Oculodentoosseous Dysplasia Recessive (ODOD) might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it is crucial. This rare genetic disorder affects the eyes, teeth, and bones, leading to various health challenges. ODOD is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected. Symptoms can include abnormal eye development, dental issues like missing or malformed teeth, and bone abnormalities. While it’s a rare condition, knowing the facts can help in early diagnosis and management. Let’s dive into 25 key facts about Oculodentoosseous Dysplasia Recessive to better understand this complex disorder.
Key Takeaways:
- Oculodentoosseous Dysplasia Recessive (ODOD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the eyes, teeth, and bones. It's inherited from both parents and can cause small eyes, dental issues, and brittle bones.
- Early diagnosis and regular check-ups are crucial for managing ODOD. Genetic testing, eye exams, and dental care can help improve the quality of life for those affected by this complex condition.
What is Oculodentoosseous Dysplasia Recessive?
Oculodentoosseous Dysplasia Recessive (ODOD) is a rare genetic disorder. It affects the eyes, teeth, and bones. Understanding this condition helps in managing its symptoms better.
- ODOD is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected.
- The disorder is caused by mutations in the GJA1 gene. This gene is crucial for cell communication.
- Symptoms often appear in early childhood. They can vary widely among individuals.
- Eye abnormalities are common. These can include microphthalmia (small eyes) and glaucoma.
- Dental issues are a hallmark of ODOD. Teeth may be small, misshapen, or missing.
- Bone abnormalities are also prevalent. These can include brittle bones and craniofacial dysmorphisms.
- The condition is extremely rare. Fewer than 100 cases have been documented worldwide.
Eye Symptoms of ODOD
The eyes are significantly affected by ODOD. These symptoms can impact vision and overall eye health.
- Microphthalmia is a common symptom. It results in abnormally small eyes.
- Glaucoma can develop early. This increases pressure in the eye, potentially leading to blindness.
- Strabismus, or crossed eyes, is often seen. This can affect depth perception and vision clarity.
- Coloboma, a defect in the eye structure, may occur. It can affect the iris, retina, or optic nerve.
- Nystagmus, or involuntary eye movement, is another possible symptom. This can cause vision problems and dizziness.
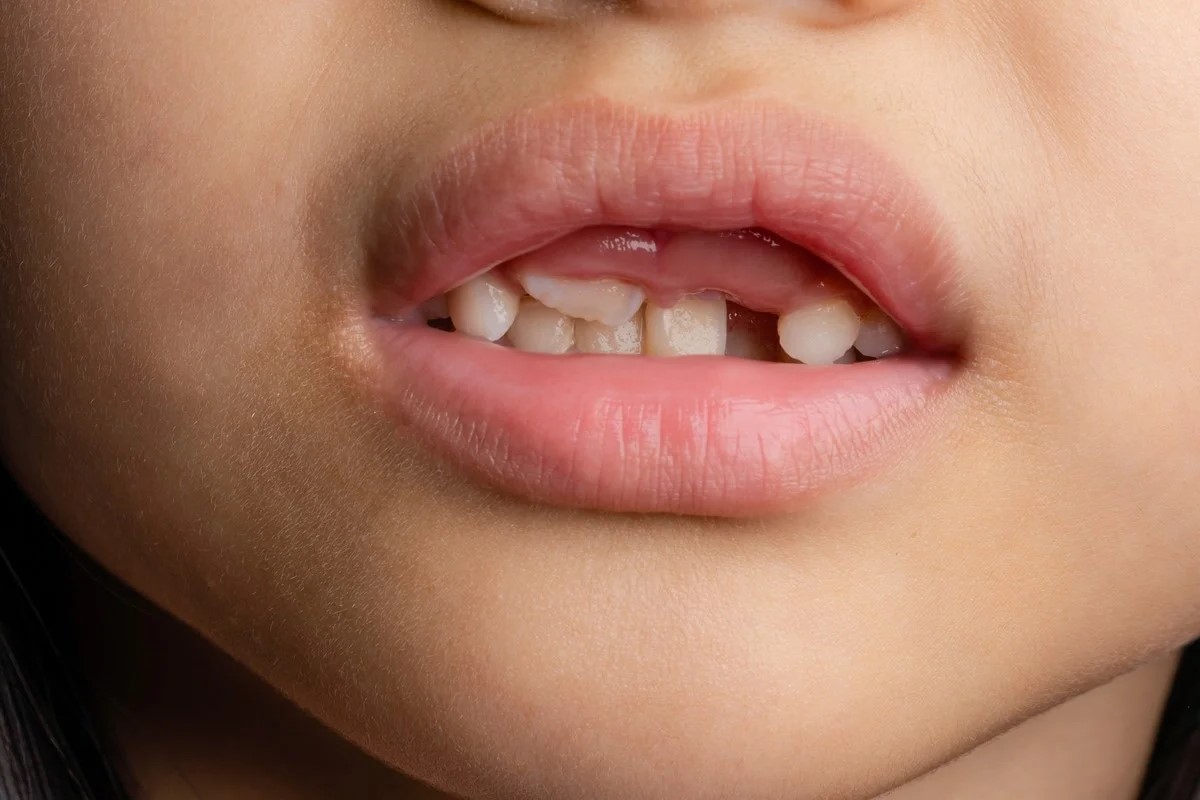
Dental Symptoms of ODOD
Dental issues are a defining feature of ODOD. These problems can affect both the appearance and function of teeth.
- Teeth may be small or misshapen. This can lead to difficulties in chewing and speaking.
- Enamel hypoplasia is common. This results in thin or missing enamel, making teeth more prone to decay.
- Delayed tooth eruption is often observed. Teeth may take longer to emerge than usual.
- Some individuals may have missing teeth. This can affect the alignment and spacing of remaining teeth.
- Dental cysts can form. These fluid-filled sacs can cause pain and swelling.
Bone Symptoms of ODOD
Bone abnormalities are another major aspect of ODOD. These can affect both the structure and strength of bones.
- Brittle bones are a frequent issue. This increases the risk of fractures and breaks.
- Craniofacial dysmorphisms are common. These can include a prominent forehead, wide-set eyes, and a small jaw.
- Scoliosis, or curvature of the spine, may develop. This can cause back pain and mobility issues.
- Short stature is often seen. Individuals may be shorter than average for their age and sex.
- Joint abnormalities can occur. These may include hypermobility or stiffness.
Diagnosis and Management of ODOD
Early diagnosis and management are crucial for improving the quality of life for those with ODOD.
- Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis. This involves analyzing the GJA1 gene for mutations.
- Regular eye exams are essential. These help monitor and manage eye-related symptoms.
- Dental care is critical. Regular check-ups and specialized treatments can address dental issues.
ODOD is a complex condition, but understanding its various aspects can help in managing its symptoms effectively.
Final Glimpse at Oculodentoosseous Dysplasia Recessive
Oculodentoosseous Dysplasia Recessive (ODOD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting eyes, teeth, and bones. Understanding ODOD helps in recognizing its symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical care. Genetic mutations in the GJA1 gene cause this condition, leading to a range of physical anomalies. Symptoms include microphthalmia, dental abnormalities, and skeletal issues. Early diagnosis and intervention can improve quality of life for those affected.
Awareness about ODOD is crucial for early detection and management. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families with a history of this disorder. While there's no cure, supportive treatments can alleviate symptoms and improve daily functioning. Staying informed and proactive in seeking medical advice can make a significant difference. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with rare conditions like ODOD. Stay curious, stay informed, and support those navigating this challenging journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
