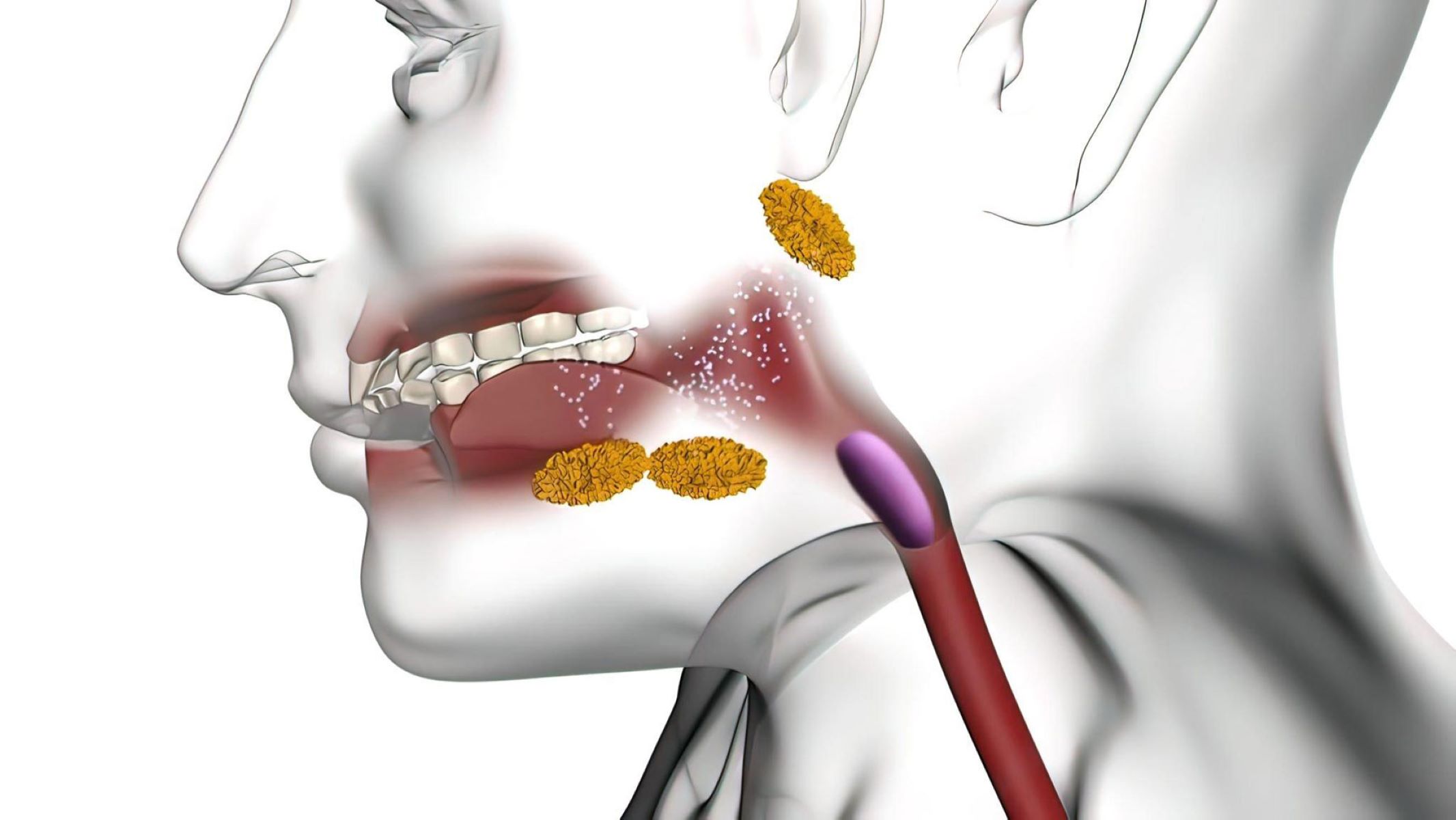
What is hypopharyngeal cancer? It's a type of head and neck cancer that starts in the hypopharynx, the lower part of the throat. This area helps with swallowing and breathing, making its health crucial. Though not as common as other cancers, it poses significant challenges due to its location and symptoms. Often, symptoms like a sore throat, ear pain, or trouble swallowing can be mistaken for less serious issues, delaying diagnosis. Risk factors include smoking, heavy alcohol use, and poor nutrition. Early detection is key for better outcomes. Understanding this cancer can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking timely medical advice.
Key Takeaways:
- Hypopharyngeal cancer is rare but serious, affecting the lower throat. Men over 50 are at higher risk, especially if they smoke and drink. Early detection and lifestyle changes can make a difference.
- Treatment options for hypopharyngeal cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and rehabilitation. Prevention through lifestyle changes and regular check-ups is important. Ongoing research aims to improve outcomes.
Understanding Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Hypopharyngeal cancer is a type of head and neck cancer that affects the lower part of the throat, known as the hypopharynx. This area is crucial for swallowing and breathing, making this cancer particularly serious. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Rare but Serious: Hypopharyngeal cancer is relatively rare, accounting for only about 3-5% of all head and neck cancers. Despite its rarity, it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, making it a serious health concern.
-
More Common in Men: Men are more likely to develop hypopharyngeal cancer than women. The ratio is approximately 3:1, meaning for every woman diagnosed, three men are affected.
-
Age Factor: Most cases occur in people over the age of 50. The risk increases with age, making regular check-ups important for early detection.
-
Smoking and Alcohol: Tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption are major risk factors. People who smoke and drink heavily are at a significantly higher risk of developing this cancer.
-
Human Papillomavirus (HPV): While HPV is a known risk factor for other head and neck cancers, its role in hypopharyngeal cancer is less clear. However, some studies suggest a possible link.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better outcomes. Unfortunately, symptoms often appear late, which complicates treatment.
-
Difficulty Swallowing: One of the earliest symptoms is difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia. This can lead to weight loss and malnutrition.
-
Sore Throat: A persistent sore throat that doesn't go away with treatment can be a warning sign. It's often mistaken for less serious conditions.
-
Ear Pain: Unexplained ear pain, especially if it's one-sided, can indicate hypopharyngeal cancer. This occurs because of nerve connections in the throat and ear.
-
Voice Changes: Hoarseness or changes in the voice may occur if the cancer affects the vocal cords or nearby areas.
-
Lump in the Neck: Swelling or a lump in the neck can be a sign that the cancer has spread to lymph nodes.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage and location of the cancer. It often involves a combination of therapies.
-
Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is a common treatment. In advanced cases, parts of the throat or neck may need to be removed.
-
Radiation Therapy: This uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It's often used after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells.
-
Chemotherapy: Drugs are used to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It can be used alone or with radiation therapy.
-
Targeted Therapy: This involves drugs that specifically target cancer cells without affecting normal cells. It's a newer treatment option with promising results.
-
Rehabilitation: Post-treatment, patients may need speech or swallowing therapy to regain normal function.
Prevention and Awareness
While not all cases can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk.
-
Quit Smoking: Avoiding tobacco in all forms is one of the best ways to lower the risk of hypopharyngeal cancer.
-
Limit Alcohol: Reducing alcohol intake can significantly decrease the risk, especially when combined with quitting smoking.
-
Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may help protect against many types of cancer, including those of the head and neck.
-
Regular Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups can help detect cancer early, when treatment is more effective.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Public health campaigns aim to raise awareness about the risks and symptoms of hypopharyngeal cancer.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving treatment and outcomes for patients with hypopharyngeal cancer.
-
Genetic Studies: Researchers are studying genetic factors that may contribute to the development of this cancer, which could lead to targeted therapies.
-
Immunotherapy: This treatment boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer. It's a promising area of research for hypopharyngeal cancer.
-
Early Detection Methods: Scientists are working on developing better screening tools for earlier detection, which could improve survival rates.
-
Patient Support: Support groups and counseling can help patients and their families cope with the emotional and psychological impact of cancer.
-
Global Initiatives: International collaborations aim to share knowledge and resources to combat hypopharyngeal cancer worldwide.
Final Thoughts on Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Hypopharyngeal cancer, a type of head and neck cancer, affects the hypopharynx, the lower part of the throat. Understanding its symptoms, like difficulty swallowing, sore throat, and ear pain, can lead to early detection. Risk factors include tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition. Regular screenings and healthy lifestyle choices can reduce risk. Treatments often involve surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Each case is unique, so a personalized treatment plan is crucial. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends plays a vital role in recovery. Staying informed and proactive about health can make a significant difference. Remember, early detection saves lives. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms, consult a healthcare provider promptly. Knowledge and awareness are powerful tools in the fight against cancer. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and prioritize your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
