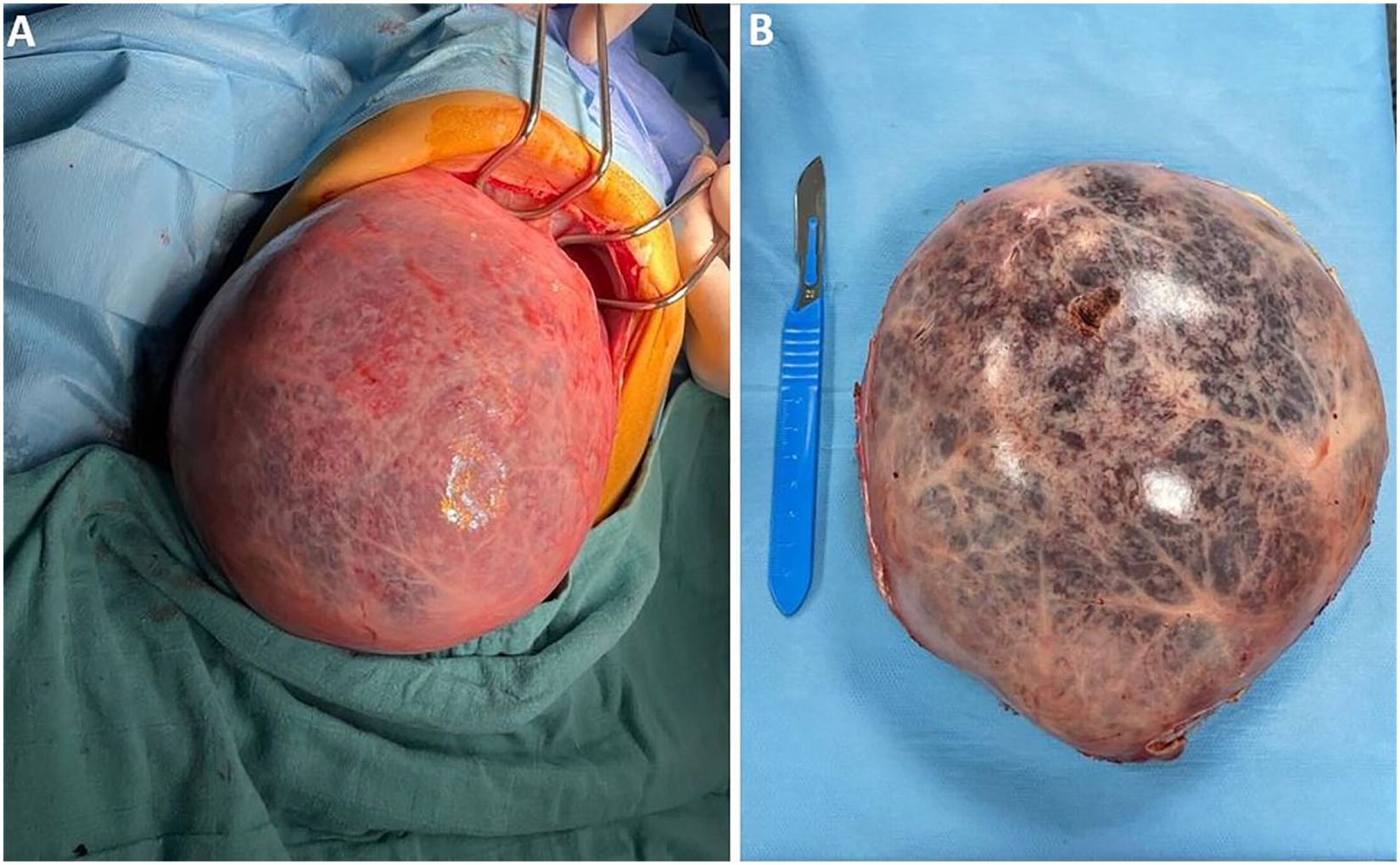
What is a Hepatic Cystic Hamartoma? A hepatic cystic hamartoma is a rare, benign liver tumor made up of various tissue types. These growths often contain cysts filled with fluid and can be found in the liver. Although they are non-cancerous, they can sometimes cause discomfort or other symptoms if they grow large enough. Hepatic cystic hamartomas are usually discovered during imaging tests for other conditions. Treatment may not always be necessary, but in some cases, surgery might be required to remove the tumor. Understanding this condition can help in managing symptoms and making informed decisions about treatment options.
Key Takeaways:
- Hepatic cystic hamartoma is a rare, non-cancerous liver condition with cysts and fibrous tissue. It can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea, but most people have a good prognosis with proper management.
- Diagnosis involves ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, and sometimes biopsy. Treatment options include observation, surgical removal, aspiration, and, rarely, liver transplant. Most individuals with this condition have a good prognosis and can live normal lives.
What is Hepatic Cystic Hamartoma?
Hepatic cystic hamartoma is a rare liver condition. It involves benign (non-cancerous) growths in the liver. These growths are made up of cysts and fibrous tissue.
-
Rare Condition: Hepatic cystic hamartoma is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
Benign Tumor: The growths are benign, meaning they do not spread to other parts of the body.
-
Cystic Nature: These tumors contain cysts filled with fluid, which can vary in size.
-
Fibrous Tissue: Alongside cysts, the tumors also contain fibrous tissue, making them firm to the touch.
Symptoms of Hepatic Cystic Hamartoma
Symptoms can vary widely. Some people may not experience any symptoms, while others might have noticeable signs.
-
Abdominal Pain: One common symptom is abdominal pain, often due to the pressure of the cysts on surrounding organs.
-
Bloating: Some individuals may experience bloating or a feeling of fullness.
-
Nausea: Nausea and vomiting can occur, especially if the cysts are large.
-
Jaundice: In rare cases, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) can develop if the cysts obstruct bile ducts.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of hepatic cystic hamartoma is not well understood. However, some factors may contribute to its development.
-
Congenital Origin: Many experts believe the condition is congenital, meaning it is present from birth.
-
Genetic Factors: There may be a genetic component, although specific genes have not been identified.
-
No Gender Preference: Both males and females are equally likely to develop hepatic cystic hamartoma.
-
Age Range: It can occur at any age, but most cases are diagnosed in middle-aged adults.
Diagnosis of Hepatic Cystic Hamartoma
Diagnosing this condition involves several steps and tests to confirm the presence of cysts and rule out other conditions.
-
Ultrasound: An ultrasound is often the first imaging test used to detect cysts in the liver.
-
CT Scan: A CT scan provides more detailed images and helps determine the size and number of cysts.
-
MRI: MRI scans offer high-resolution images, useful for assessing the structure of the cysts.
-
Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to examine the tissue and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the size and symptoms of the cysts. Some cases may not require any intervention.
-
Observation: Small, asymptomatic cysts often just need regular monitoring.
-
Surgical Removal: Larger cysts causing symptoms may need to be surgically removed.
-
Aspiration: In some cases, fluid from the cysts can be drained to relieve symptoms.
-
Liver Transplant: Rarely, a liver transplant may be necessary if the cysts severely affect liver function.
Prognosis and Outlook
The prognosis for hepatic cystic hamartoma is generally good, especially with proper management.
-
Good Prognosis: Most individuals with this condition have a good prognosis and can live normal lives.
-
Low Recurrence: After surgical removal, the likelihood of cysts recurring is low.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor for any changes.
-
Minimal Impact: For many, the condition has minimal impact on daily life and activities.
-
Research Ongoing: Research continues to better understand this rare condition and improve treatment options.
Final Thoughts on Hepatic Cystic Hamartoma
Hepatic cystic hamartoma, a rare liver condition, often puzzles both patients and doctors. These benign tumors, though non-cancerous, can cause discomfort and require monitoring. Understanding the symptoms, such as abdominal pain and bloating, helps in early detection. Regular check-ups and imaging tests are crucial for managing this condition. While surgery remains the primary treatment, not all cases need immediate intervention. Lifestyle changes, like a healthy diet and avoiding alcohol, can also play a role in managing symptoms. Awareness and education about hepatic cystic hamartoma empower patients to make informed decisions. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Stay proactive about your liver health, and don't hesitate to seek medical attention if you notice any unusual symptoms. Knowledge is your best tool in navigating this rare condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
