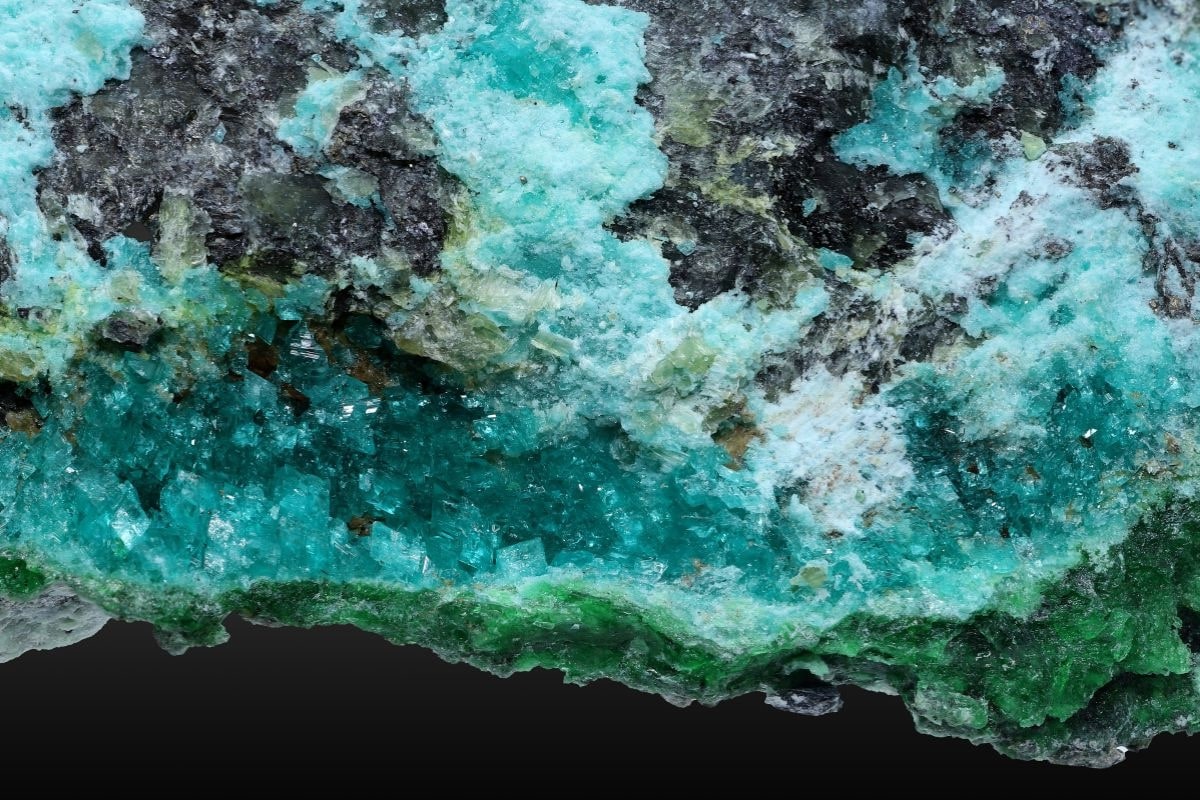
Hellyerite might not be a household name, but this intriguing mineral has a story worth telling. What exactly is hellyerite? It's a rare nickel carbonate mineral, often found in serpentinized ultramafic rocks. Its striking green color and unique crystal structure make it a fascinating subject for mineral enthusiasts and geologists alike. Named after the Hellyer River in Tasmania, where it was first discovered, hellyerite is not just a pretty face. Its formation involves complex geological processes, providing insights into Earth's dynamic history. While not commonly used in everyday applications, hellyerite's rarity and beauty make it a sought-after specimen for collectors. Whether you're a budding geologist or just curious about the natural world, hellyerite offers a glimpse into the intricate and colorful tapestry of minerals that make up our planet. Dive into the world of hellyerite and uncover the secrets of this captivating mineral.
Key Takeaways:
- Hellyerite, a rare mineral with a distinctive pale green color, forms in nickel-rich environments and holds significance in geology, industry, and as a collector's item. Its unique properties make it a subject of fascination and study.
- Despite its rarity, hellyerite plays a crucial role in understanding geological processes, serving as a valuable resource for nickel exploration, and inspiring scientific research and artistic creativity. Its scarcity and specific properties present challenges for further study and preservation.
What is Hellyerite?
Hellyerite is a rare mineral that captures the interest of geologists and mineral enthusiasts alike. It is known for its unique properties and intriguing formation process. Let's explore some fascinating facts about this mineral.
-
Unique Composition: Hellyerite is a nickel carbonate mineral with the chemical formula NiCO₃·6H₂O. Its composition makes it distinct from other minerals.
-
Named After a Mine: This mineral gets its name from the Hellyer Mine in Tasmania, Australia, where it was first discovered.
-
Color and Appearance: Typically, hellyerite appears as pale green or bluish-green crystals. Its color is due to the presence of nickel.
-
Crystal Structure: It forms in the trigonal crystal system, which is a common structure for carbonate minerals.
-
Hydrated Mineral: Hellyerite contains water molecules in its structure, classifying it as a hydrated mineral.
How is Hellyerite Formed?
Understanding the formation of hellyerite provides insight into the geological processes that create such unique minerals.
-
Formation Environment: Hellyerite forms in the oxidized zones of nickel sulfide deposits. These environments are rich in nickel and carbonate ions.
-
Weathering Process: The mineral forms through the weathering of nickel-rich rocks, where nickel ions combine with carbonate ions in the presence of water.
-
Associated Minerals: Often found alongside other nickel minerals like garnierite and annabergite, hellyerite shares its environment with these companions.
-
Geological Significance: Its presence can indicate the past geological conditions and processes that occurred in a region.
Where Can Hellyerite Be Found?
Though rare, hellyerite has been discovered in several locations worldwide. Each site offers a glimpse into the mineral's distribution.
-
Tasmania, Australia: The Hellyer Mine is the most famous location for hellyerite, where it was first identified.
-
New Zealand: Small deposits have been found in New Zealand, adding to the mineral's geographic range.
-
Russia: Some occurrences have been reported in Russia, showcasing its presence in diverse geological settings.
-
United States: Hellyerite has been identified in a few locations in the U.S., though it remains a rare find.
Why is Hellyerite Important?
Despite its rarity, hellyerite holds significance in various fields, from geology to industry.
-
Research Interest: Geologists study hellyerite to understand the processes of nickel mineralization and carbonate formation.
-
Nickel Source: As a nickel-bearing mineral, it can be a minor source of nickel, an essential metal for various industrial applications.
-
Collector's Item: Due to its rarity and unique appearance, hellyerite is sought after by mineral collectors.
-
Educational Value: It serves as a teaching tool in geology, illustrating mineral formation and the role of nickel in the Earth's crust.
What Makes Hellyerite Unique?
Several characteristics set hellyerite apart from other minerals, making it a subject of fascination.
-
Rarity: Its scarcity adds to its allure, as it is not commonly found in many mineral collections.
-
Distinctive Color: The pale green hue of hellyerite is a visual cue to its nickel content, distinguishing it from other carbonates.
-
Hydration Level: The presence of six water molecules in its structure is unusual for carbonate minerals, contributing to its uniqueness.
-
Environmental Indicator: Its formation can signal specific environmental conditions, such as the presence of nickel-rich deposits.
How is Hellyerite Used?
While not widely used, hellyerite has niche applications that highlight its properties.
-
Scientific Studies: Researchers analyze hellyerite to gain insights into mineralogy and geochemistry.
-
Nickel Exploration: Its presence can guide exploration efforts for nickel, a valuable industrial metal.
-
Educational Displays: Museums and educational institutions use hellyerite specimens to teach about mineral diversity.
-
Artistic Inspiration: The mineral's color and form can inspire artists and designers in their creative works.
What Challenges Exist in Studying Hellyerite?
Studying hellyerite presents unique challenges due to its rarity and specific properties.
-
Limited Availability: The scarcity of hellyerite samples makes it difficult for researchers to conduct extensive studies.
-
Complex Formation: Understanding the precise conditions that lead to its formation requires detailed geological analysis.
-
Preservation Issues: As a hydrated mineral, hellyerite can lose water over time, altering its structure and appearance.
-
Analytical Techniques: Advanced techniques are needed to analyze its composition and properties accurately.
-
Field Accessibility: Many hellyerite deposits are located in remote or difficult-to-access areas, complicating field studies.
Hellyerite: A Glimpse into Earth's Mysteries
Hellyerite, with its unique greenish-blue hue, offers more than just visual appeal. This mineral, primarily found in nickel-rich environments, serves as a window into Earth's geological processes. Its formation involves the alteration of serpentine rocks, highlighting the dynamic nature of our planet's crust. Beyond its scientific significance, hellyerite's rarity makes it a sought-after specimen for collectors and researchers alike. Its presence in specific locations, like Tasmania, underscores the diverse mineral wealth hidden beneath our feet. Understanding hellyerite not only enriches our knowledge of mineralogy but also emphasizes the intricate connections between Earth's components. As we continue to study such minerals, we gain insights into the planet's history and the ongoing changes shaping its future. Hellyerite stands as a testament to the wonders of geology, reminding us of the endless discoveries awaiting exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
