Polymorphic Macular Degeneration is a complex eye condition that affects the central part of the retina, known as the macula. This condition can lead to vision loss, making everyday tasks like reading or recognizing faces challenging. Understanding this condition is crucial for those affected and their loved ones. In this blog post, we'll share 25 facts about Polymorphic Macular Degeneration to help you grasp its impact, causes, symptoms, and potential treatments. Whether you're seeking information for yourself or someone you care about, these facts will provide valuable insights into managing and living with this eye condition. Let's dive in and uncover the essential details you need to know.
Key Takeaways:
- Polymorphic Macular Degeneration (PMD) affects the central vision and can occur at any age. Early detection and healthy lifestyle choices can help manage the condition and support eye health.
- Regular eye check-ups, adaptive technologies, and a balanced diet are essential for living well with PMD. Stay informed about the latest research and treatments to make informed decisions about care.
What is Polymorphic Macular Degeneration?
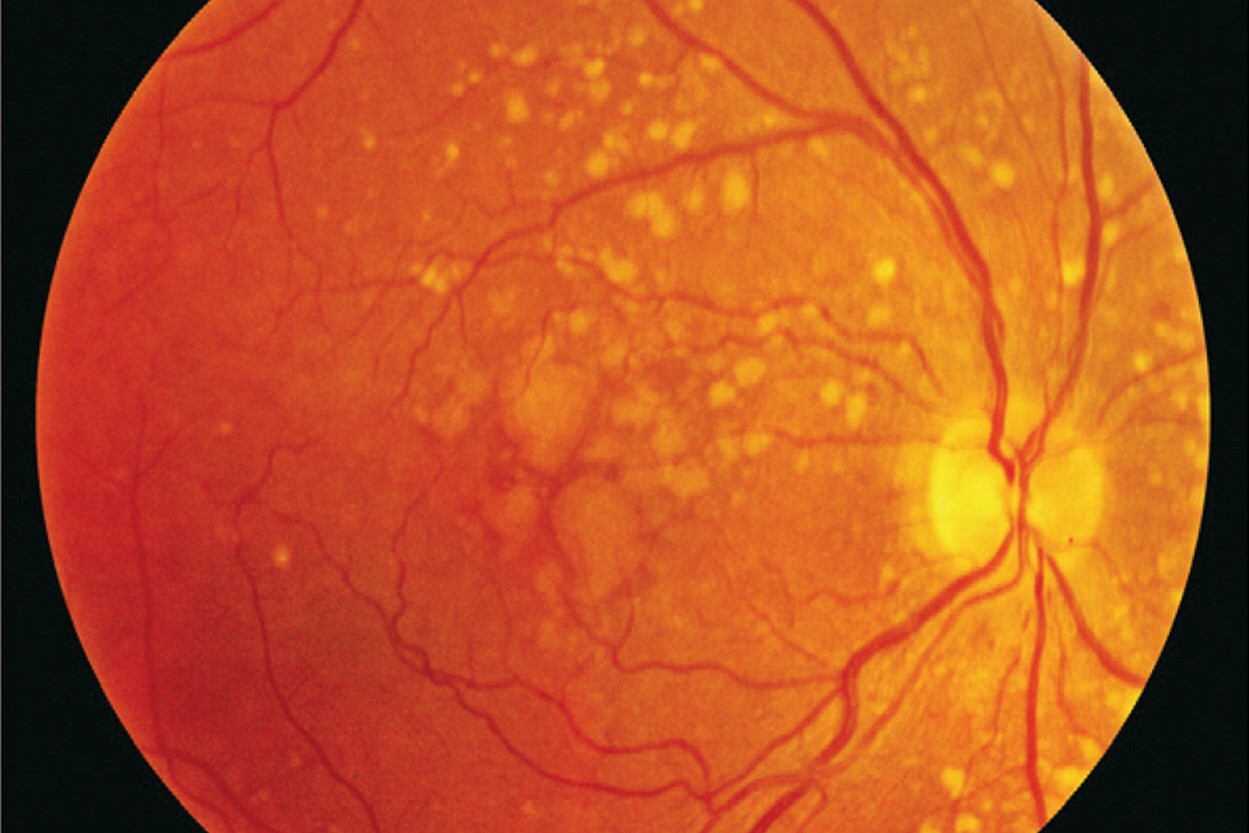
Polymorphic Macular Degeneration (PMD) is a rare eye condition that affects the central part of the retina, known as the macula. This condition can lead to vision loss and other complications. Here are some intriguing facts about PMD.
- PMD primarily affects the macula, the part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision.
- The term "polymorphic" indicates that the disease can present in various forms and severities.
- PMD is often confused with age-related macular degeneration (AMD), but they are distinct conditions.
- Unlike AMD, PMD can affect individuals of all ages, not just the elderly.
- Symptoms of PMD can include blurred vision, dark spots in the central vision, and difficulty recognizing faces.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of PMD can help in early detection and management. Here are some key points to consider.
- The exact cause of PMD is still unknown, but genetic factors may play a significant role.
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to UV light, may also contribute to the development of PMD.
- Smoking is a known risk factor for many eye diseases, including PMD.
- A family history of macular degeneration increases the risk of developing PMD.
- Poor diet, particularly one low in antioxidants, can exacerbate the condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management of PMD. Here are some symptoms and diagnostic methods.
- Early symptoms may include slight blurriness or difficulty reading.
- As the condition progresses, central vision may become increasingly distorted.
- An eye exam, including a dilated eye exam, is crucial for diagnosing PMD.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test that helps in diagnosing PMD.
- Fluorescein angiography can also be used to detect abnormalities in the blood vessels of the retina.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for PMD, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
- Anti-VEGF injections are commonly used to treat abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina.
- Laser therapy can help seal leaking blood vessels and reduce vision loss.
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT) uses light-activated drugs to target abnormal blood vessels.
- Nutritional supplements, particularly those high in antioxidants, can support eye health.
- Low vision aids, such as magnifying glasses and special lenses, can help improve quality of life.
Living with Polymorphic Macular Degeneration
Living with PMD can be challenging, but there are ways to adapt and maintain a good quality of life.
- Regular eye check-ups are essential for monitoring the progression of PMD.
- Adaptive technologies, like screen readers and voice-activated devices, can assist with daily tasks.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can benefit overall eye health.
- Staying informed about the latest research and treatments can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their care.
Final Thoughts on Polymorphic Macular Degeneration
Polymorphic Macular Degeneration (PMD) is a complex condition affecting the central part of the retina, leading to vision loss. Understanding PMD helps in early detection and better management. Genetic factors, age, and lifestyle choices play significant roles in its development. Regular eye check-ups and a healthy diet rich in antioxidants can slow down its progression. While there's no cure, treatments like anti-VEGF injections and laser therapy can help manage symptoms. Staying informed and proactive about eye health is crucial. If you or a loved one shows signs of PMD, consult an eye specialist promptly. Remember, early intervention can make a big difference. Stay vigilant, take care of your eyes, and spread awareness about this condition. Your vision is precious; protect it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
