Diffuse Panbronchiolitis might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it is crucial. This rare lung disease primarily affects individuals of East Asian descent, particularly in Japan. Characterized by chronic inflammation of the small airways, it can lead to severe respiratory issues if left untreated. Symptoms often include a persistent cough, shortness of breath, and excessive sputum production. While the exact cause remains unknown, genetic factors and environmental triggers are believed to play a role. Early diagnosis and treatment with macrolide antibiotics have significantly improved patient outcomes. Let's dive into 30 intriguing facts about this condition to better understand its impact and management.
Key Takeaways:
- Diffuse Panbronchiolitis (DPB) is a rare lung disease that mainly affects people of East Asian descent, causing symptoms like chronic cough and shortness of breath. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the disease.
- While there is no cure for DPB, treatments like macrolide antibiotics and pulmonary rehabilitation can help improve quality of life. Ongoing research is exploring new genetic insights and potential therapies for this challenging condition.
What is Diffuse Panbronchiolitis?
Diffuse Panbronchiolitis (DPB) is a rare, chronic inflammatory lung disease. It primarily affects the small airways, known as bronchioles, leading to severe respiratory issues. Understanding DPB is crucial for those affected and their families.
-
DPB mainly affects people of East Asian descent. The disease is most commonly found in Japan, Korea, and China.
-
The exact cause of DPB remains unknown. Researchers believe a combination of genetic and environmental factors may contribute.
-
Symptoms often resemble those of chronic bronchitis. Persistent cough, sputum production, and shortness of breath are common.
-
DPB is more common in men than women. The male-to-female ratio is approximately 2:1.
-
The disease usually appears in middle-aged adults. Most patients are diagnosed between the ages of 40 and 60.
Diagnosis and Symptoms
Diagnosing DPB can be challenging due to its rarity and similarity to other respiratory conditions. Here are some key facts about its diagnosis and symptoms.
-
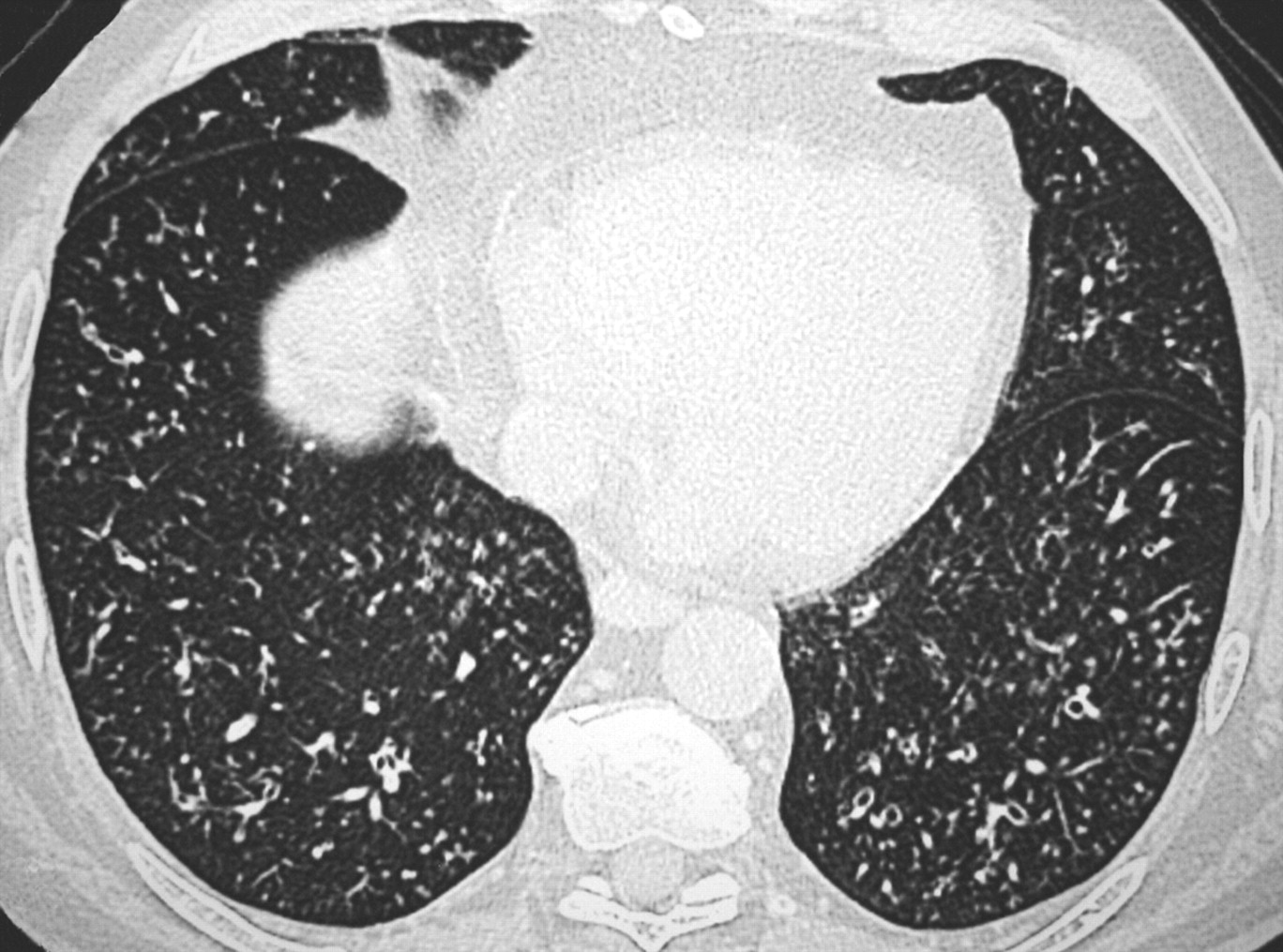
High-resolution CT scans are crucial for diagnosis. These scans reveal characteristic patterns in the lungs.
-
Nasal symptoms often precede lung symptoms. Chronic sinusitis is a common early sign.
-
Pulmonary function tests help assess lung damage. These tests measure airflow and lung volume.
-
Bronchoscopy can aid in diagnosis. This procedure allows doctors to examine the airways and collect tissue samples.
-
Blood tests may show elevated levels of certain antibodies. These antibodies can indicate an immune response.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for DPB, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some important facts about treatment options.
-
Macrolide antibiotics are the cornerstone of treatment. These antibiotics have anti-inflammatory properties that help control the disease.
-
Long-term antibiotic therapy is often necessary. Patients may need to take antibiotics for several months or even years.
-
Inhaled bronchodilators can help open airways. These medications make breathing easier.
-
Corticosteroids may be used in severe cases. These drugs reduce inflammation but have significant side effects.
-
Oxygen therapy may be required for advanced cases. Supplemental oxygen helps maintain adequate blood oxygen levels.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Genetic predisposition and environmental factors play a significant role in DPB. Understanding these factors can provide insights into the disease's development.
-
HLA-B54 is a genetic marker associated with DPB. This marker is more common in affected individuals.
-
Smoking is not a primary risk factor. Unlike many other lung diseases, smoking does not significantly increase the risk of DPB.
-
Air pollution may contribute to disease development. Exposure to pollutants can exacerbate symptoms.
-
Living in rural areas may increase risk. Rural residents in East Asia have higher DPB rates.
-
Family history can be a risk factor. Having relatives with DPB increases the likelihood of developing the disease.
Prognosis and Quality of Life
Living with DPB can be challenging, but proper management can improve prognosis and quality of life. Here are some facts about living with DPB.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment improve outcomes. Prompt medical intervention can slow disease progression.
-
Regular follow-up is essential. Ongoing medical care helps monitor and manage symptoms.
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation can enhance quality of life. Exercise and education programs improve lung function and overall well-being.
-
Nutritional support may be necessary. Maintaining a healthy diet supports overall health.
-
Mental health support is crucial. Coping with a chronic illness can be emotionally challenging.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand DPB and develop new treatments. Here are some exciting developments in the field.
-
Genetic studies are uncovering new insights. Researchers are identifying additional genetic markers linked to DPB.
-
New anti-inflammatory drugs are being tested. These drugs may offer alternative treatment options.
-
Stem cell therapy shows promise. Early studies suggest stem cells could help repair lung damage.
-
International collaboration is increasing. Researchers worldwide are working together to study DPB.
-
Patient registries are being established. These databases collect information to improve understanding and treatment of DPB.
Final Thoughts on Diffuse Panbronchiolitis
Understanding diffuse panbronchiolitis can help patients and caregivers manage the condition better. This chronic lung disease, primarily affecting people of East Asian descent, causes inflammation in the small airways. Symptoms like chronic cough, sputum production, and shortness of breath can significantly impact daily life. Early diagnosis and treatment, including antibiotics and supportive care, improve outcomes. Awareness of the disease's genetic links and environmental triggers can aid in prevention and management. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options is crucial for those affected. By recognizing the signs and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can lead healthier lives despite the challenges posed by diffuse panbronchiolitis. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with any health condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
