What is a neonatal ovarian cyst? A neonatal ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms on the ovary of a newborn baby girl. These cysts are usually detected through prenatal ultrasounds or shortly after birth. While they might sound alarming, most neonatal ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own without intervention. However, some may require monitoring or even surgical removal if they grow too large or cause complications. Understanding these cysts can help parents feel more at ease and prepared. Let's dive into 30 intriguing facts about neonatal ovarian cysts to shed light on this common yet often misunderstood condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Neonatal ovarian cysts are common in newborn girls, often detected before or after birth. Most resolve on their own, but some may require medical attention for monitoring or treatment.
- While most neonatal ovarian cysts have a positive outlook, some may cause complications like pain or potential impact on fertility. Regular follow-up with a doctor is important for monitoring and managing any issues.
What is a Neonatal Ovarian Cyst?
Neonatal ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries of newborn girls. They are often detected during prenatal ultrasounds or shortly after birth. These cysts can vary in size and may resolve on their own or require medical intervention.
-
Common Occurrence: Neonatal ovarian cysts are relatively common, occurring in about 1 in 2,500 live births.
-
Prenatal Detection: Many neonatal ovarian cysts are detected during routine prenatal ultrasounds, often in the third trimester.
-
Size Variation: These cysts can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.
-
Simple vs. Complex: Simple cysts are filled with clear fluid, while complex cysts may contain debris or blood.
-
Hormonal Influence: Maternal hormones, particularly estrogen, play a significant role in the development of these cysts.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Most neonatal ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, meaning they don't cause any noticeable symptoms. However, some may present signs that lead to further investigation.
-
Asymptomatic Nature: Many cysts do not cause any symptoms and are found incidentally.
-
Abdominal Distension: In rare cases, large cysts can cause abdominal swelling or distension.
-
Pain and Irritability: If a cyst twists (torsion) or ruptures, it can cause pain and irritability in the newborn.
-
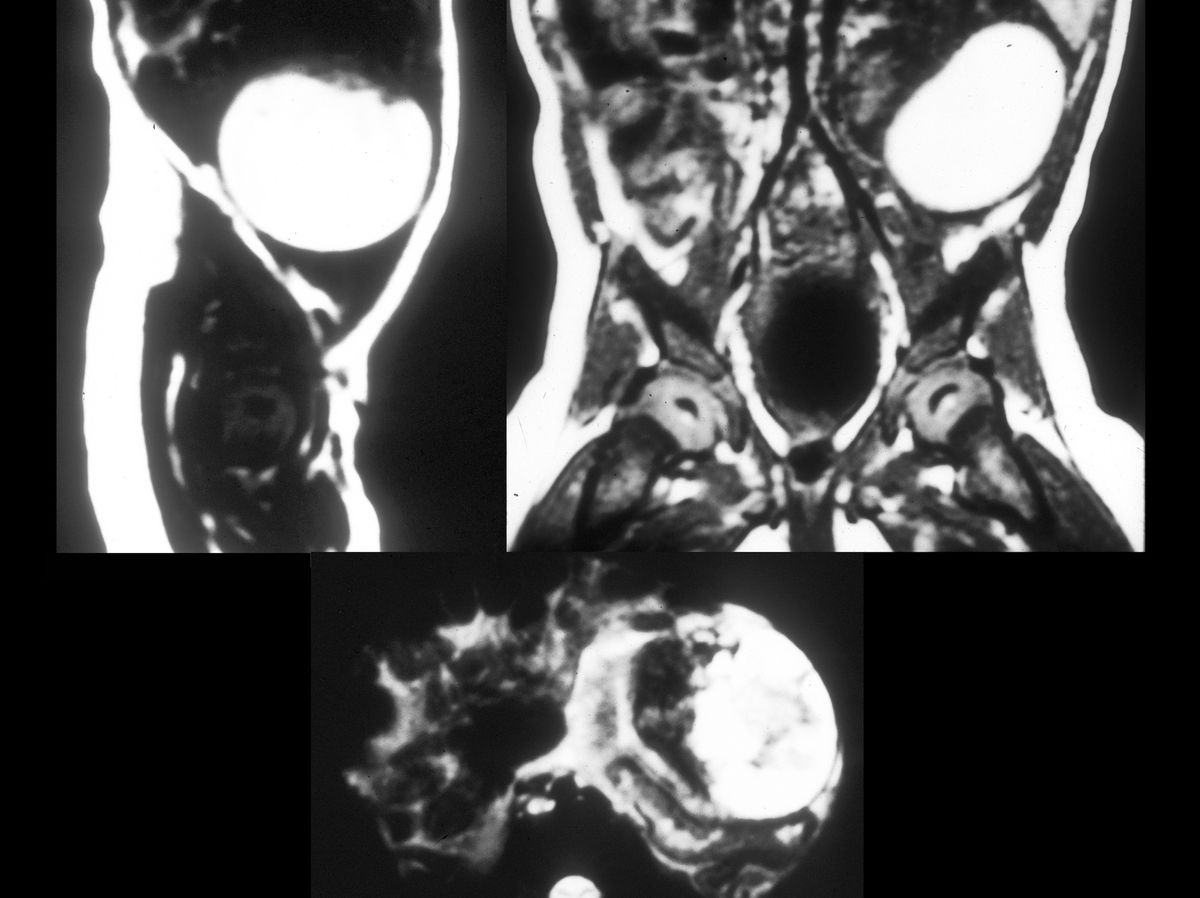
Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound is the primary tool for diagnosing neonatal ovarian cysts, providing detailed images of the cyst's size and structure.
-
MRI and CT Scans: In some cases, MRI or CT scans may be used to get a clearer picture of the cyst.
Treatment Options
Treatment for neonatal ovarian cysts depends on the size and type of the cyst, as well as the presence of symptoms.
-
Watchful Waiting: Many simple cysts resolve on their own and only require regular monitoring with ultrasounds.
-
Hormonal Therapy: In some cases, hormonal therapy may be used to help shrink the cyst.
-
Surgical Intervention: Surgery may be necessary if the cyst is large, complex, or causing symptoms.
-
Laparoscopy: Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery is often preferred for removing cysts.
-
Open Surgery: In more complicated cases, open surgery may be required to remove the cyst.
Potential Complications
While many neonatal ovarian cysts resolve without issue, there are potential complications that parents and healthcare providers should be aware of.
-
Ovarian Torsion: A cyst can cause the ovary to twist, cutting off its blood supply and leading to severe pain and potential damage.
-
Rupture: A cyst can rupture, causing pain and potentially leading to infection or other complications.
-
Infection: Although rare, cysts can become infected, requiring antibiotic treatment.
-
Impact on Fertility: In rare cases, complications from cysts can affect the future fertility of the child.
-
Recurrence: Some children may develop new cysts even after treatment.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
The long-term outlook for children with neonatal ovarian cysts is generally positive, especially with early detection and appropriate management.
-
High Resolution Rate: Many cysts resolve on their own within the first few months of life.
-
Low Recurrence Rate: Most children do not experience recurrent cysts after successful treatment.
-
Normal Ovarian Function: In most cases, the affected ovary continues to function normally after the cyst resolves or is removed.
-
Minimal Long-Term Effects: Most children do not experience long-term health issues related to neonatal ovarian cysts.
-
Regular Follow-Up: Regular follow-up with a pediatrician or pediatric gynecologist is important to monitor for any potential issues.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve the understanding and management of neonatal ovarian cysts, leading to better outcomes for affected children.
-
Genetic Factors: Researchers are exploring the role of genetic factors in the development of neonatal ovarian cysts.
-
Advanced Imaging Techniques: New imaging techniques are being developed to improve the accuracy of cyst diagnosis and monitoring.
-
Non-Surgical Treatments: Studies are investigating non-surgical treatments that could help shrink cysts without the need for invasive procedures.
-
Long-Term Studies: Long-term studies are being conducted to better understand the impact of neonatal ovarian cysts on future health and fertility.
-
International Collaboration: Researchers around the world are collaborating to share knowledge and improve the care of children with neonatal ovarian cysts.
Final Thoughts on Neonatal Ovarian Cysts
Neonatal ovarian cysts, though rare, are important to understand for parents and healthcare providers. These cysts, often detected through prenatal ultrasounds, can vary in size and complexity. Most are benign and resolve on their own without intervention. However, larger or more complex cysts might require monitoring or even surgical removal to prevent complications like torsion or rupture.
Awareness and early detection play crucial roles in managing these cysts effectively. Regular prenatal check-ups and ultrasounds can help identify any abnormalities early on. If a cyst is detected, working closely with a pediatric specialist ensures the best care and outcomes for the newborn.
Understanding the nature of neonatal ovarian cysts helps alleviate fears and equips parents with the knowledge needed to navigate this condition. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
