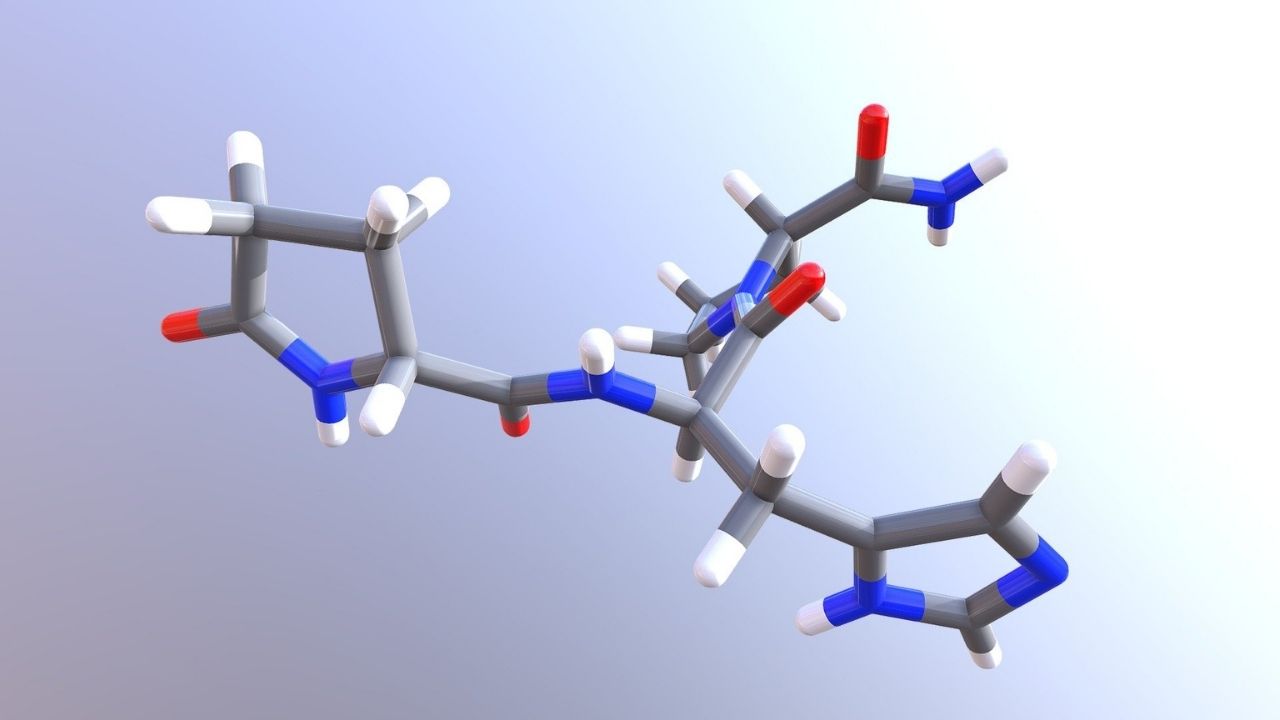
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH), a small but mighty peptide, plays a crucial role in regulating the thyroid gland. This hormone, produced in the hypothalamus, stimulates the release of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland. TRH impacts metabolism, growth, and development. Without it, the body’s energy levels and overall health could suffer. Understanding TRH can help in grasping how our bodies maintain balance. From its discovery in the 1960s to its medical applications today, TRH remains a key player in endocrinology. Ready to dive into 30 fascinating facts about this essential hormone? Let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- TRH is a tiny but mighty hormone that controls thyroid function and metabolism. It also affects mood, memory, and digestion, and may hold promise for treating conditions like depression and Alzheimer's.
- TRH isn't just for humans; it's found in many animals and helps regulate their thyroid function and reproductive processes. Research on TRH in animals can teach us more about its potential in humans.
What is Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)?
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH) is a small peptide hormone produced in the hypothalamus. It plays a crucial role in regulating the thyroid gland and overall metabolism. Here are some fascinating facts about TRH.
- TRH is composed of just three amino acids: glutamic acid, histidine, and proline.
- It was first discovered in 1969 by Nobel laureates Roger Guillemin and Andrew Schally.
- TRH stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary gland.
- TSH, in turn, prompts the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism.
- TRH also influences the release of prolactin, another hormone produced by the pituitary gland.
How TRH Affects the Body
TRH has a wide range of effects on the body, beyond just thyroid regulation. Understanding these effects can provide insight into its importance.
- TRH can affect mood and emotional states by influencing neurotransmitter systems in the brain.
- It has been shown to have antidepressant effects in some studies.
- TRH can enhance cognitive function and memory.
- It plays a role in regulating body temperature.
- TRH can influence gastrointestinal motility, affecting digestion.
TRH in Medical Research
TRH has been the subject of extensive research due to its potential therapeutic applications. Here are some key findings from medical studies.
- TRH analogs are being investigated as potential treatments for depression and bipolar disorder.
- Research suggests that TRH could help in managing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- TRH has been studied for its potential to treat spinal cord injuries.
- It may have protective effects against certain types of brain damage.
- TRH is being explored as a treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
TRH and the Endocrine System
The endocrine system relies on hormones like TRH to maintain balance and function properly. Let's look at how TRH interacts with this system.
- TRH is part of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis, a critical hormonal feedback loop.
- It helps maintain homeostasis by regulating thyroid hormone levels.
- TRH secretion can be influenced by stress, illness, and other factors.
- The hypothalamus releases TRH in response to low thyroid hormone levels in the blood.
- TRH levels can be measured in the blood to diagnose thyroid disorders.
Interesting Facts About TRH
Here are some lesser-known but intriguing facts about TRH that highlight its complexity and significance.
- TRH is also found in other parts of the brain, not just the hypothalamus.
- It can be synthesized artificially for research and medical use.
- TRH has a very short half-life, lasting only a few minutes in the bloodstream.
- It is rapidly degraded by enzymes in the blood and tissues.
- TRH receptors are present in various tissues, including the heart and pancreas.
TRH in Animals
TRH is not unique to humans; it is found in many animals, playing similar roles across species.
- TRH has been identified in mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
- It regulates thyroid function in animals just as it does in humans.
- TRH can influence reproductive functions in some animal species.
- In fish, TRH helps regulate osmoregulation, the process of maintaining fluid balance.
- Research on TRH in animals can provide insights into its functions and potential applications in humans.
Final Thoughts on TRH
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH) plays a crucial role in regulating the thyroid gland, impacting metabolism, growth, and development. This tiny peptide, produced in the hypothalamus, triggers the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland. TSH then stimulates the thyroid to produce hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are vital for various bodily functions.
Understanding TRH's function helps in diagnosing and treating thyroid disorders. For instance, abnormal TRH levels can indicate hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, guiding appropriate medical interventions. Researchers continue to explore TRH's potential in treating conditions beyond thyroid issues, such as depression and neurodegenerative diseases.
In essence, TRH is more than just a hormone; it's a key player in maintaining overall health. Keeping an eye on its levels can provide valuable insights into one's well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
