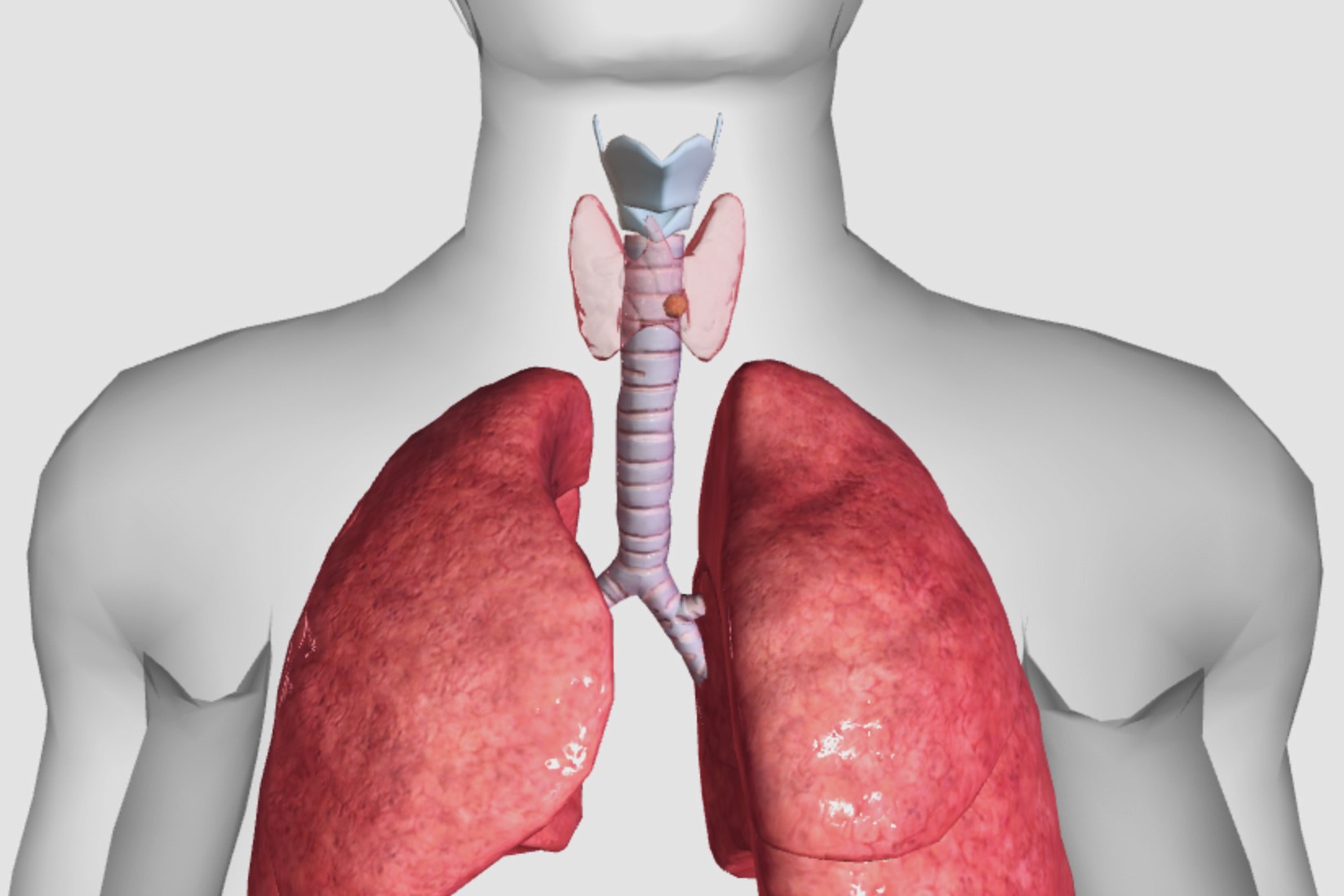
Nonmedullary thyroid carcinoma (NMTC) is a type of thyroid cancer that originates from follicular cells. These cells are responsible for producing and storing thyroid hormones. NMTC includes two main types: papillary thyroid carcinoma and follicular thyroid carcinoma. Both types are more common than medullary thyroid carcinoma and have different characteristics and treatment approaches. Understanding NMTC is crucial because early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. This article will provide you with 30 essential facts about NMTC, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or just curious, these facts will help you grasp the essentials of this condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Nonmedullary Thyroid Carcinoma (NMTC) is the most common type of thyroid cancer, with papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) being the most prevalent subtype, making up about 80% of NMTC cases.
- Recognizing symptoms like neck lumps, difficulty swallowing, and hoarseness can lead to early detection of NMTC, which is crucial for better treatment outcomes.
What is Nonmedullary Thyroid Carcinoma?
Nonmedullary thyroid carcinoma (NMTC) is a type of thyroid cancer that originates from follicular cells. These cells are responsible for producing thyroid hormones. NMTC is the most common type of thyroid cancer and includes several subtypes.
- NMTC accounts for about 90% of all thyroid cancers.
- The main subtypes of NMTC are papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) and follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC).
- PTC is the most common subtype, making up approximately 80% of NMTC cases.
- FTC is less common, accounting for about 10-15% of NMTC cases.
- NMTC can occur at any age but is most frequently diagnosed in people between 30 and 50 years old.
Symptoms of Nonmedullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Recognizing the symptoms of NMTC early can lead to better outcomes. Symptoms can vary but often include noticeable changes in the neck area.
- A lump or swelling in the neck is a common symptom.
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing may occur if the tumor presses on the esophagus or trachea.
- Hoarseness or changes in voice can be a sign if the cancer affects the vocal cords.
- Persistent cough not related to a cold can also be a symptom.
- Some patients may experience neck pain that radiates to the ears.
Risk Factors for Nonmedullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Understanding the risk factors can help in early detection and prevention. Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing NMTC.
- Exposure to high levels of radiation, especially during childhood, is a significant risk factor.
- A family history of thyroid cancer increases the risk.
- Certain genetic mutations, such as those in the RET or BRAF genes, are linked to NMTC.
- Iodine deficiency in the diet can contribute to the development of NMTC.
- Women are more likely to develop NMTC than men, with a ratio of about 3:1.
Diagnosis of Nonmedullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Several methods are used to diagnose NMTC.
- A physical exam often reveals a lump in the neck.
- Ultrasound imaging helps to visualize the thyroid and detect abnormalities.
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is commonly used to obtain tissue samples for analysis.
- Blood tests can measure thyroid function and detect specific markers.
- Genetic testing may be recommended if there is a family history of thyroid cancer.
Treatment Options for Nonmedullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Treatment for NMTC depends on the stage and type of cancer. Multiple options are available to manage the condition effectively.
- Surgery is the primary treatment for NMTC, often involving the removal of part or all of the thyroid gland.
- Radioactive iodine therapy is used to destroy any remaining cancerous cells after surgery.
- Thyroid hormone therapy helps to suppress the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which can promote cancer growth.
- External beam radiation therapy may be used in cases where surgery is not an option.
- Targeted therapy drugs, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, are used for advanced NMTC.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for NMTC is generally favorable, especially when detected early. Survival rates vary based on several factors.
- The 5-year survival rate for PTC is over 95%.
- FTC has a slightly lower 5-year survival rate, around 85-90%.
- Early-stage NMTC has a better prognosis compared to advanced stages.
- Younger patients tend to have better outcomes than older patients.
- Regular follow-up and monitoring are essential for maintaining good health after treatment.
Final Thoughts on Nonmedullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Nonmedullary thyroid carcinoma (NMTC) isn't just another medical term. It's a significant health concern affecting many people worldwide. Understanding its symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options can make a huge difference in early detection and management. Regular check-ups and being aware of family history play crucial roles in catching NMTC early. Advances in medical research continue to improve treatment outcomes, offering hope to those diagnosed. Staying informed and proactive about health can lead to better outcomes and peace of mind. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to managing health issues. Keep these facts in mind, share them with loved ones, and always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Stay healthy, stay informed!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
