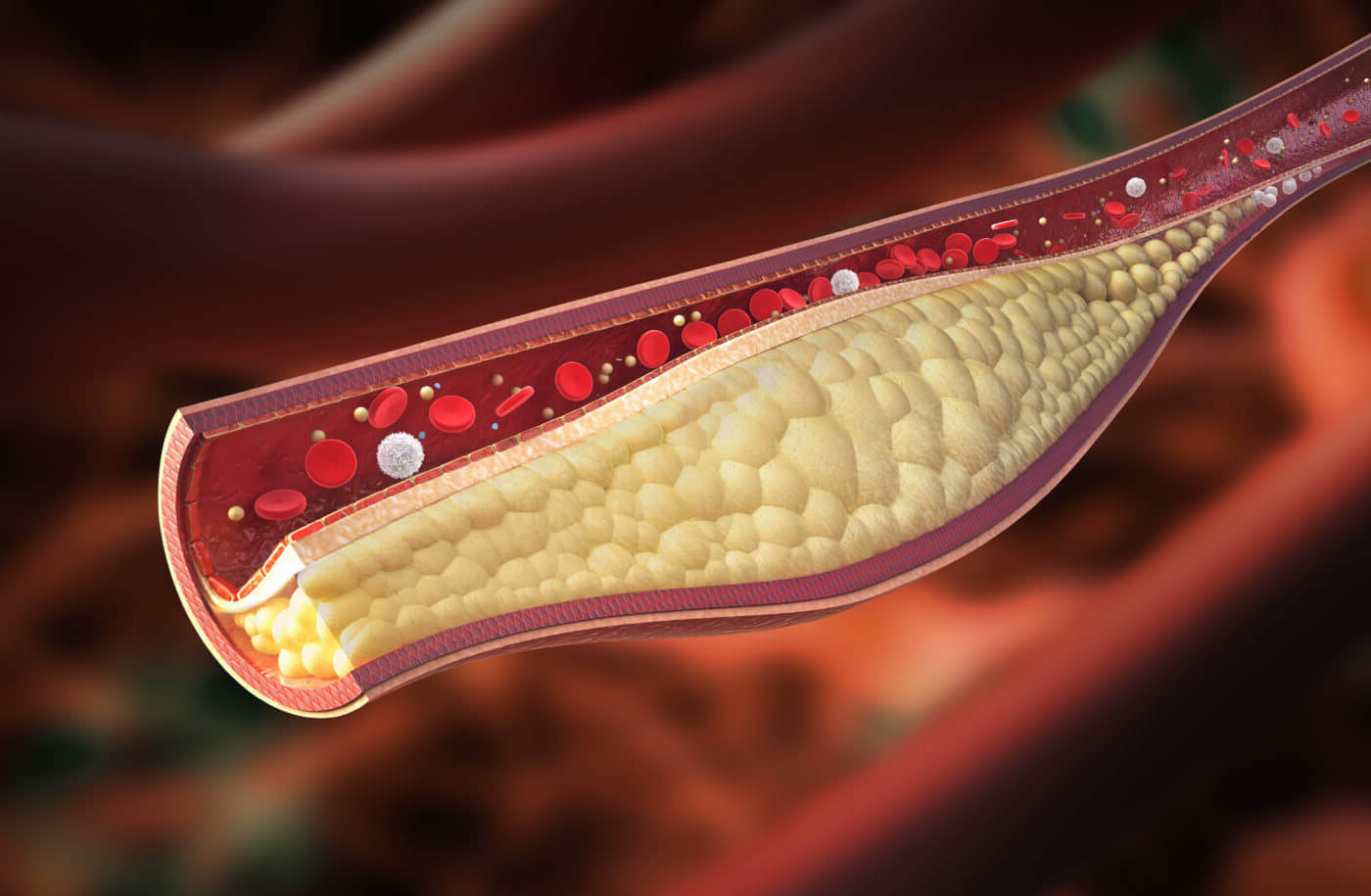
Atherosclerosis is a condition where arteries become narrowed and hardened due to a buildup of plaque. This can lead to serious problems like heart attacks, strokes, and even death. But what exactly causes this condition? Plaque consists of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, it can restrict blood flow, making it difficult for oxygen-rich blood to reach vital organs. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Understanding these risks can help in prevention and management. Ready to learn more? Here are 34 facts about atherosclerosis that will help you understand this condition better.
Key Takeaways:
- Atherosclerosis is a condition where arteries get clogged, leading to serious health issues. It's caused by factors like high cholesterol, smoking, and lack of exercise. Prevention involves healthy habits and regular check-ups.
- Atherosclerosis can cause heart attacks, strokes, and other complications. Research is ongoing to better understand and treat this condition, offering hope for future advancements in prevention and treatment.
What is Atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a condition where arteries become narrowed and hardened due to plaque buildup. This can lead to serious health issues like heart attacks and strokes. Understanding this condition is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health.
- Atherosclerosis is derived from Greek words meaning "hard gruel," referring to the hardened, fatty deposits in arteries.
- Plaque in arteries consists of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood.
- This condition can affect any artery in the body, including those in the heart, brain, arms, legs, pelvis, and kidneys.
- Atherosclerosis is a slow, progressive disease that can start in childhood and worsen with age.
- High cholesterol levels are a significant risk factor for developing atherosclerosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. Knowing these can help in prevention and management.
- Smoking is a major risk factor, as it damages the lining of arteries and promotes plaque buildup.
- High blood pressure can injure the inner walls of arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque formation.
- Diabetes increases the risk of atherosclerosis by contributing to higher blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels.
- Obesity is linked to higher levels of bad cholesterol and lower levels of good cholesterol, increasing the risk.
- Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, all of which are risk factors.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Atherosclerosis often goes unnoticed until it causes significant health problems. Recognizing symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis is essential.
- Chest pain or angina is a common symptom when atherosclerosis affects the arteries of the heart.
- Shortness of breath can occur if the heart is not getting enough oxygen-rich blood.
- Pain in the legs or arms may indicate peripheral artery disease, a form of atherosclerosis.
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the limbs could be a sign of a stroke caused by atherosclerosis in brain arteries.
- Diagnosing atherosclerosis typically involves blood tests, imaging tests like ultrasounds or CT scans, and sometimes angiography.
Treatment Options
Managing atherosclerosis involves lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical procedures.
- Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking are crucial for managing atherosclerosis.
- Medications like statins can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce plaque buildup.
- Blood pressure medications are often prescribed to manage hypertension, a risk factor for atherosclerosis.
- Antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin, can help prevent blood clots that might form on plaques.
- In severe cases, surgical procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore proper blood flow.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing atherosclerosis involves adopting healthy habits and regular medical check-ups.
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce the risk.
- Regular physical activity, such as 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days, is beneficial.
- Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can lower the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Regular health screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes can help catch risk factors early.
- Avoiding tobacco in all forms is one of the most effective ways to prevent atherosclerosis.
Impact on Health
Atherosclerosis can have far-reaching effects on overall health, leading to various complications.
- Heart attacks occur when plaque ruptures and forms a blood clot that blocks blood flow to the heart.
- Strokes can result from atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to the brain, causing brain cells to die.
- Peripheral artery disease can lead to pain, numbness, and even tissue death in the limbs.
- Chronic kidney disease may develop if atherosclerosis affects the arteries leading to the kidneys.
- Erectile dysfunction can be an early sign of atherosclerosis in men, as it affects blood flow.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand and treat atherosclerosis, offering hope for future advancements.
- Genetic studies are exploring how inherited factors contribute to the risk of atherosclerosis.
- New medications are being developed to more effectively lower cholesterol and reduce plaque.
- Research into anti-inflammatory treatments is ongoing, as inflammation plays a role in plaque formation.
- Advances in imaging technology are improving the ability to detect and monitor atherosclerosis early.
Final Thoughts on Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries become clogged with fatty substances, can lead to serious health issues like heart attacks and strokes. Knowing the risk factors—such as high cholesterol, smoking, and lack of exercise—can help in prevention. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle play a crucial role in managing this condition.
Symptoms might not show up until an artery is significantly blocked, so early detection is key. Treatments range from lifestyle changes to medications and, in severe cases, surgery. Understanding the importance of diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking can make a big difference.
Remember, knowledge is power. Staying informed about atherosclerosis can help you take proactive steps to protect your heart health. Share this information with loved ones to spread awareness and encourage healthier choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
