What is fetal aminopterin syndrome? Fetal aminopterin syndrome is a rare condition caused by exposure to the drug aminopterin during pregnancy. This drug, once used as a chemotherapy agent and for inducing abortions, can lead to severe birth defects if taken by pregnant women. Symptoms of this syndrome include growth retardation, skeletal abnormalities, and facial malformations. Affected infants may also experience intellectual disabilities and other developmental issues. Understanding the risks associated with aminopterin is crucial for expecting mothers and healthcare providers. This post will delve into 30 key facts about fetal aminopterin syndrome, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and long-term effects.
Key Takeaways:
- Fetal Aminopterin Syndrome (FAS) is a rare condition caused by exposure to the drug aminopterin during pregnancy, leading to severe and varied effects on fetal development.
- Preventing FAS involves avoiding exposure to aminopterin and similar teratogens during pregnancy, and ongoing research aims to better understand the condition and develop more effective treatments.
What is Fetal Aminopterin Syndrome?
Fetal Aminopterin Syndrome (FAS) is a rare condition caused by exposure to the drug aminopterin during pregnancy. Aminopterin, a folic acid antagonist, was once used as a chemotherapeutic agent and for inducing abortions. Its effects on fetal development can be severe and varied.
- Aminopterin was first synthesized in 1947 and used as a chemotherapy drug.
- FAS results from the teratogenic effects of aminopterin on a developing fetus.
- Teratogens are substances that can cause congenital abnormalities or birth defects.
- Folic acid antagonists like aminopterin interfere with DNA synthesis, crucial for cell division and growth.
Symptoms of Fetal Aminopterin Syndrome
The symptoms of FAS can be diverse, affecting multiple systems in the body. These symptoms often lead to significant developmental challenges.
- Growth retardation is a common symptom, leading to low birth weight and short stature.
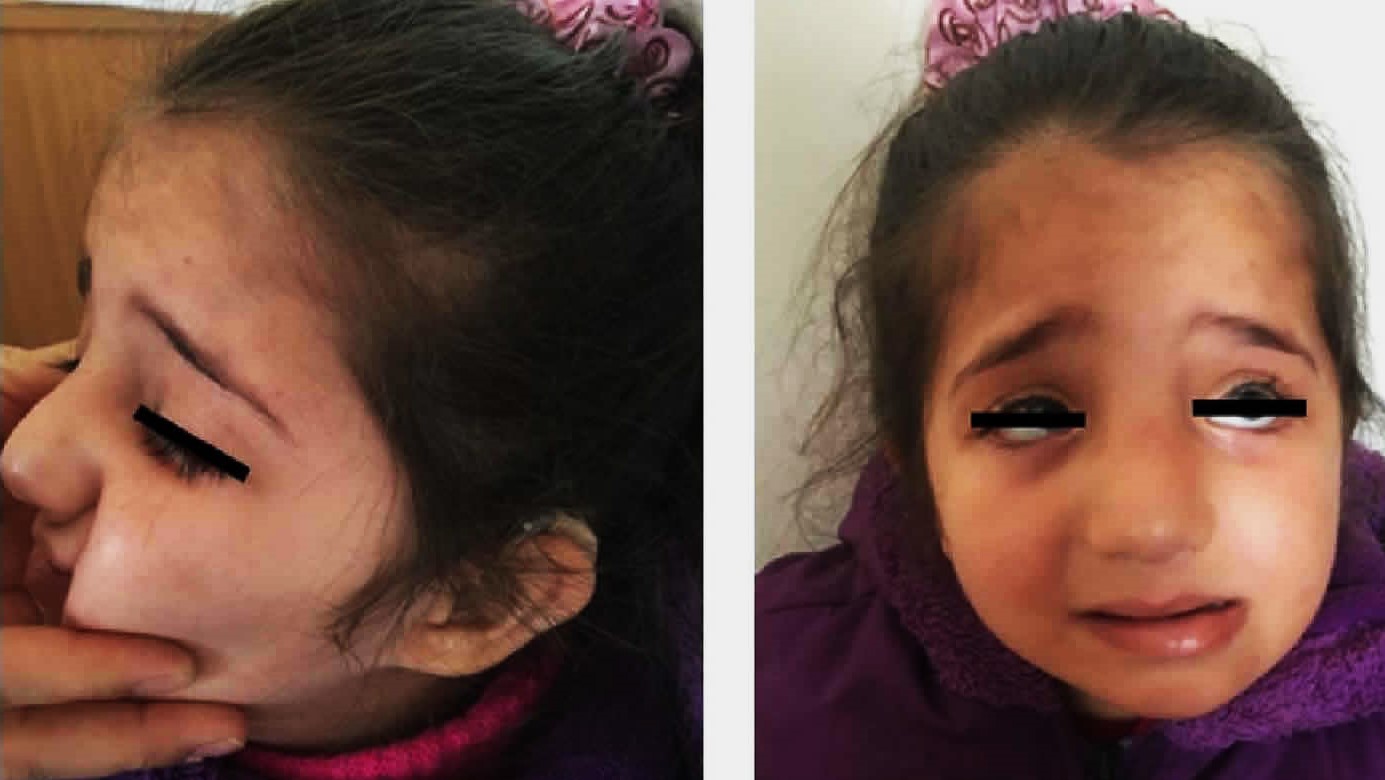
- Craniofacial abnormalities include a small head, wide-set eyes, and a flat nasal bridge.
- Limb defects such as missing or underdeveloped fingers and toes can occur.
- Neural tube defects like spina bifida may develop due to disrupted folic acid metabolism.
Diagnosis and Detection
Diagnosing FAS involves a combination of clinical examination and medical history. Early detection can help manage symptoms more effectively.
- Prenatal ultrasound can sometimes detect physical abnormalities associated with FAS.
- Amniocentesis may be used to analyze amniotic fluid for signs of exposure.
- Genetic counseling is recommended for families with a history of aminopterin exposure.
- Physical examination after birth can identify characteristic features of FAS.
Historical Context
Understanding the history of aminopterin helps explain its impact and why it is no longer in use for certain purposes.
- Aminopterin was initially used to treat leukemia in the 1940s.
- Abortifacient use of aminopterin was discontinued due to its severe side effects on fetuses.
- Methotrexate, a related drug, replaced aminopterin for many medical uses due to its safer profile.
- Historical cases of FAS helped shape modern regulations on drug use during pregnancy.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for FAS, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Physical therapy can aid in improving motor skills and strength.
- Surgical interventions may correct some physical deformities.
- Special education programs support cognitive and developmental needs.
- Nutritional support ensures adequate growth and development.
Prevention and Awareness
Preventing FAS involves avoiding exposure to aminopterin and similar teratogens during pregnancy.
- Public health campaigns educate about the risks of certain medications during pregnancy.
- Medical guidelines advise against the use of folic acid antagonists in pregnant women.
- Prenatal vitamins with folic acid are recommended to prevent neural tube defects.
- Awareness programs help healthcare providers recognize and manage FAS.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand FAS and develop more effective treatments.
- Genetic studies explore the mechanisms by which aminopterin causes birth defects.
- Animal models help researchers study the effects of folic acid antagonists on development.
- Clinical trials test new therapies for managing symptoms of FAS.
- Public health research focuses on improving prevention strategies.
Real-Life Cases
Examining real-life cases of FAS provides insight into the condition's impact on individuals and families.
- Case studies document the diverse presentations and outcomes of FAS.
- Personal stories highlight the challenges and triumphs of living with FAS.
Final Thoughts on Fetal Aminopterin
Fetal aminopterin, a drug once used for cancer treatment, has a dark history. It was found to cause severe birth defects when administered to pregnant women. This led to its discontinuation for such use. Understanding its effects has been crucial for medical research and ethics in drug testing. The tragic outcomes highlighted the importance of rigorous testing and ethical considerations in medicine. While fetal aminopterin is no longer in use, its legacy serves as a reminder of the potential risks involved in drug development. This knowledge continues to shape modern medical practices, ensuring safer treatments for future generations. By learning from past mistakes, the medical community strives to prevent similar tragedies. The story of fetal aminopterin underscores the need for caution and thorough research in the pursuit of medical advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
