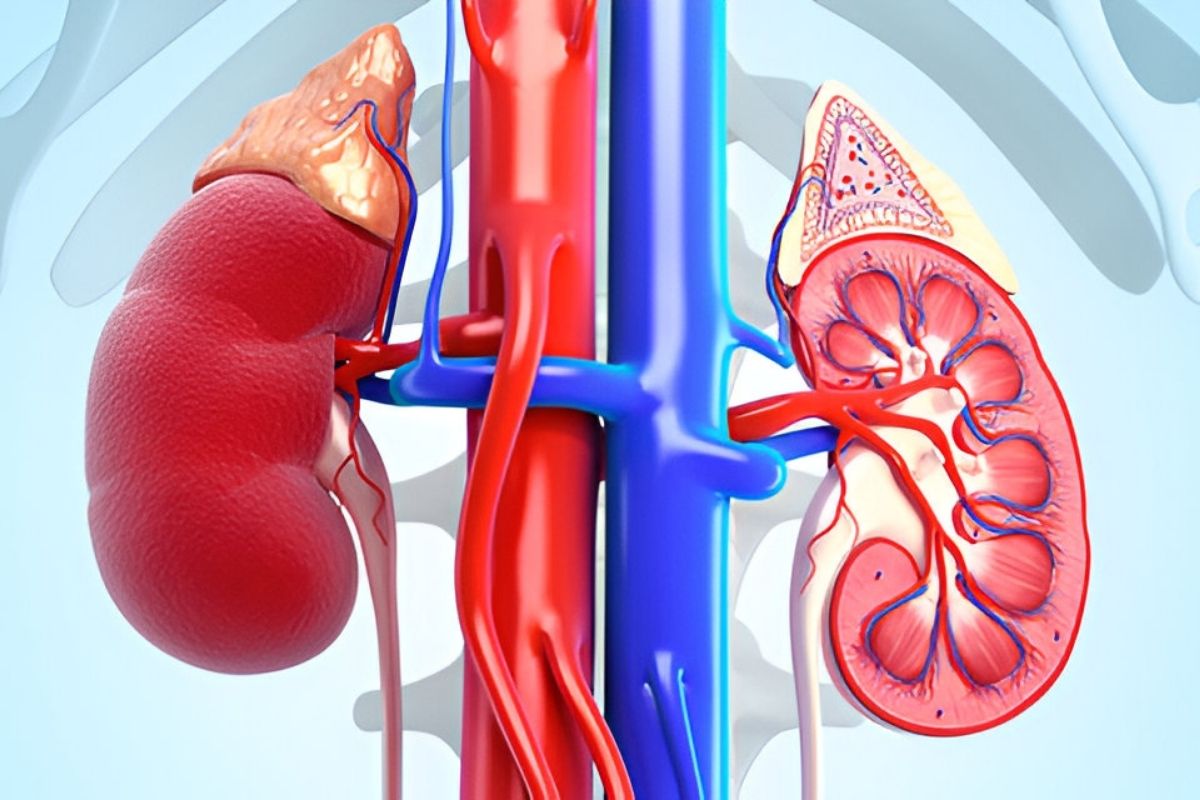
Radio-renal syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects both the kidneys and the bones. This condition can lead to a variety of health issues, including kidney problems and skeletal abnormalities. What causes Radio-renal syndrome? The syndrome is caused by mutations in specific genes that play a crucial role in kidney and bone development. These genetic changes disrupt normal cellular functions, leading to the symptoms associated with the disorder. Understanding the genetic basis of Radio-renal syndrome is essential for diagnosing and managing the condition effectively. In this blog post, we'll delve into 35 intriguing facts about Radio-renal syndrome, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments.
Key Takeaways:
- Radio-renal syndrome is a rare condition caused by exposure to high levels of radiation, leading to severe kidney damage and symptoms like nausea and fatigue.
- Prevention involves radiation safety, regular check-ups, and public awareness. Research and advancements offer hope for better management and prevention of this syndrome.
What is Radio-renal Syndrome?
Radio-renal syndrome is a rare condition that affects the kidneys and can be triggered by exposure to radiation. This syndrome is not widely known, so let's dive into some fascinating facts about it.
-
Rare Condition: Radio-renal syndrome is extremely rare, with only a handful of documented cases worldwide.
-
Radiation Exposure: The syndrome is primarily caused by exposure to high levels of radiation, often from medical treatments or nuclear accidents.
-
Kidney Damage: It specifically targets the kidneys, leading to severe damage and impaired function.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and swelling due to fluid retention.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosing radio-renal syndrome can be challenging due to its rarity and the similarity of its symptoms to other kidney disorders.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in early detection and prevention of radio-renal syndrome.
-
Medical Treatments: Radiation therapy for cancer is a significant risk factor, especially if the kidneys are within the radiation field.
-
Nuclear Accidents: Exposure to radiation from nuclear accidents, such as Chernobyl, has been linked to cases of radio-renal syndrome.
-
Occupational Hazards: Workers in nuclear power plants or industries dealing with radioactive materials are at higher risk.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more susceptible to radiation-induced kidney damage.
-
Age Factor: Older adults are more vulnerable due to the natural decline in kidney function with age.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for managing radio-renal syndrome effectively.
-
Early Symptoms: Early symptoms can be non-specific, such as fatigue and loss of appetite, making early diagnosis difficult.
-
Advanced Symptoms: As the condition progresses, symptoms like high blood pressure, anemia, and electrolyte imbalances may occur.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests can reveal elevated levels of creatinine and urea, indicating kidney dysfunction.
-
Imaging Studies: Imaging studies like ultrasound or CT scans can help assess the extent of kidney damage.
-
Biopsy: In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for radio-renal syndrome, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Medications: Medications to control blood pressure and manage symptoms like nausea and vomiting are commonly prescribed.
-
Dialysis: In severe cases, dialysis may be required to perform the kidney's functions.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Dietary modifications, such as reducing salt intake, can help manage symptoms and prevent further kidney damage.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring of kidney function is essential to detect any changes early and adjust treatment accordingly.
-
Supportive Care: Supportive care, including counseling and support groups, can help patients cope with the emotional and psychological impact of the condition.
Prevention and Awareness
Raising awareness and taking preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing radio-renal syndrome.
-
Radiation Safety: Following strict radiation safety protocols in medical and occupational settings can minimize exposure.
-
Protective Equipment: Using protective equipment, such as lead aprons, can help shield the kidneys from radiation.
-
Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups for individuals at risk can help detect early signs of kidney damage.
-
Public Awareness: Increasing public awareness about the risks of radiation exposure and the importance of kidney health is crucial.
-
Research and Funding: Supporting research and funding for studies on radio-renal syndrome can lead to better understanding and treatment options.
Interesting Facts
Here are some intriguing facts about radio-renal syndrome that you might not know.
-
Historical Cases: The first documented cases of radio-renal syndrome were reported in the aftermath of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings.
-
Animal Studies: Studies on animals exposed to radiation have provided valuable insights into the mechanisms of kidney damage.
-
Radiation Units: The severity of radio-renal syndrome is often measured in units called Grays (Gy), which quantify the absorbed radiation dose.
-
Protective Measures: Advances in radiation therapy techniques have significantly reduced the risk of radio-renal syndrome in cancer patients.
-
Global Incidence: Despite its rarity, cases of radio-renal syndrome have been reported in various countries, highlighting the global nature of the risk.
Future Directions
Research and advancements in medical technology hold promise for better management and prevention of radio-renal syndrome.
-
Genetic Research: Ongoing genetic research aims to identify individuals who may be more susceptible to radiation-induced kidney damage.
-
New Therapies: Scientists are exploring new therapies that can protect the kidneys from radiation damage or repair existing damage.
-
Improved Diagnostics: Advances in diagnostic tools and techniques can lead to earlier detection and more accurate diagnosis of radio-renal syndrome.
-
Patient Education: Educating patients about the risks and symptoms of radio-renal syndrome can empower them to seek timely medical attention.
-
Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between medical professionals, researchers, and policymakers is essential to address the challenges posed by radio-renal syndrome effectively.
Final Thoughts on Radio-renal Syndrome
Radio-renal syndrome, a rare condition, intertwines kidney and bone abnormalities. Understanding radio-renal syndrome helps in early diagnosis and better management. Symptoms often include kidney malformations, skeletal anomalies, and sometimes hearing loss. Genetic factors play a significant role, making family history crucial for diagnosis.
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Regular check-ups with specialists, including nephrologists and orthopedists, are essential. Advances in genetic research offer hope for better treatments in the future.
Awareness and education about radio-renal syndrome can lead to earlier detection and improved outcomes. Sharing knowledge empowers patients and families, fostering a supportive community. Stay informed, seek expert advice, and advocate for those affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
