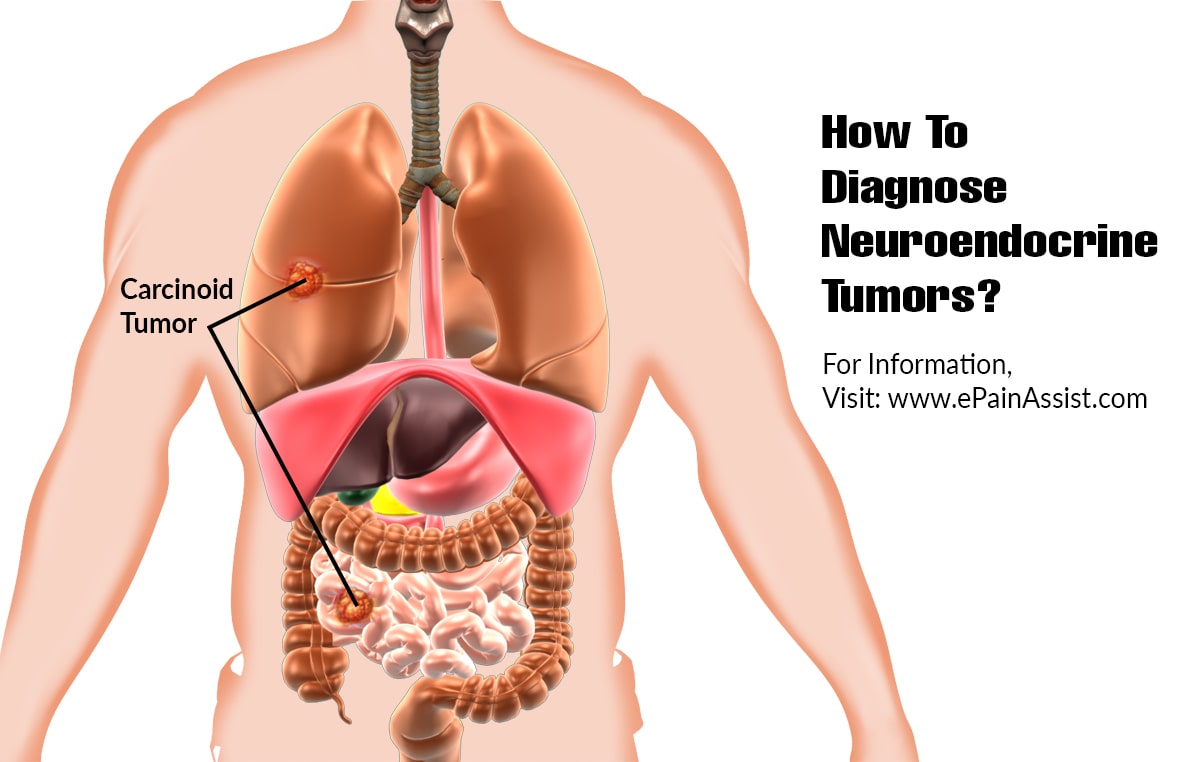
Origin of GI NETs
GI NETs develop from neuroendocrine cells, which are specialized cells that release hormones into the bloodstream. These cells are scattered throughout the digestive system. -
Common Locations
The most frequent sites for GI NETs are the small intestine, rectum, and appendix. However, they can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract. -
Slow Growth Rate
Many GI NETs grow slowly, which can make them difficult to detect early. This slow growth often leads to a delay in diagnosis. -
Hormone Production
Some GI NETs produce hormones that can cause symptoms like flushing, diarrhea, or wheezing. These symptoms are part of a condition known as carcinoid syndrome. -
Incidence Rate
The incidence of GI NETs has been increasing over the past few decades. This rise is partly due to improved diagnostic techniques.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for managing GI NETs effectively.
-
Asymptomatic Nature
Many GI NETs do not cause symptoms until they are advanced. This asymptomatic nature can complicate early detection. -
Common Symptoms
When symptoms do occur, they may include abdominal pain, weight loss, or changes in bowel habits. These symptoms are often mistaken for other gastrointestinal issues. -
Diagnostic Imaging
Imaging techniques like CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans are commonly used to locate and assess the extent of GI NETs. -
Biopsy Confirmation
A biopsy is essential for confirming the diagnosis of a GI NET. This involves taking a small tissue sample for examination under a microscope. -
Blood and Urine Tests
Specific blood and urine tests can detect hormone levels associated with GI NETs, aiding in diagnosis and monitoring.
Treatment Options
Treatment for GI NETs varies depending on the tumor's location, size, and whether it has spread.
-
Surgical Removal
Surgery is often the first-line treatment for localized GI NETs. Removing the tumor can be curative if it hasn't spread. -
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies, like somatostatin analogs, help control hormone-related symptoms and slow tumor growth. -
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be used for advanced GI NETs, especially if they have spread to other parts of the body. -
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is less common but can be used to treat specific areas where the tumor has spread. -
Liver-Directed Therapies
For GI NETs that have metastasized to the liver, treatments like radiofrequency ablation or embolization may be considered.
Prognosis and Survival
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates for GI NETs can provide hope and guidance for patients and their families.
-
Variable Prognosis
The prognosis for GI NETs varies widely based on factors like tumor size, location, and stage at diagnosis. -
Survival Rates
Overall survival rates for GI NETs have improved due to advancements in treatment and early detection. -
Importance of Follow-Up
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is crucial for monitoring the disease and managing any complications. -
Quality of Life
With appropriate treatment, many patients with GI NETs can maintain a good quality of life for many years. -
Research and Clinical Trials
Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to explore new treatments and improve outcomes for GI NET patients.
Risk Factors and Prevention
While the exact cause of GI NETs is not fully understood, certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing these tumors.
-
Genetic Syndromes
Some genetic syndromes, like Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1), increase the risk of developing GI NETs. -
Family History
A family history of neuroendocrine tumors can be a risk factor, suggesting a potential genetic component. -
Age and Gender
GI NETs are more common in adults over 50 and slightly more prevalent in men than women. -
Diet and Lifestyle
While no specific diet is linked to GI NETs, maintaining a healthy lifestyle may reduce overall cancer risk. -
Prevention Strategies
Currently, there are no specific prevention strategies for GI NETs, but regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms can aid early detection.
Living with GI NETs
Living with a GI NET diagnosis involves managing symptoms and maintaining a positive outlook.
-
Symptom Management
Medications and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms like diarrhea and flushing. -
Nutritional Support
A balanced diet and nutritional support can improve overall health and well-being for GI NET patients. -
Emotional Support
Emotional and psychological support is vital for patients and their families to cope with the challenges of living with a chronic condition. -
Patient Advocacy
Joining support groups and advocacy organizations can provide valuable resources and a sense of community. -
Regular Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are essential for managing the disease effectively.
Advances in Research
Research into GI NETs is ongoing, with new discoveries and treatments on the horizon.
-
Genetic Research
Genetic research is uncovering more about the mutations and pathways involved in GI NET development. -
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is being explored as a potential treatment option for GI NETs, harnessing the body's immune system to fight cancer. -
Biomarker Discovery
New biomarkers are being identified, which could lead to earlier detection and personalized treatment approaches. -
Combination Therapies
Combining different treatment modalities is showing promise in improving outcomes for GI NET patients. -
Patient Registries
Patient registries are helping researchers gather data and improve understanding of GI NETs on a global scale.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding GI NETs that need clarification.
-
Rare but Not Impossible
While GI NETs are rare, they are not impossible to diagnose and treat effectively. -
Not Always Cancerous
Not all GI NETs are cancerous; some are benign and may not require aggressive treatment. -
Misunderstood Symptoms
Symptoms of GI NETs are often misunderstood or attributed to other conditions, delaying diagnosis. -
Treatment Options Exist
There are multiple treatment options available, and many patients respond well to therapy. -
Hope for the Future
Advancements in research and treatment continue to offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for GI NET patients.
Understanding the Bigger Picture
Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are complex, but knowing the facts can help. These tumors, often found in the digestive system, can vary in behavior and symptoms. Early detection is key, as it can significantly impact treatment options and outcomes. Symptoms might be subtle, like abdominal pain or changes in bowel habits, making awareness crucial. Treatments range from surgery to medication, depending on the tumor's type and stage. Research continues to evolve, offering hope for better therapies and outcomes. Patients and families should seek support and information from healthcare professionals and support groups. Knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. By staying informed, you can better navigate the challenges of NETs and advocate for yourself or loved ones. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; resources and communities are available to help along the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
