Ethylmalonic Aciduria is a rare metabolic disorder that affects the body's ability to process certain fats and proteins. This condition, often diagnosed in infancy, can lead to a variety of symptoms including developmental delays, muscle weakness, and seizures. Caused by mutations in the ETHE1 gene, it disrupts the normal function of mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of cells. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Understanding Ethylmalonic Aciduria can help families and healthcare providers better navigate the challenges associated with this disorder. Let's dive into 30 essential facts about this condition to shed light on its complexities.
Key Takeaways:
- Ethylmalonic Aciduria is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down certain fats and proteins, leading to developmental delays, seizures, and skin abnormalities. Early diagnosis and proper management are crucial for improving outcomes.
- Living with Ethylmalonic Aciduria requires a comprehensive approach to care, including education, routine, communication with healthcare providers, advocacy, mental health support, and planning for the future. Supportive care and therapies can help improve daily functioning.
What is Ethylmalonic Aciduria?
Ethylmalonic Aciduria (EMA) is a rare metabolic disorder. It affects the body's ability to break down certain fats and proteins. This condition can lead to a variety of health issues, often starting in infancy.
- Ethylmalonic Aciduria is a genetic disorder. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
- The condition is caused by mutations in the ETHE1 gene. This gene provides instructions for making an enzyme involved in breaking down sulfur-containing compounds.
- Symptoms of EMA often appear in the first few months of life. They can include developmental delays, muscle weakness, and seizures.
- Ethylmalonic acid builds up in the body. This buildup can be detected through urine tests.
- Newborn screening can sometimes identify EMA. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing the condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how EMA is diagnosed can help in early detection and treatment. Here are some key points to consider.
- Hypotonia or low muscle tone is a common symptom. It can make it difficult for infants to hold up their heads or sit up.
- Failure to thrive is another symptom. Affected infants may not gain weight or grow as expected.
- Metabolic acidosis is often present. This condition occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body.
- Developmental delays are frequently observed. Children with EMA may take longer to reach milestones like walking or talking.
- Seizures can occur in some cases. These may be difficult to control with standard medications.
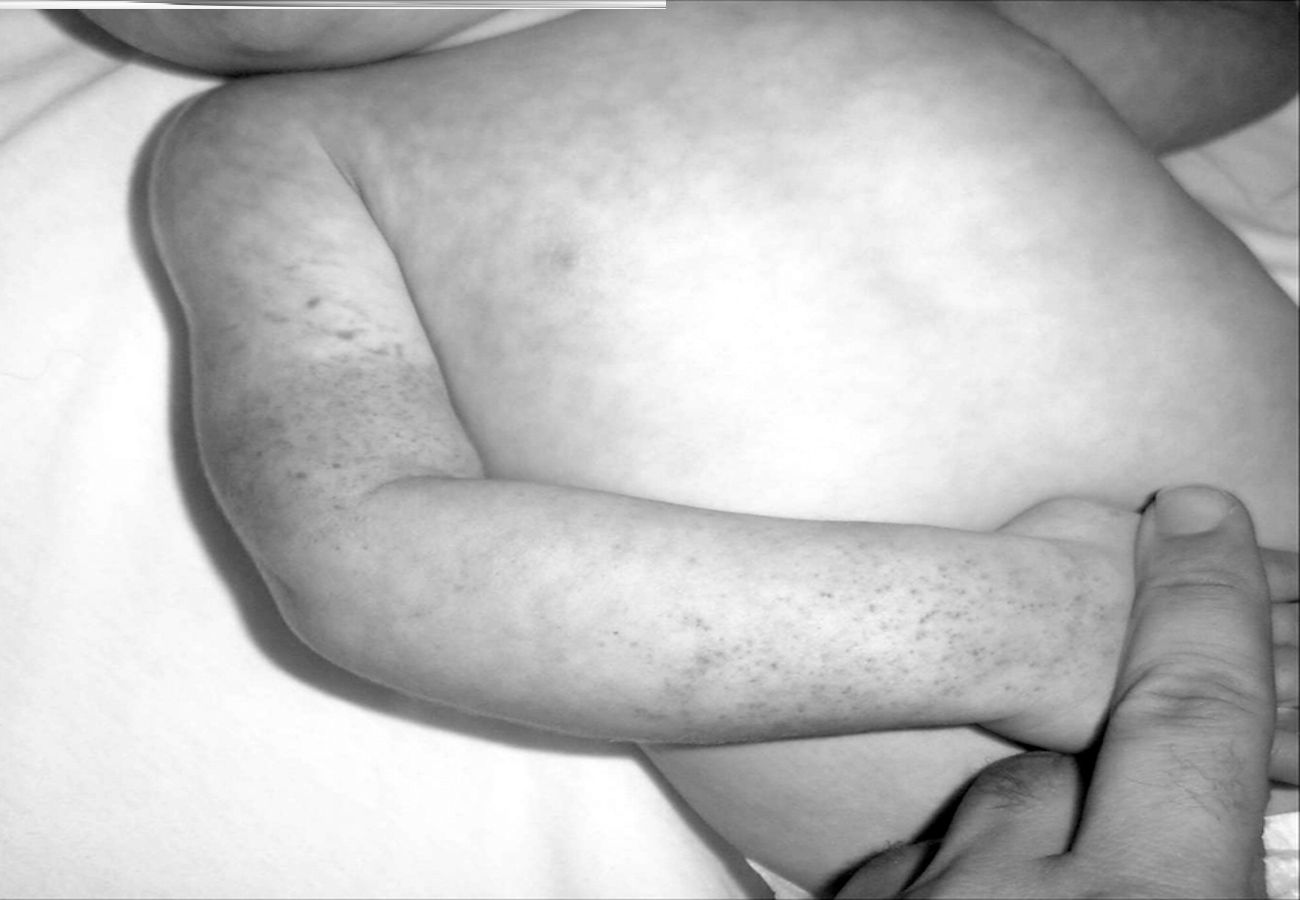
- Skin abnormalities such as rashes or lesions may appear. These skin issues can be persistent and difficult to treat.
- Blood tests can reveal elevated levels of certain acids. These tests are crucial for diagnosing EMA.
- Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis. Identifying mutations in the ETHE1 gene provides a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for EMA, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Dietary management is essential. A low-protein, high-carbohydrate diet can help reduce the buildup of harmful acids.
- Supplementation with certain vitamins and minerals may be beneficial. For example, carnitine supplements can help the body process fats more effectively.
- Medications can help manage symptoms. Anticonvulsants may be prescribed to control seizures.
- Physical therapy can improve muscle strength and coordination. This can help children achieve developmental milestones.
- Regular monitoring is crucial. Frequent blood and urine tests can help track the effectiveness of treatments.
- Emergency care plans should be in place. Infections or other stressors can worsen symptoms, so having a plan can be lifesaving.
Prognosis and Research
The prognosis for individuals with EMA varies. Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of this condition.
- Life expectancy can be reduced. However, early diagnosis and proper management can improve outcomes.
- Quality of life can be significantly impacted. Supportive care and therapies can help improve daily functioning.
- Research is ongoing. Scientists are studying the underlying mechanisms of EMA to develop better treatments.
- Clinical trials may be available. Participation in trials can provide access to new therapies and contribute to scientific knowledge.
- Support groups can offer valuable resources. Connecting with other families facing similar challenges can provide emotional and practical support.
Living with Ethylmalonic Aciduria
Living with EMA requires a comprehensive approach to care. Here are some tips for managing daily life with this condition.
- Education is key. Understanding the condition helps families make informed decisions about care.
- Routine can be beneficial. Establishing a daily routine can help manage symptoms and reduce stress.
- Communication with healthcare providers is crucial. Regular check-ups and open communication can help manage the condition effectively.
- Advocacy can make a difference. Advocating for better healthcare and research funding can improve outcomes for everyone with EMA.
- Mental health support is important. Counseling and support groups can help families cope with the emotional challenges of living with a chronic condition.
- Planning for the future is essential. Preparing for potential challenges can help families navigate the complexities of EMA.
Final Thoughts on Ethylmalonic Aciduria
Ethylmalonic Aciduria, a rare metabolic disorder, affects the body's ability to process certain fats and proteins. This condition can lead to severe symptoms like developmental delays, muscle weakness, and seizures. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the disease and improving the quality of life for those affected. Genetic testing plays a vital role in identifying the disorder, allowing for timely intervention. While there's no cure, dietary management and supportive therapies can help mitigate symptoms. Research continues to explore new treatments and better understand the condition. Awareness and education about Ethylmalonic Aciduria are essential for early detection and support. By staying informed, we can contribute to a better future for individuals living with this challenging disorder.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
