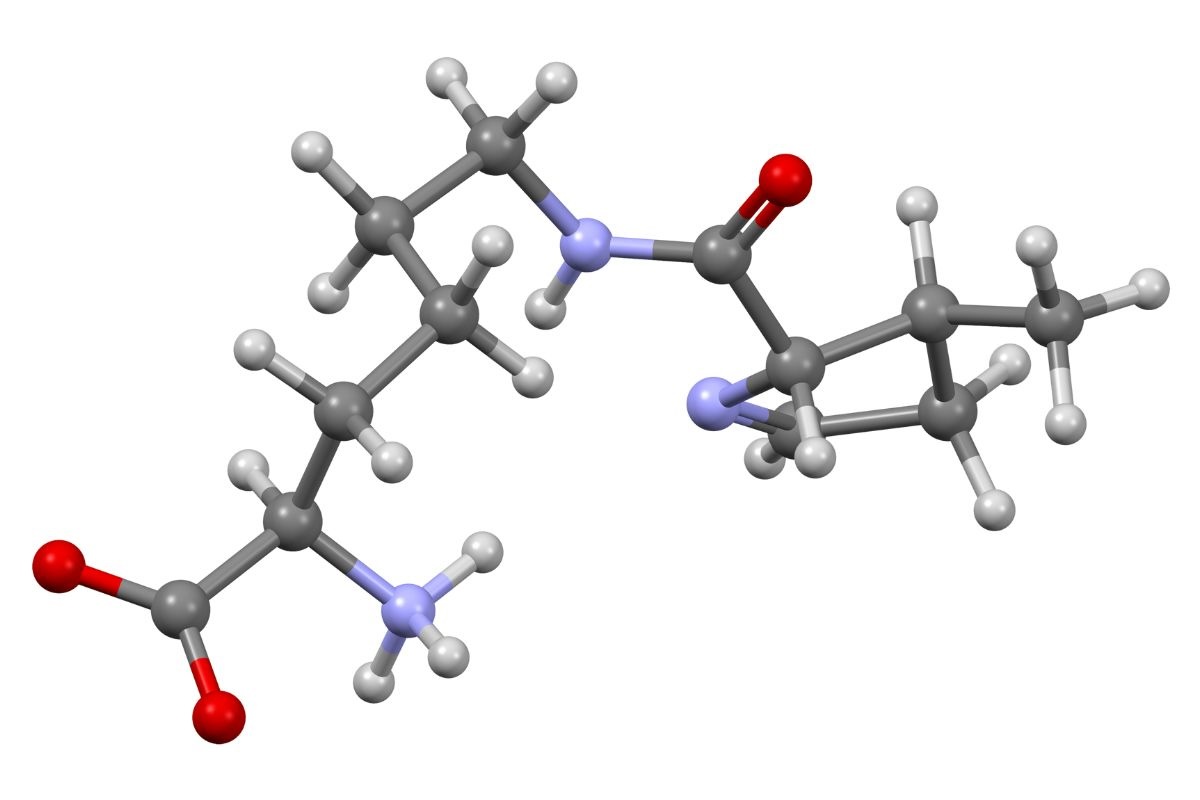
Pyrrolysine is a rare amino acid that plays a crucial role in the biology of certain microorganisms. Often referred to as the 22nd amino acid, it is unique because it is directly encoded by the genetic code, unlike most other non-standard amino acids. Pyrrolysine is found in some methanogenic archaea and bacteria, where it is involved in methane production. This amino acid is incorporated into proteins by a special tRNA and a unique codon, UAG, which usually signals a stop in protein synthesis. Understanding pyrrolysine can provide insights into genetic coding, protein synthesis, and microbial metabolism. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 40 fascinating facts about pyrrolysine!
Key Takeaways:
- Pyrrolysine is a rare amino acid with unique properties, essential for methane metabolism and genetic code expansion in certain microorganisms, inspiring exciting research and potential applications in synthetic biology and drug development.
- Despite its challenges, pyrrolysine's discovery has challenged long-held beliefs about the genetic code, and its potential applications in creating novel proteins and biocatalysts make it an intriguing subject for future scientific exploration.
What is Pyrrolysine?
Pyrrolysine is an unusual amino acid found in some organisms. It is the 22nd amino acid discovered and has unique properties.
- Pyrrolysine is encoded by the UAG stop codon in certain archaea and bacteria.
- It was first discovered in 2002 in a methane-producing archaeon called Methanosarcina barkeri.
- Unlike the 20 standard amino acids, pyrrolysine is not found in humans or most other organisms.
- It is synthesized from two molecules of lysine, another amino acid.
- Pyrrolysine is incorporated into proteins by a specialized tRNA and a unique aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
Unique Properties of Pyrrolysine
Pyrrolysine has some distinct characteristics that set it apart from other amino acids.
- It contains a pyrroline ring, which is rare among amino acids.
- Pyrrolysine is involved in the metabolism of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- It is essential for the function of certain methyltransferase enzymes.
- The presence of pyrrolysine allows these enzymes to catalyze reactions that would otherwise be impossible.
- Pyrrolysine can form covalent bonds with other molecules, enhancing its versatility in biochemical reactions.
How Pyrrolysine is Encoded
The genetic encoding of pyrrolysine is a fascinating process that differs from the standard amino acids.
- The UAG codon, usually a stop signal, is repurposed to encode pyrrolysine in specific organisms.
- This repurposing requires a special sequence called the PYLIS element in the mRNA.
- The PYLIS element forms a secondary structure that allows the ribosome to recognize the UAG codon as pyrrolysine.
- This mechanism is an example of genetic code expansion, where new amino acids are added to the genetic repertoire.
- Pyrrolysine's incorporation into proteins is a rare but natural example of synthetic biology.
Biological Significance of Pyrrolysine
Pyrrolysine plays a crucial role in the biology of certain microorganisms.
- It is vital for the survival of methanogenic archaea in anaerobic environments.
- These archaea use pyrrolysine-containing enzymes to produce methane from substrates like acetate and methylamines.
- Methane production is a key part of the global carbon cycle.
- Pyrrolysine-containing enzymes are more efficient than their counterparts lacking this amino acid.
- The presence of pyrrolysine allows these organisms to thrive in extreme conditions.
Research and Applications
Research on pyrrolysine has led to some exciting potential applications.
- Scientists are exploring the use of pyrrolysine in synthetic biology to create novel proteins.
- Pyrrolysine can be used to introduce new chemical functionalities into proteins.
- This amino acid could be used to develop new biocatalysts for industrial processes.
- Pyrrolysine's unique properties make it a valuable tool for studying protein structure and function.
- Researchers are investigating the potential of pyrrolysine in drug development.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its potential, there are challenges in working with pyrrolysine.
- Synthesizing pyrrolysine in the lab is complex and expensive.
- Incorporating pyrrolysine into proteins in non-native organisms requires advanced genetic engineering techniques.
- There is still much to learn about the regulation of pyrrolysine biosynthesis.
- Understanding the evolutionary origins of pyrrolysine could provide insights into the flexibility of the genetic code.
- Future research may uncover new organisms that use pyrrolysine or similar amino acids.
Fun Facts about Pyrrolysine
Here are some interesting tidbits about this unique amino acid.
- Pyrrolysine is sometimes referred to as the "22nd amino acid" because it was discovered after the standard 20 and selenocysteine.
- The discovery of pyrrolysine challenged the long-held belief that the genetic code was universal and unchangeable.
- Pyrrolysine's structure was determined using X-ray crystallography.
- The name "pyrrolysine" comes from its pyrroline ring and its derivation from lysine.
- Pyrrolysine is one of only two amino acids that are not universally encoded by the genetic code.
Pyrrolysine in Popular Culture
While not widely known, pyrrolysine has made its way into some niche areas of popular culture.
- Pyrrolysine has been featured in scientific documentaries about extremophiles and their unique biochemistry.
- It has been mentioned in academic lectures and courses on synthetic biology and genetic engineering.
- Some science fiction stories have speculated about the use of pyrrolysine in creating synthetic life forms.
- Pyrrolysine's discovery has been celebrated in scientific circles as a milestone in understanding life's complexity.
- The study of pyrrolysine continues to inspire researchers to explore the boundaries of biology and chemistry.
The Final Scoop on Pyrrolysine
Pyrrolysine, the 22nd amino acid, is a fascinating piece of the genetic puzzle. Found in some methane-producing microorganisms, it plays a crucial role in their metabolic processes. Unlike the 20 standard amino acids, pyrrolysine is encoded by the UAG stop codon, which usually signals the end of protein synthesis. This unique feature allows these microbes to thrive in extreme environments, contributing to our understanding of life's adaptability.
Scientists are still uncovering the full potential of pyrrolysine. Its unique properties could lead to breakthroughs in synthetic biology and biotechnology. By studying this amino acid, researchers hope to develop new methods for producing biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and other valuable compounds.
Pyrrolysine's discovery has expanded our knowledge of the genetic code and protein synthesis. As research continues, who knows what other secrets this remarkable amino acid might reveal?
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
