Entropy is a term that often pops up in science classes, but what does it really mean? In simple terms, entropy measures disorder or randomness in a system. Imagine your room after a week without cleaning—clothes everywhere, books scattered, and gadgets misplaced. That's a high-entropy situation! On the other hand, a neatly organized room represents low entropy. This concept isn't just limited to messy rooms; it applies to everything from the universe's expansion to the melting of ice. Understanding entropy helps explain why certain processes are irreversible and why energy tends to spread out. Ready to dive into 40 fascinating facts about entropy? Let's get started!
What is Entropy?
Entropy is a concept from thermodynamics and statistical mechanics. It measures the amount of disorder or randomness in a system. Here are some fascinating facts about entropy:
-
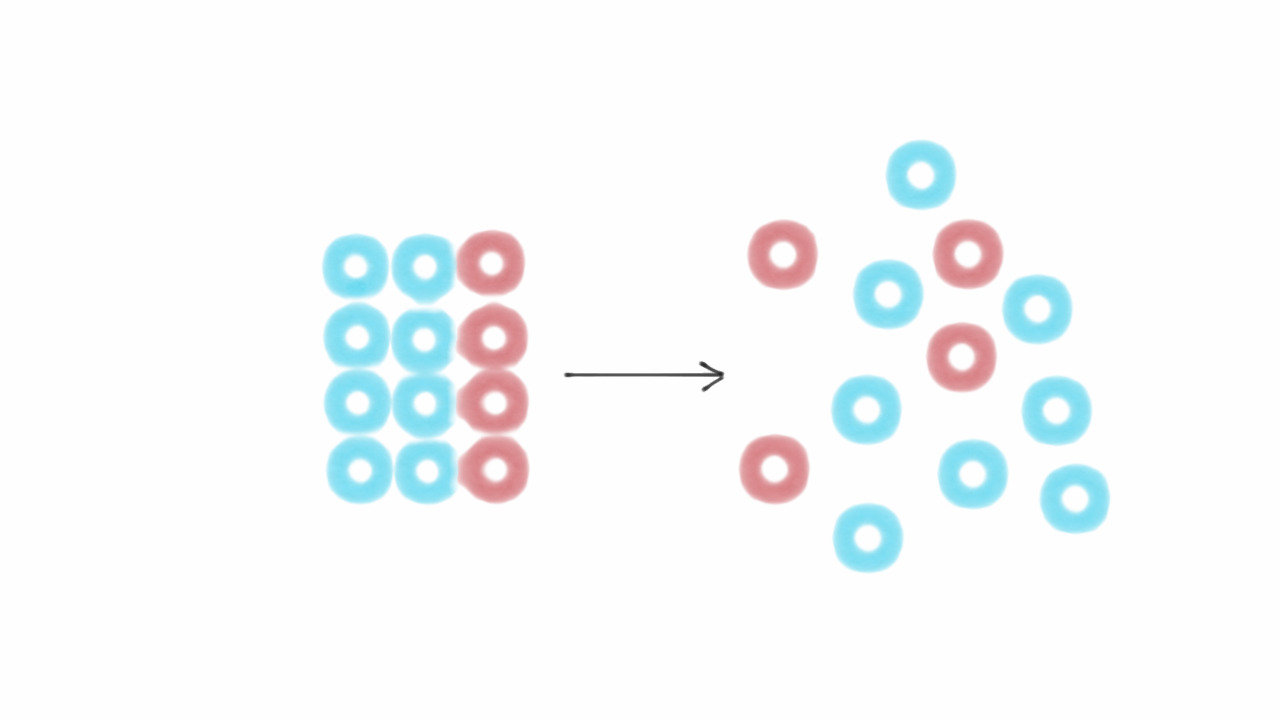
Entropy is a measure of disorder. It quantifies how much energy in a system is unavailable to do work.
-
The second law of thermodynamics states that entropy always increases. This means systems naturally progress from order to disorder.
-
Entropy is often associated with the arrow of time. It gives a direction to time, moving from past to future.
-
Ludwig Boltzmann developed the statistical definition of entropy. He related it to the number of microscopic configurations that correspond to a thermodynamic system's macroscopic state.
-
Entropy is measured in joules per kelvin (J/K). This unit reflects the energy dispersed per degree of temperature.
Entropy in Everyday Life
Entropy isn't just a scientific concept; it affects daily life in many ways. Here are some examples:
-
Ice melting is an example of increasing entropy. As ice melts, it transitions from a structured solid to a disordered liquid.
-
Mixing different substances increases entropy. For instance, mixing sugar in tea disperses the sugar molecules, increasing disorder.
-
Entropy explains why it's easier to make a mess than to clean it up. Creating order requires energy, while disorder happens naturally.
-
Food digestion increases entropy. Breaking down complex food molecules into simpler ones releases energy and increases disorder.
-
Entropy affects battery life. Over time, the chemical reactions in batteries become less efficient, increasing disorder and reducing battery life.
Entropy in the Universe
Entropy plays a crucial role in the universe's behavior and evolution. Here are some cosmic facts:
-
The universe started with low entropy. The Big Bang created a highly ordered state, which has been increasing in disorder ever since.
-
Black holes have the highest entropy. They contain vast amounts of information and disorder.
-
The heat death of the universe is a state of maximum entropy. It predicts a future where all energy is evenly distributed, and no work can be done.
-
Stars increase entropy as they burn fuel. Fusion reactions in stars convert hydrogen into helium, releasing energy and increasing disorder.
-
Entropy affects the formation of galaxies. Gravitational forces cause matter to clump together, increasing local order but overall disorder.
Entropy in Information Theory
Entropy isn't limited to physical systems; it also applies to information. Here are some intriguing facts:
-
Claude Shannon introduced the concept of entropy in information theory. He used it to measure the uncertainty in a set of possible messages.
-
Information entropy quantifies the amount of surprise in a message. More unpredictable messages have higher entropy.
-
Data compression relies on entropy. By reducing redundancy, compression algorithms decrease the entropy of data.
-
Cryptography uses entropy to secure information. High-entropy keys are harder to predict and crack.
-
Entropy in information theory is measured in bits. This unit reflects the amount of information content.
Entropy and Life
Life itself is a battle against entropy. Here are some ways living organisms deal with disorder:
-
Living organisms maintain low entropy internally. They use energy to create order and sustain life.
-
Photosynthesis decreases entropy locally. Plants convert sunlight into chemical energy, creating ordered structures.
-
Metabolism increases entropy. Breaking down nutrients releases energy and increases disorder.
-
Reproduction creates new ordered systems. Offspring represent a new, low-entropy state.
-
Evolution is driven by entropy. Random mutations increase genetic diversity, leading to adaptation and survival.
Entropy in Technology
Modern technology often deals with entropy. Here are some examples:
-
Heat engines operate based on entropy. They convert heat into work, increasing disorder in the process.
-
Refrigerators decrease entropy locally. They remove heat from inside, creating a cooler, more ordered space.
-
Computers generate entropy. Processing information produces heat, increasing disorder.
-
Entropy affects data storage. Over time, data can degrade, increasing disorder.
-
Quantum computing aims to control entropy. It seeks to perform calculations with minimal energy loss and disorder.
Fun Facts about Entropy
Here are some lighter, fun facts about entropy:
-
Entropy is related to the concept of time travel. Reversing entropy would theoretically allow backward time travel.
-
Entropy explains why perpetual motion machines are impossible. They would violate the second law of thermodynamics.
-
Entropy is a key theme in science fiction. Many stories explore the consequences of increasing disorder.
-
Entropy can be seen in art. Some artists create works that intentionally increase disorder over time.
-
Entropy is a popular topic in philosophy. It raises questions about the nature of time and existence.
Entropy in Chemistry
Chemistry heavily relies on entropy. Here are some chemical facts:
-
Chemical reactions often increase entropy. Reactions tend to produce more disordered products.
-
Entropy affects solubility. Substances dissolve when the resulting solution has higher entropy.
-
Catalysts influence entropy. They lower the energy barrier for reactions, increasing disorder.
-
Entropy drives diffusion. Molecules move from high to low concentration, increasing disorder.
-
Entropy is crucial in phase transitions. Changes between solid, liquid, and gas involve changes in disorder.
The Final Word on Entropy
Entropy, a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, plays a crucial role in understanding the universe's natural order. From explaining why ice melts to why your room gets messy, entropy touches every aspect of our lives. It’s not just about chaos; it’s about the direction of processes and the flow of energy.
Understanding entropy helps us grasp why certain reactions occur and why some don’t. It’s a key player in fields like chemistry, physics, and even information theory. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or just curious, knowing about entropy enriches your comprehension of the world.
So next time you see something falling apart or energy spreading out, remember, entropy is at work. It’s a fascinating concept that reminds us of the inherent order and disorder in the universe. Keep exploring, and you’ll find even more intriguing facts about this essential principle.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


