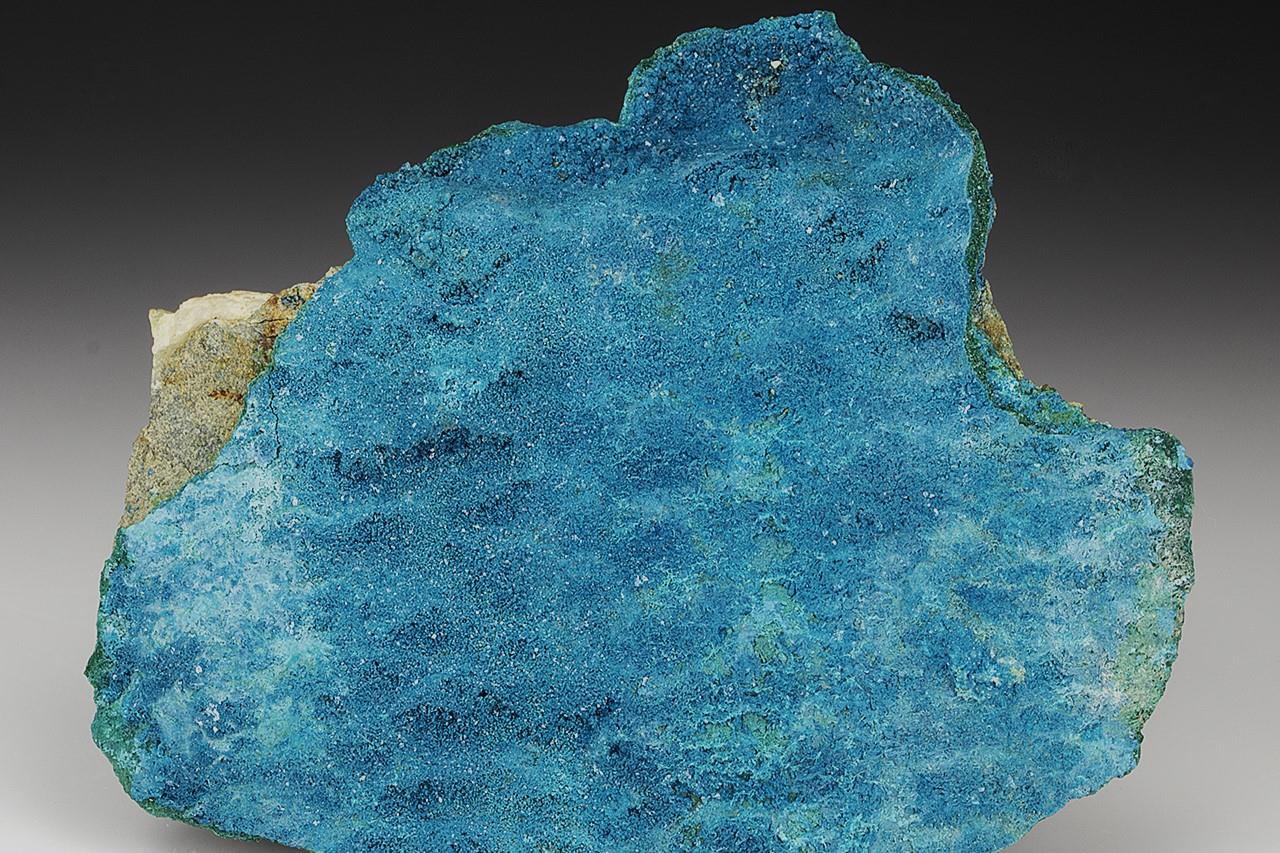
Langite, a striking blue-green mineral, captures the imagination of rock enthusiasts and geologists alike. But what exactly is Langite? This mineral is a hydrated copper sulfate, often found in the oxidized zones of copper deposits. Its vibrant color and unique crystal structure make it a favorite among collectors. Langite forms in environments where copper minerals undergo weathering, creating a stunning array of hues. Found in places like Cornwall, England, and the Czech Republic, it often appears alongside other minerals such as brochantite and malachite. Langite's rarity and beauty make it a sought-after specimen for both amateur and professional collectors. Whether you're a budding geologist or simply curious about the natural world, Langite offers a fascinating glimpse into the processes that shape our planet. Its presence in historical mining regions adds a layer of intrigue, connecting us to the earth's rich geological history.
Key Takeaways:
- Langite, a vibrant blue-green mineral, forms in copper deposits and has a unique crystal structure. It's found in Europe, the US, Australia, Africa, and South America, and has various uses, including in jewelry and scientific research.
- Langite's delicate nature requires special care when collecting and preserving. It should be stored in a dry environment, handled gently, and displayed in a protective case to prevent damage. Accurate labeling ensures its provenance is preserved for future study.
What is Langite?
Langite is a fascinating mineral that captures the interest of geologists and collectors alike. Its vibrant blue-green color and unique properties make it a standout in the mineral world. Here are some intriguing facts about this captivating mineral.
-
Langite is a copper sulfate mineral. It forms in the oxidized zones of copper deposits, often found in association with other secondary copper minerals.
-
The mineral was named after Viktor von Lang, an Austrian physicist known for his contributions to crystallography. His work helped pave the way for understanding the structure of minerals.
-
Langite typically appears in shades of blue and green. This striking coloration is due to the presence of copper in its chemical composition.
-
It has a monoclinic crystal system, which means its crystal structure is characterized by three unequal axes, with one inclined to the other two.
-
Langite is often found in fibrous or acicular (needle-like) forms. These delicate structures add to its visual appeal and make it a favorite among mineral collectors.
Where Can Langite Be Found?
Langite is not just a pretty mineral; it has a story to tell about its origins and locations. Let's explore where this mineral can be found around the world.
-
Langite is commonly found in Europe. Notable locations include Cornwall in England and the Harz Mountains in Germany, where it occurs in old copper mines.
-
It can also be found in the United States, particularly in Arizona and Utah. These regions have rich copper deposits that provide the perfect environment for langite formation.
-
Australia is another source of langite, with occurrences in the copper-rich areas of New South Wales and Queensland.
-
Langite has been discovered in Africa, specifically in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it forms in the oxidized zones of copper-cobalt deposits.
-
The mineral is also present in South America, with notable finds in Chile, a country known for its extensive copper mining operations.
How is Langite Formed?
Understanding the formation of langite provides insight into the geological processes that create this mineral. Here's a closer look at how langite comes to be.
-
Langite forms through the oxidation of copper sulfide minerals. This process occurs when copper deposits are exposed to air and water, leading to the formation of secondary minerals like langite.
-
The mineral often forms in the presence of sulfate-rich solutions. These solutions facilitate the transformation of primary copper minerals into secondary ones, including langite.
-
Langite can form as a result of weathering processes. Over time, exposure to the elements breaks down primary copper minerals, allowing langite to crystallize.
-
It is commonly found in the oxidized zones of copper deposits. These zones are rich in secondary minerals, making them prime locations for langite formation.
-
Langite can also form in mine dumps and tailings. These man-made environments provide the necessary conditions for the mineral to develop over time.
What are the Uses of Langite?
While langite is primarily a collector's mineral, it has some interesting applications and uses. Let's delve into how this mineral is utilized.
-
Langite is highly prized by mineral collectors. Its vibrant color and unique crystal forms make it a sought-after specimen for display and study.
-
The mineral is used in educational settings. It serves as a teaching tool for geology students learning about mineral formation and crystallography.
-
Langite can be used in jewelry, although its softness limits its use to decorative pieces rather than everyday wear.
-
It is sometimes used in scientific research. Researchers study langite to better understand the processes involved in the formation of secondary copper minerals.
-
Langite can be used as a reference material. Its distinct properties make it a useful standard for identifying similar minerals in the field.
What are the Physical Properties of Langite?
Langite's physical properties contribute to its allure and make it a fascinating subject for study. Here are some key characteristics of this mineral.
-
Langite has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3. This means it is relatively soft and can be scratched by harder substances.
-
The mineral has a vitreous to silky luster. This gives it a shiny appearance, enhancing its visual appeal.
-
Langite has a specific gravity of 3.2 to 3.3. This density is typical for copper minerals and contributes to its weighty feel.
-
It is transparent to translucent. This optical property allows light to pass through the mineral, adding to its aesthetic value.
-
Langite exhibits perfect cleavage in one direction. This means it can be easily split along a specific plane, a characteristic that influences how it is cut and shaped.
What are the Chemical Properties of Langite?
The chemical composition of langite is what gives it its unique characteristics. Let's explore the chemistry behind this intriguing mineral.
-
Langite's chemical formula is Cu4(SO4)(OH)6·2H2O. This indicates it is a hydrated copper sulfate mineral.
-
The presence of copper gives langite its blue-green color. Copper ions absorb certain wavelengths of light, resulting in the mineral's distinctive hue.
-
Langite contains hydroxide ions. These ions play a role in the mineral's formation and stability.
-
The mineral is soluble in acids. This property is important for understanding how langite interacts with its environment.
-
Langite can alter to other minerals over time. Exposure to different environmental conditions can lead to changes in its chemical composition.
What Makes Langite Unique?
Langite stands out among minerals for several reasons. Here are some aspects that make it truly unique.
-
Langite's vibrant color is one of its most striking features. The blue-green hue is not only eye-catching but also indicative of its copper content.
-
The mineral's fibrous and acicular forms are rare. These delicate structures are not commonly found in other minerals, adding to langite's uniqueness.
-
Langite's formation process is complex. The combination of oxidation, weathering, and sulfate-rich solutions creates a mineral with a fascinating geological history.
-
It is often found in historical mining regions. This connection to mining history adds an element of intrigue to langite specimens.
-
Langite's association with other secondary copper minerals. This relationship provides insight into the mineralogical processes occurring in copper deposits.
How is Langite Collected and Preserved?
Collecting and preserving langite requires special care due to its delicate nature. Here are some tips for handling this beautiful mineral.
-
Langite should be stored in a dry environment. Moisture can cause the mineral to deteriorate over time, so proper storage is essential.
-
Handling langite with care is important. Its softness and perfect cleavage make it susceptible to damage, so gentle handling is recommended.
-
Using a soft brush to clean langite. This helps remove dust and debris without scratching the mineral's surface.
-
Displaying langite in a protective case. This prevents accidental damage and keeps the mineral safe from environmental factors.
-
Labeling langite specimens with care. Accurate labeling ensures that the mineral's provenance and characteristics are preserved for future study.
Langite: A Glimpse into Nature's Wonders
Langite, a copper sulfate mineral, is a fascinating subject for both geologists and mineral enthusiasts. Its vibrant blue-green hue and unique crystal structure make it a standout in the mineral world. Found primarily in oxidized zones of copper deposits, langite's formation is a testament to the intricate processes of nature. This mineral not only captivates with its beauty but also provides insights into the geochemical conditions of its environment. Collectors value langite for its rarity and aesthetic appeal, while scientists study it to understand more about mineral formation and transformation. Whether you're a seasoned collector or just curious about the natural world, langite offers a window into the complexity and beauty of Earth's geological processes. Its presence reminds us of the richness and diversity of the planet's mineral kingdom, sparking curiosity and appreciation for the wonders beneath our feet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
