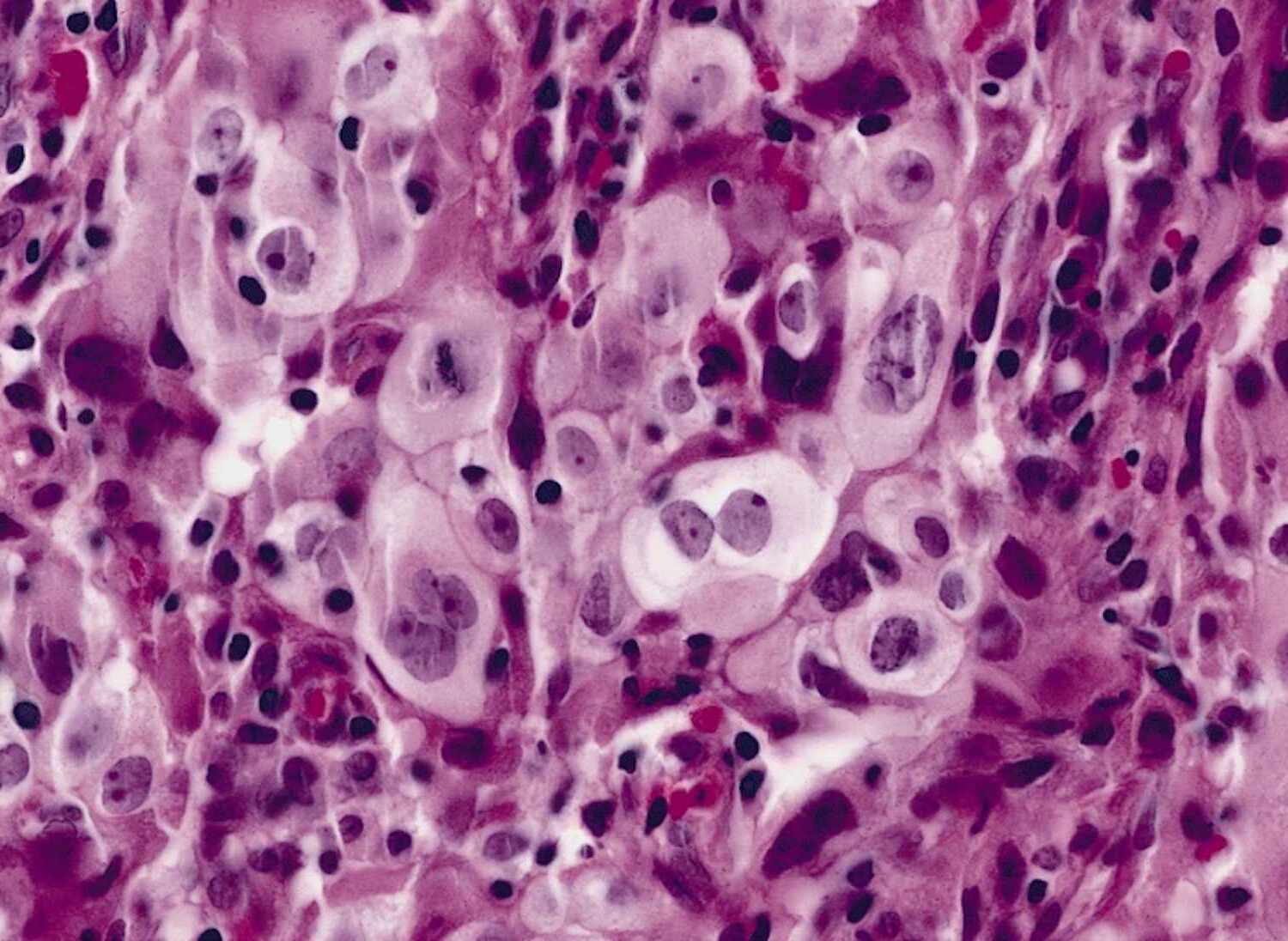
Giant-cell carcinoma of the lung is a rare and aggressive form of lung cancer. But what exactly makes it so unique? Unlike other lung cancers, this type is characterized by large, abnormal cells that grow rapidly. It falls under the non-small cell lung cancer category, which accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. However, giant-cell carcinoma is much less common, making up only a small fraction of these cases. Why does this matter? Understanding its distinct features can help in diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms often mimic other lung conditions, including persistent cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Early detection is crucial for better outcomes, as this cancer tends to spread quickly. Treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation, depending on the stage and overall health of the patient. Knowing these facts can empower individuals to seek timely medical advice and explore available treatments.
Key Takeaways:
- Giant-cell carcinoma of the lung is a rare and aggressive type of non-small cell lung cancer, known for its rapid growth and large abnormal cells. Early detection and understanding symptoms are crucial for timely treatment.
- Smoking, exposure to carcinogens, family history, age, and gender differences are risk factors for giant-cell carcinoma. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and participation in clinical trials.
What is Giant-Cell Carcinoma of the Lung?
Giant-cell carcinoma of the lung is a rare and aggressive type of non-small cell lung cancer. It is characterized by large, abnormal cells that can grow and spread rapidly. Understanding this disease can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment.
-
Rare Occurrence: This type of cancer is quite uncommon, making up only about 0.3% to 1.3% of all lung cancers. Its rarity can make diagnosis challenging.
-
Aggressive Nature: Known for its rapid growth, giant-cell carcinoma often spreads quickly to other parts of the body, complicating treatment efforts.
-
Large Abnormal Cells: The cancer is named for its large, abnormal cells that can be seen under a microscope. These cells are significantly larger than normal lung cells.
-
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: It falls under the category of non-small cell lung cancers, which are the most common type of lung cancer, though giant-cell carcinoma itself is rare.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing symptoms early can lead to a quicker diagnosis and potentially better outcomes. However, symptoms can often be mistaken for other less serious conditions.
-
Persistent Cough: A cough that doesn't go away or worsens over time is a common symptom. It can sometimes be mistaken for a lingering cold.
-
Chest Pain: Pain in the chest area, especially when breathing deeply or coughing, might indicate the presence of this cancer.
-
Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a warning sign. The body may lose weight as it fights the cancer.
-
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak is another symptom. This fatigue can be more severe than typical tiredness.
-
Diagnostic Imaging: X-rays and CT scans are often used to detect abnormalities in the lungs. These imaging tests can reveal tumors or unusual growths.
-
Biopsy Confirmation: A biopsy, where a small sample of lung tissue is taken and examined, is necessary to confirm the presence of giant-cell carcinoma.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what might increase the risk of developing giant-cell carcinoma can help in prevention and early detection.
-
Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for all types of lung cancer, including giant-cell carcinoma. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can damage lung cells.
-
Exposure to Carcinogens: Being exposed to certain chemicals and substances, such as asbestos or radon, can increase the risk.
-
Family History: A family history of lung cancer can also be a risk factor. Genetics may play a role in susceptibility.
-
Age Factor: Most cases occur in older adults, typically those over 60. Age can be a contributing factor due to accumulated exposure to risk factors over time.
-
Gender Differences: Some studies suggest that men may be more likely to develop this type of cancer than women, though the reasons are not fully understood.
Treatment Options
Treatment for giant-cell carcinoma of the lung can vary based on the stage of the cancer and the overall health of the patient.
-
Surgery: If the cancer is detected early and has not spread, surgery to remove the tumor may be an option.
-
Chemotherapy: This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
-
Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to target and destroy cancer cells. This can be effective in shrinking tumors.
-
Targeted Therapy: Some treatments focus on specific abnormalities in cancer cells. These therapies can be less harmful to normal cells.
-
Clinical Trials: Patients may have the opportunity to participate in clinical trials, which test new treatments and approaches.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The outlook for patients with giant-cell carcinoma of the lung can vary widely based on several factors.
-
Early Detection: Catching the cancer early can significantly improve the prognosis. Early-stage cancers are more treatable.
-
Stage of Cancer: The stage at which the cancer is diagnosed plays a crucial role in survival rates. Advanced stages are more challenging to treat.
-
Overall Health: A patient's overall health and ability to tolerate treatment can impact survival. Healthier individuals may have better outcomes.
-
Treatment Response: How well the cancer responds to treatment can affect prognosis. Some tumors may be more resistant to certain therapies.
-
Ongoing Research: Research continues to improve understanding and treatment of this rare cancer. Advances in medical science offer hope for better outcomes in the future.
Final Thoughts on Giant-Cell Carcinoma of the Lung
Giant-cell carcinoma of the lung, a rare and aggressive form of cancer, demands attention due to its unique characteristics and challenges in treatment. Understanding its symptoms, such as persistent cough and chest pain, can lead to earlier diagnosis, which is crucial for better outcomes. While treatment options like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation exist, their effectiveness varies, making research into new therapies vital.
Awareness of risk factors like smoking and exposure to harmful substances can aid in prevention. Support from healthcare professionals and loved ones plays a significant role in managing the emotional and physical toll of this disease. Staying informed and proactive about lung health is essential.
By spreading knowledge about giant-cell carcinoma, we can foster a community that supports those affected and encourages advancements in medical research. Let's continue to learn and share information to combat this challenging condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
