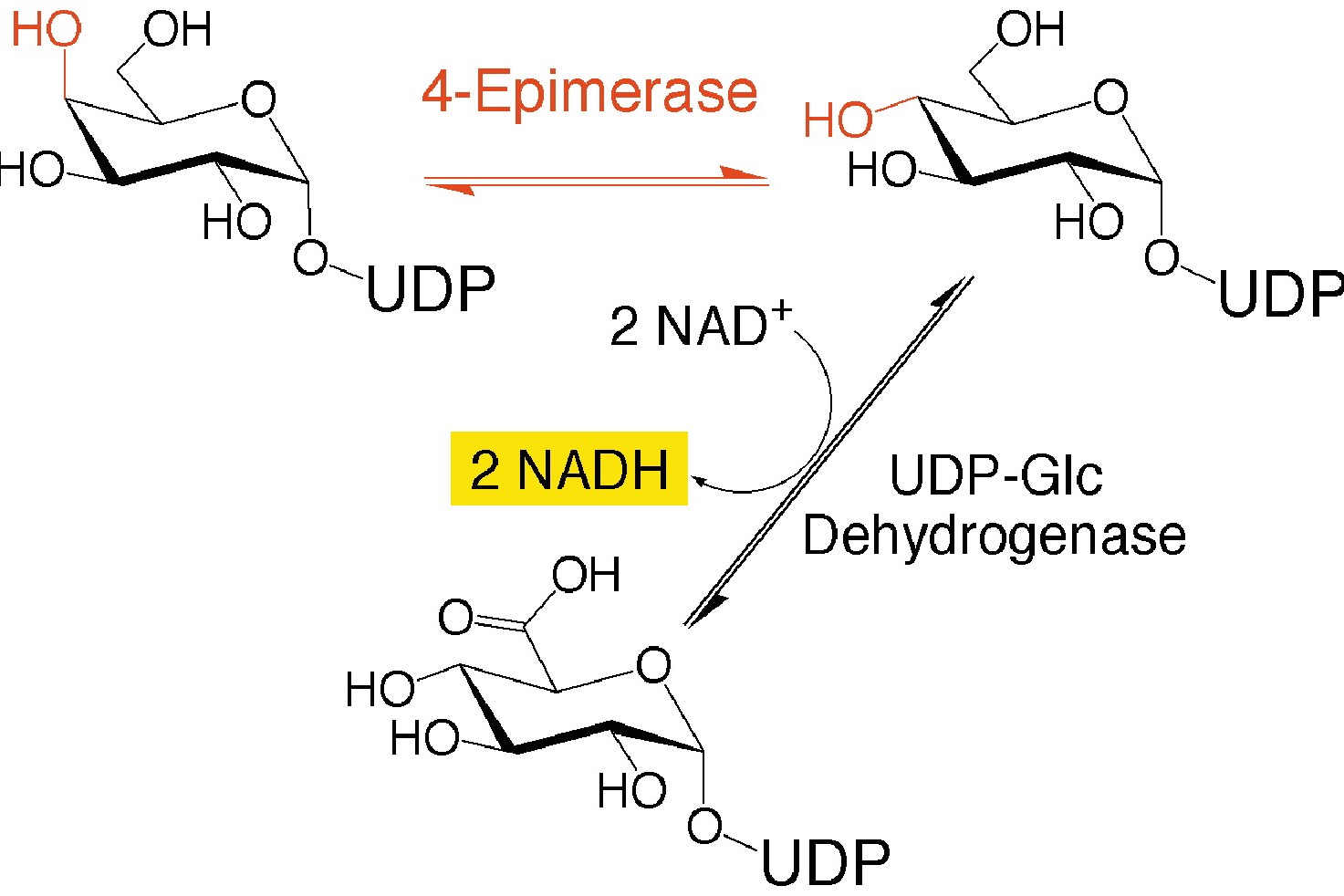
What is Udp-Galactose-4-Epimerase Deficiency? This rare genetic disorder affects how the body processes certain sugars. Caused by mutations in the GALE gene, it disrupts the conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, including liver problems, intellectual disability, and cataracts. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to manage the condition effectively. Treatment often involves dietary restrictions to limit galactose intake. Understanding this condition can help families and healthcare providers better support those affected. Stay informed and proactive to ensure the best outcomes for individuals with Udp-Galactose-4-Epimerase Deficiency.
Key Takeaways:
- GALE deficiency is a rare genetic disorder affecting sugar processing. It can lead to liver damage, cataracts, and developmental delays. A galactose-restricted diet and regular monitoring are crucial for managing the condition.
- GALE deficiency affects liver function, eye health, and brain development. Dietary restrictions, nutritional supplements, and regular check-ups are important for managing the condition and preventing complications.
What is UDP-Galactose-4-Epimerase Deficiency?
UDP-Galactose-4-Epimerase Deficiency, also known as GALE deficiency, is a rare genetic disorder affecting the body's ability to process certain sugars. This condition can lead to various health issues, from mild to severe. Here are some intriguing facts about this disorder.
-
Genetic Origin: GALE deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means both parents must carry the defective gene for a child to be affected.
-
Enzyme Deficiency: The disorder is caused by a deficiency in the enzyme UDP-galactose-4-epimerase, which is crucial for converting UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose.
-
Types of GALE Deficiency: There are three types: generalized, peripheral, and intermediate. Each type varies in severity and symptoms.
-
Newborn Screening: In some regions, newborns are screened for GALE deficiency as part of routine metabolic disorder testing.
-
Symptoms in Infants: Infants with GALE deficiency may exhibit symptoms like poor feeding, vomiting, and jaundice.
-
Long-term Effects: If untreated, the disorder can lead to developmental delays, liver damage, and cataracts.
-
Dietary Management: A galactose-restricted diet can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
-
Lactose Intolerance: Individuals with GALE deficiency often need to avoid lactose, as their bodies cannot properly process it.
-
Galactosemia: GALE deficiency is a form of galactosemia, a broader category of disorders affecting galactose metabolism.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure enzyme activity and genetic testing to identify mutations.
How Does GALE Deficiency Affect the Body?
Understanding the impact of GALE deficiency on the body helps in managing the condition better. Here are some effects:
-
Liver Function: The liver may become enlarged and function poorly due to the accumulation of galactose-1-phosphate.
-
Eye Health: Cataracts can develop due to the buildup of galactitol in the lens of the eye.
-
Brain Development: High levels of galactose can affect brain development, leading to intellectual disabilities.
-
Growth: Children with GALE deficiency may experience growth retardation if the condition is not managed properly.
-
Bone Health: Osteopenia or osteoporosis can occur due to imbalances in calcium metabolism.
-
Immune System: Some individuals may have a weakened immune system, making them more susceptible to infections.
-
Reproductive Health: Females with GALE deficiency may experience ovarian dysfunction, leading to fertility issues.
-
Blood Sugar Levels: Hypoglycemia can occur due to impaired glucose production.
-
Muscle Tone: Hypotonia, or reduced muscle tone, is common in affected infants.
-
Hearing: Some individuals may develop hearing loss due to nerve damage.
Treatment and Management of GALE Deficiency
Managing GALE deficiency involves a combination of dietary changes and medical interventions. Here are some key points:
-
Dietary Restrictions: Avoiding foods high in galactose, such as dairy products, is crucial.
-
Nutritional Supplements: Supplements like calcium and vitamin D may be necessary to support bone health.
-
Regular Monitoring: Frequent blood tests are needed to monitor galactose levels and liver function.
-
Enzyme Replacement Therapy: Research is ongoing to develop enzyme replacement therapies for GALE deficiency.
-
Genetic Counseling: Families with a history of GALE deficiency can benefit from genetic counseling to understand risks and options.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing the condition.
-
Education: Educating patients and families about the disorder is essential for effective management.
-
Emergency Care: Individuals with GALE deficiency should have a plan in place for managing acute symptoms like hypoglycemia.
-
Regular Check-ups: Routine visits to a metabolic specialist can help manage the condition and prevent complications.
-
Research and Advances: Ongoing research aims to better understand GALE deficiency and develop new treatments.
Final Thoughts on Udp-Galactose-4-Epimerase Deficiency
Udp-Galactose-4-Epimerase Deficiency, though rare, has significant impacts on those affected. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can make a huge difference in managing the condition. Early diagnosis is key, as it allows for timely intervention and better outcomes. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families, helping them navigate the complexities of this disorder. While research continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest developments is crucial. Support groups and resources can offer much-needed assistance and community for those dealing with this condition. By spreading awareness and knowledge, we can contribute to better care and support for individuals with Udp-Galactose-4-Epimerase Deficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
