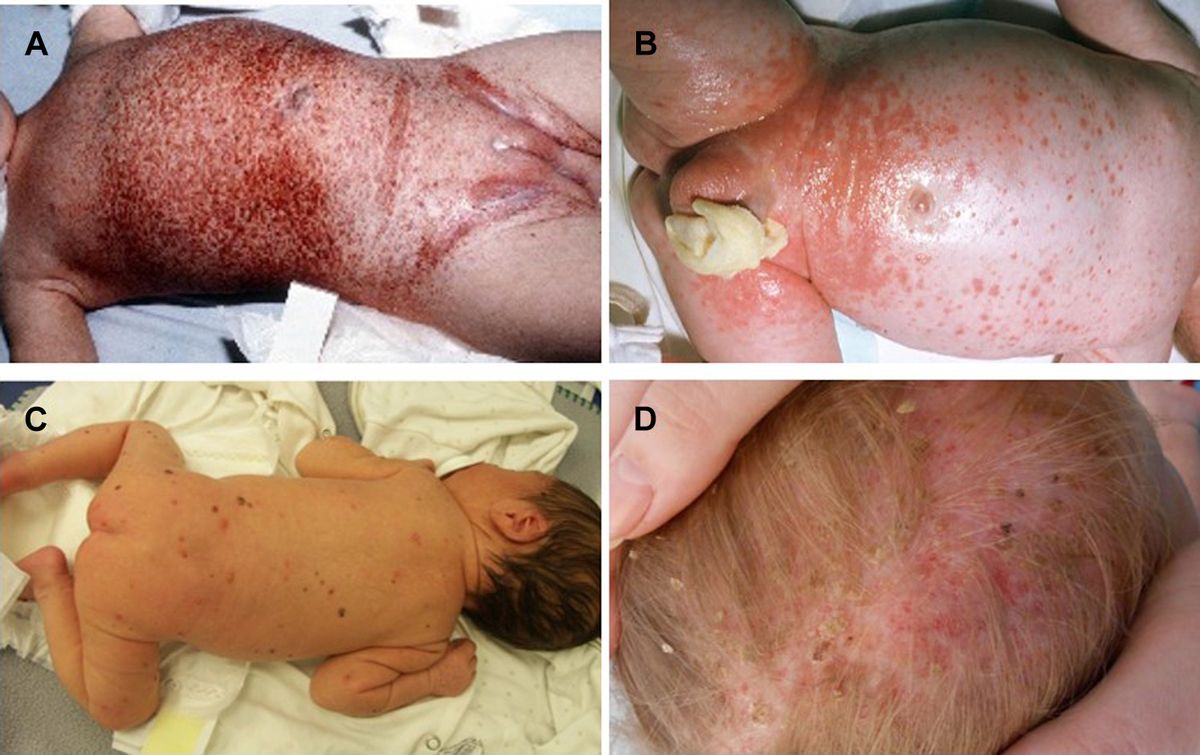
Letterer–Siwe Disease is a rare disorder that primarily affects children under the age of three. It falls under the umbrella of Langerhans cell histiocytosis, a condition where the body produces too many Langerhans cells, a type of white blood cell. These cells can accumulate in various tissues and organs, leading to a range of symptoms. Common signs include skin rashes, fever, and an enlarged liver or spleen. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, which may involve chemotherapy, radiation, or steroids. Understanding this disease can help caregivers and medical professionals provide better care for affected children.
Key Takeaways:
- Letterer–Siwe Disease is a rare condition that affects young children, causing symptoms like fever, skin rash, and bone pain. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
- Treatment for Letterer–Siwe Disease includes chemotherapy, steroids, and radiation therapy. Research and support from organizations like the Histiocytosis Association are essential for improving understanding and treatment options.
What is Letterer–Siwe Disease?
Letterer–Siwe disease is a rare and serious condition that primarily affects young children. It is one of the forms of Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), a disorder where the body produces too many Langerhans cells, a type of white blood cell. This disease can impact various organs and systems in the body.
- Letterer–Siwe disease is named after two doctors, Erich Letterer and Sture Siwe, who first described the condition in the 1920s.
- It is most commonly diagnosed in children under the age of 2.
- The disease is part of a group of disorders known as histiocytoses, which involve an overproduction of immune cells.
- Langerhans cells, which are overproduced in this disease, normally help the body fight infections.
Symptoms of Letterer–Siwe Disease
Recognizing the symptoms early can be crucial for managing the disease. The symptoms can vary widely depending on which organs are affected.
- Common symptoms include fever, skin rash, and an enlarged liver or spleen.
- The skin rash often appears as small, scaly bumps that can be mistaken for other skin conditions.
- Children may also experience bone pain or fractures due to the disease affecting the bones.
- Anemia and other blood-related issues can occur because the disease can impact the bone marrow.
Diagnosis of Letterer–Siwe Disease
Diagnosing Letterer–Siwe disease involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests.
- A biopsy of affected tissue is often required to confirm the diagnosis.
- Blood tests can show abnormalities in blood cell counts and liver function.
- Imaging studies like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs can help identify the extent of organ involvement.
- Genetic testing may be used to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatment Options for Letterer–Siwe Disease
Treatment aims to control symptoms and manage the overproduction of Langerhans cells. Early intervention can improve outcomes.
- Chemotherapy is commonly used to treat the disease.
- Steroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and immune system activity.
- In some cases, radiation therapy is used to target specific areas affected by the disease.
- Bone marrow or stem cell transplants may be considered for severe cases.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook
The prognosis for Letterer–Siwe disease can vary depending on the severity and response to treatment.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
- Some children may achieve long-term remission with appropriate treatment.
- However, the disease can be fatal if not treated promptly and effectively.
- Long-term follow-up care is essential to monitor for potential complications and recurrence.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research is crucial for understanding and improving the treatment of Letterer–Siwe disease.
- Researchers are exploring new chemotherapy drugs and treatment protocols.
- Studies are being conducted to understand the genetic and molecular basis of the disease.
- Advances in stem cell research may offer new treatment options in the future.
- Clinical trials are ongoing to test the effectiveness of new therapies.
Support and Resources
Support from healthcare providers, family, and patient organizations can be invaluable for those affected by Letterer–Siwe disease.
- Organizations like the Histiocytosis Association provide resources and support for patients and families.
Key Points on Letterer–Siwe Disease
Letterer–Siwe disease, a rare disorder, primarily affects young children. It involves the abnormal proliferation of Langerhans cells, leading to symptoms like fever, skin rashes, and organ involvement. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes. Treatments often include chemotherapy, steroids, and sometimes bone marrow transplants.
Understanding the disease's symptoms and treatment options can help in managing it effectively. Awareness among parents and healthcare providers is essential for early intervention. Though rare, advancements in medical research continue to improve the prognosis for affected children.
Staying informed and vigilant can make a significant difference in the lives of those impacted by this condition. Knowledge empowers families to seek timely medical advice and appropriate care, ultimately improving the quality of life for young patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
