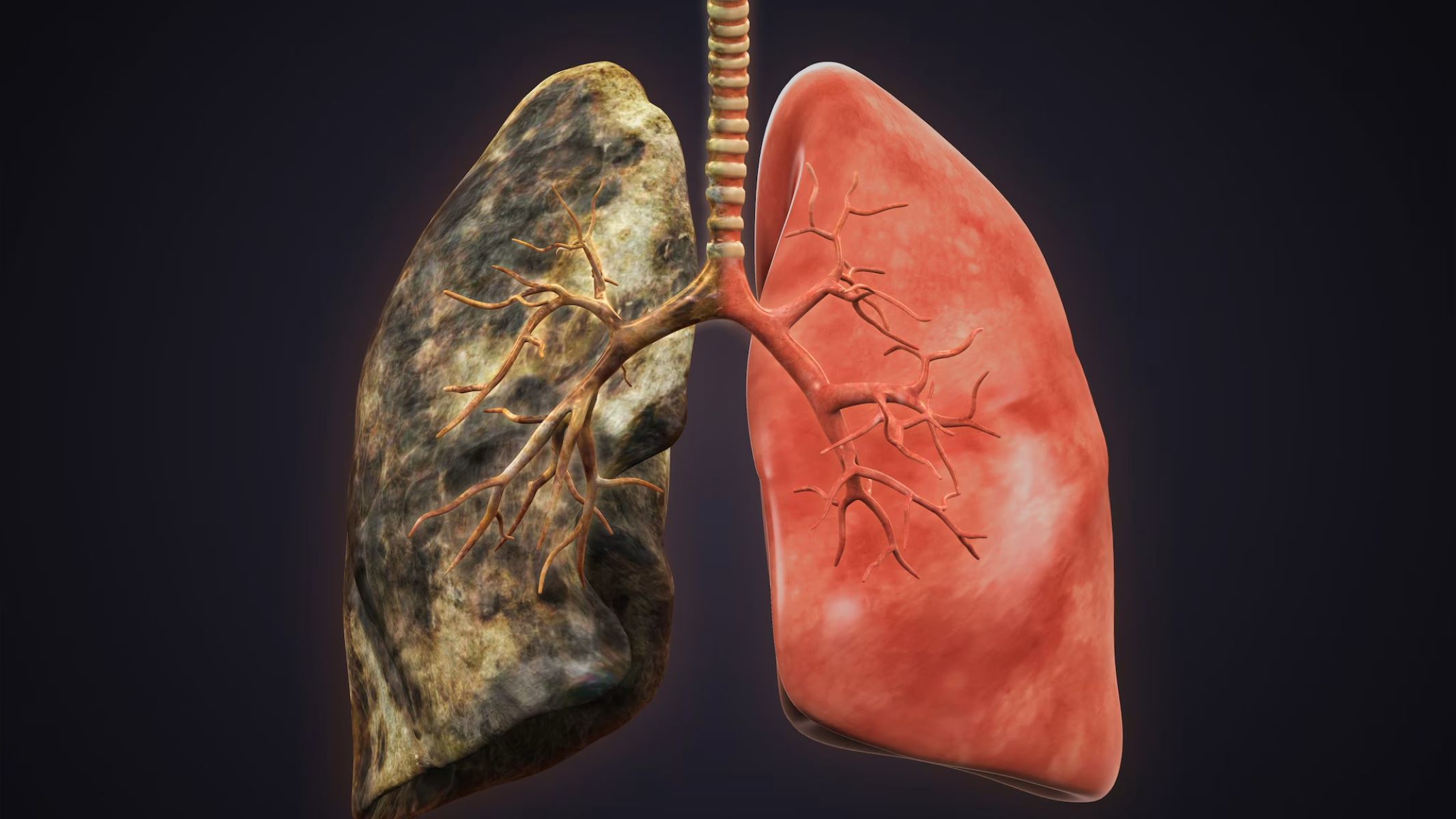
Kaolin pneumoconiosis, often called "potter's rot," is a lung disease caused by inhaling kaolin dust. But what exactly is kaolin pneumoconiosis? This condition primarily affects workers in industries like ceramics, mining, and paper manufacturing, where kaolin clay is prevalent. When tiny particles of this clay are inhaled over time, they can settle in the lungs, leading to inflammation and scarring. Symptoms often mimic those of other respiratory illnesses, including coughing, shortness of breath, and chest pain. While protective gear and improved ventilation have reduced cases, awareness remains crucial for those at risk. Understanding the causes and symptoms can help in early detection and prevention. With proper precautions, workers can continue their craft without compromising their health. Stay informed and breathe easy!
Key Takeaways:
- Kaolin Pneumoconiosis is a lung disease caused by inhaling kaolin dust, affecting workers in industries like mining and ceramics. Protective gear and regular check-ups are crucial for prevention and management.
- Research and technology advancements are helping to reduce the impact of kaolin pneumoconiosis, with innovations in nanotechnology, PPE, and remote monitoring. Education and sustainable practices are also key in protecting workers.
What is Kaolin Pneumoconiosis?
Kaolin Pneumoconiosis is a lung disease caused by inhaling kaolin dust. Kaolin, also known as china clay, is a soft white clay used in the production of ceramics, paper, and other products. Let's explore some interesting facts about this condition.
-
Kaolin's Origin: Kaolin is named after the Kao-ling mountain in China, where it was first discovered. This clay has been used for centuries in pottery and porcelain.
-
Occupational Hazard: Workers in industries like mining, ceramics, and paper manufacturing are at higher risk of developing this lung disease due to prolonged exposure to kaolin dust.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include coughing, shortness of breath, and chest pain. These symptoms can worsen over time if exposure continues.
-
Diagnosis: Doctors often use chest X-rays and lung function tests to diagnose kaolin pneumoconiosis. These tests help determine the extent of lung damage.
-
Prevention: Wearing protective gear, such as masks and respirators, can significantly reduce the risk of inhaling harmful dust particles.
How Does Kaolin Affect the Lungs?
Understanding how kaolin impacts lung health is crucial for those working with this material. The fine particles can settle in the lungs, leading to various health issues.
-
Particle Size Matters: The smaller the kaolin particles, the deeper they can penetrate into the lungs, causing more damage.
-
Inflammation: Inhaled kaolin dust can cause inflammation in the lung tissues, leading to scarring and reduced lung function.
-
Chronic Exposure: Long-term exposure can lead to chronic lung diseases, making it difficult for affected individuals to breathe normally.
-
Silica Content: Some kaolin deposits contain silica, which can exacerbate lung damage and increase the risk of developing silicosis, another lung disease.
-
Lung Defense Mechanisms: The body has natural defenses, like mucus and cilia, to trap and expel dust particles. However, excessive exposure can overwhelm these defenses.
Treatment and Management
While there's no cure for kaolin pneumoconiosis, certain treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Medications: Doctors may prescribe bronchodilators to help open airways and make breathing easier.
-
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: This program includes exercise training, education, and support to help patients manage their symptoms.
-
Oxygen Therapy: For severe cases, supplemental oxygen may be necessary to ensure adequate oxygen levels in the blood.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups and lung function tests are essential for monitoring the progression of the disease.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking and avoiding further exposure to dust can help slow the progression of lung damage.
Historical Context and Research
Kaolin pneumoconiosis has been studied for many years, with researchers continually seeking to understand and mitigate its effects.
-
First Documented Cases: The first cases of kaolin pneumoconiosis were reported in the early 20th century among workers in the pottery industry.
-
Research Advances: Ongoing research aims to develop better protective equipment and workplace practices to reduce exposure.
-
Regulations: Many countries have implemented regulations to limit workers' exposure to kaolin dust, improving workplace safety.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Health organizations conduct awareness campaigns to educate workers and employers about the risks and prevention methods.
-
Technological Innovations: Advances in technology have led to improved dust control measures in industries using kaolin.
Global Impact and Statistics
Kaolin pneumoconiosis affects workers worldwide, with varying prevalence depending on industry practices and regulations.
-
Global Prevalence: The prevalence of kaolin pneumoconiosis varies globally, with higher rates in countries with less stringent occupational safety regulations.
-
Economic Impact: The disease can lead to significant economic costs due to healthcare expenses and lost productivity.
-
Industry-Specific Data: Certain industries, like ceramics and mining, report higher rates of kaolin pneumoconiosis among their workers.
-
Worker Advocacy: Labor unions and worker advocacy groups play a crucial role in pushing for better safety standards and compensation for affected workers.
-
International Collaboration: Countries collaborate on research and policy-making to address occupational lung diseases, including kaolin pneumoconiosis.
Future Directions and Innovations
The fight against kaolin pneumoconiosis continues, with new strategies and technologies emerging to protect workers.
-
Nanotechnology: Researchers are exploring the use of nanotechnology to create more effective dust filtration systems.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Innovations in PPE design aim to provide better protection and comfort for workers.
-
Remote Monitoring: Technology allows for remote monitoring of air quality in workplaces, alerting workers to dangerous dust levels.
-
Education and Training: Enhanced training programs focus on teaching workers how to minimize exposure and recognize early symptoms.
-
Sustainable Practices: Industries are adopting more sustainable practices to reduce dust emissions and protect both workers and the environment.
Bringing It All Together
Kaolin pneumoconiosis, a lung condition caused by inhaling kaolin dust, is more common than many realize. Workers in industries like mining, ceramics, and paper manufacturing face higher risks. Symptoms often mimic other respiratory issues, making early diagnosis tricky. Regular health check-ups and workplace safety measures are crucial for prevention. Wearing protective gear and ensuring proper ventilation can significantly reduce exposure. While treatment focuses on managing symptoms, avoiding further exposure is key to preventing progression. Awareness and education about this condition can lead to better health outcomes for those at risk. Understanding the importance of safety protocols in workplaces handling kaolin can make a big difference. If you or someone you know works in an industry involving kaolin, staying informed and proactive about health can help manage and prevent this condition. Knowledge truly is power when it comes to protecting lung health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
