Muscular Atrophy Ataxia Retinitis Pigmentosa Diabetes Mellitus is a mouthful, but it's a serious condition worth understanding. This rare genetic disorder combines muscle wasting, coordination problems, vision loss, and diabetes. Imagine dealing with all these challenges at once! Muscular Atrophy weakens muscles, making everyday tasks tough. Ataxia affects balance and coordination, leading to clumsiness or falls. Retinitis Pigmentosa causes vision to deteriorate over time, often leading to blindness. Diabetes Mellitus disrupts blood sugar levels, requiring constant management. Learning about this condition can help those affected and their families navigate the complexities. Let's dive into 30 facts that shed light on this challenging disorder.
Key Takeaways:
- Muscular atrophy, ataxia, retinitis pigmentosa, and diabetes mellitus can intersect and affect the body in various ways, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and intervention for better outcomes.
- Research into gene therapy, stem cells, new medications, and clinical trials offers hope for better treatments and potential cures for these conditions, while patient advocacy groups play a crucial role in funding research and raising awareness.
Understanding Muscular Atrophy
Muscular atrophy involves the wasting away of muscle tissue. This condition can result from various causes, including lack of physical activity, aging, or diseases.
- Muscular atrophy can be caused by prolonged inactivity, such as being bedridden or immobilized.
- Neurological conditions like ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) can lead to muscle atrophy.
- Malnutrition is a significant factor that can cause muscles to waste away.
- Aging naturally leads to muscle loss, known as sarcopenia.
- Physical therapy and regular exercise can help slow down or reverse muscle atrophy.
Exploring Ataxia
Ataxia refers to a lack of muscle coordination affecting voluntary movements like walking, picking up objects, or even speaking.
- Ataxia can be hereditary or acquired due to injury, stroke, or other conditions.
- Friedreich's ataxia is a genetic form that affects the nervous system and movement.
- Cerebellar ataxia results from damage to the cerebellum, the part of the brain that controls coordination.
- Symptoms include unsteady gait, poor coordination, and difficulty with fine motor tasks.
- No cure exists for ataxia, but treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
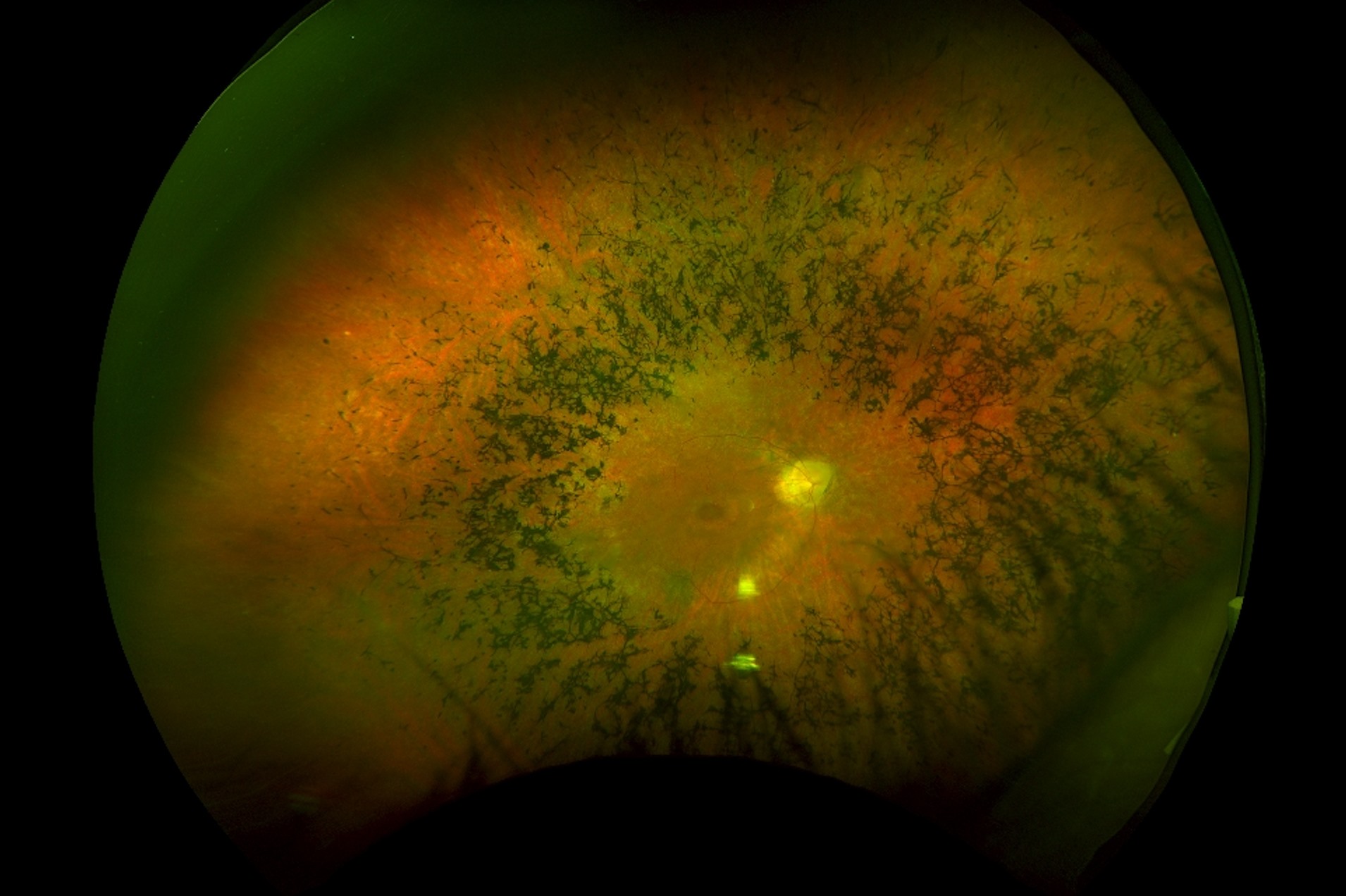
Retinitis Pigmentosa Insights
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a group of genetic disorders that affect the retina's ability to respond to light, leading to a gradual loss of vision.
- RP often starts with night blindness, making it hard to see in low light.
- Peripheral vision loss follows, eventually leading to tunnel vision.
- Genetic mutations are the primary cause of RP, affecting the photoreceptor cells in the retina.
- No cure currently exists, but research is ongoing to find treatments.
- Vitamin A supplements may slow the progression of some forms of RP.
Diabetes Mellitus Overview
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body's inability to produce or use insulin effectively.
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Type 2 diabetes is more common and often linked to lifestyle factors like diet and exercise.
- Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
- Symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss.
- Management involves lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels.
The Connection Between These Conditions
While muscular atrophy, ataxia, retinitis pigmentosa, and diabetes mellitus may seem unrelated, they can intersect in various ways.
- Diabetes can lead to muscle atrophy due to poor blood circulation and nerve damage.
- Diabetic neuropathy can cause ataxia-like symptoms due to nerve damage affecting coordination.
- Retinitis pigmentosa can occur in individuals with certain types of diabetes, particularly those with genetic predispositions.
- Exercise is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing muscle atrophy.
- Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for all these conditions.
Advances in Research and Treatment
Ongoing research aims to find better treatments and potential cures for these conditions.
- Gene therapy holds promise for treating genetic disorders like retinitis pigmentosa and some forms of ataxia.
- Stem cell research is exploring ways to regenerate damaged tissues and organs.
- New medications are being developed to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Clinical trials offer hope for patients by testing innovative treatments.
- Patient advocacy groups play a crucial role in funding research and raising awareness.
Final Thoughts on Muscular Atrophy Ataxia Retinitis Pigmentosa Diabetes Mellitus
Muscular Atrophy Ataxia Retinitis Pigmentosa Diabetes Mellitus (MAARD) is a complex condition that affects multiple systems in the body. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help those affected manage their health more effectively. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for improving quality of life. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and physical therapy can make a significant difference. Genetic counseling might also be beneficial for families with a history of MAARD. Staying informed and proactive can empower individuals to take control of their health. Remember, knowledge is power. By spreading awareness about MAARD, we can support those affected and contribute to ongoing research efforts. Stay curious, stay informed, and never underestimate the power of community support.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
