Metallothionein is a small protein found in many living organisms, including humans. It plays a crucial role in binding heavy metals like zinc, copper, and cadmium, helping to detoxify the body. But what exactly makes metallothionein so special? This protein not only protects cells from metal toxicity but also aids in regulating essential metal ions, which are vital for various biological processes. Understanding metallothionein can offer insights into how our bodies handle metal exposure and maintain metal balance. Ready to learn more? Here are 30 intriguing facts about this remarkable protein that highlight its importance in health and science.
Key Takeaways:
- Metallothionein is a tiny but mighty protein that helps regulate metal ions in living organisms, protecting cells from damage and supporting essential functions like immune health and wound healing.
- This fascinating protein has diverse roles, from influencing taste perception to being a potential biomarker for diseases. It continues to be a hot topic in scientific research, with new discoveries unfolding regularly.
What is Metallothionein?
Metallothionein is a fascinating protein found in many living organisms. It plays a crucial role in various biological processes, particularly in metal ion metabolism and detoxification. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this essential protein.
-
Metallothionein is a low-molecular-weight protein. It typically has a molecular weight of around 6,000 to 7,000 Daltons, making it relatively small compared to other proteins.
-
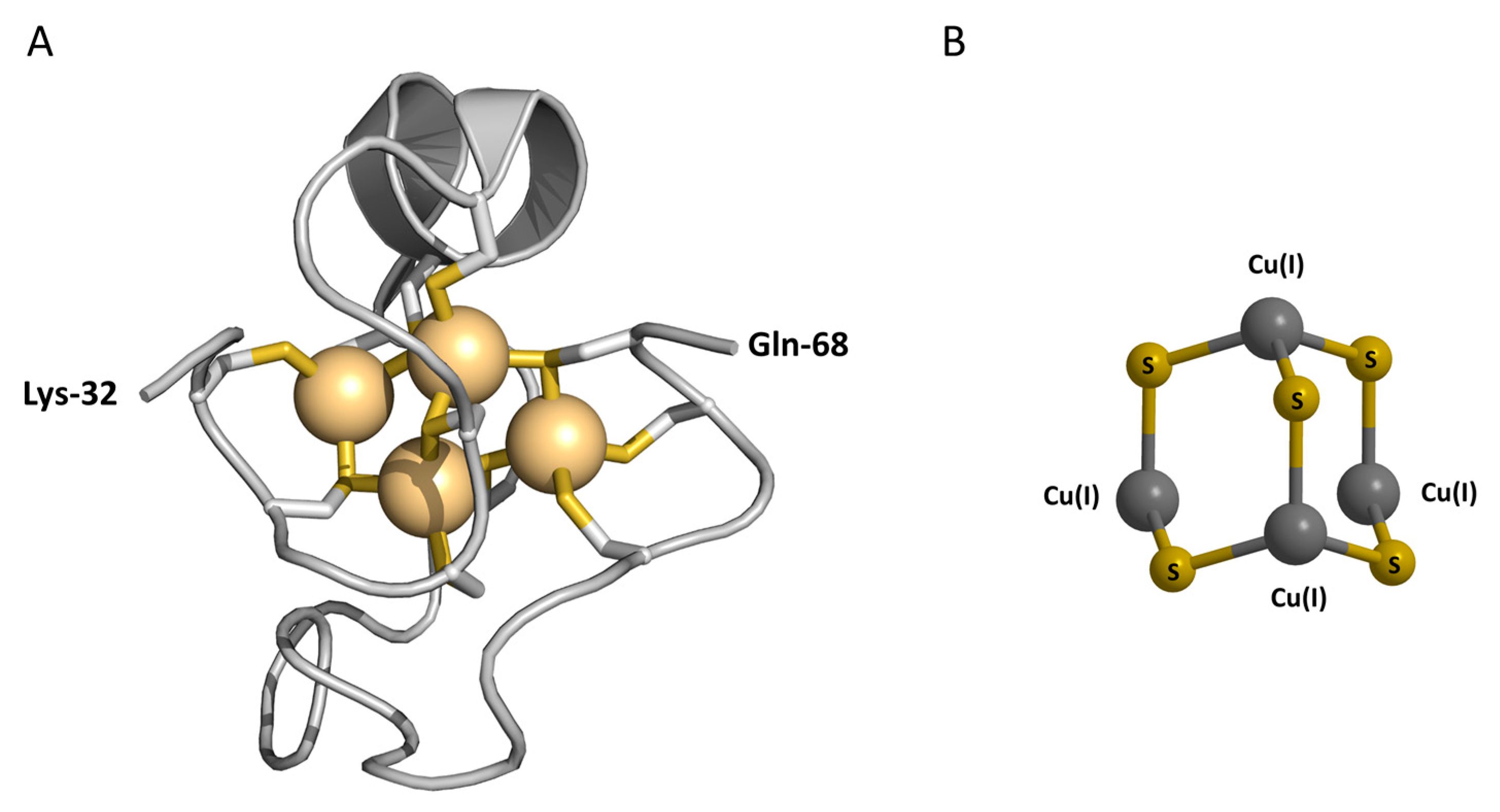
It contains a high percentage of cysteine residues. These amino acids are essential for binding metal ions, which is one of the primary functions of metallothionein.
-
Metallothionein can bind to various metal ions. These include zinc, copper, cadmium, and mercury, among others. This binding helps regulate metal ion concentrations in cells.
-
The protein was first discovered in horse kidneys. Researchers identified metallothionein in 1957 while studying the kidneys of horses.
-
It plays a role in detoxification. By binding to toxic metal ions like cadmium and mercury, metallothionein helps protect cells from metal-induced damage.
-
Metallothionein is found in almost all living organisms. From bacteria to humans, this protein is widespread across different species.
Functions of Metallothionein
Metallothionein is not just a metal-binding protein; it has several vital functions in the body. Here are some key roles it plays:
-
Regulates metal ion homeostasis. Metallothionein helps maintain the balance of essential metal ions like zinc and copper in cells.
-
Protects against oxidative stress. By binding to metal ions, metallothionein can prevent the formation of harmful free radicals.
-
Supports immune function. Zinc-bound metallothionein is crucial for the proper functioning of the immune system.
-
Aids in wound healing. Zinc, an essential component of metallothionein, is vital for tissue repair and regeneration.
-
Involved in gene expression. Metallothionein can influence the expression of certain genes, particularly those related to metal ion metabolism.
-
Acts as a reservoir for metal ions. The protein can store metal ions and release them when needed, ensuring a steady supply for various cellular processes.
Metallothionein in Health and Disease
The role of metallothionein extends beyond normal physiological functions; it also has implications in health and disease.
-
Linked to cancer. Abnormal levels of metallothionein have been observed in various cancers, suggesting a potential role in tumor development and progression.
-
Involved in neurodegenerative diseases. Changes in metallothionein levels have been associated with conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
-
Protects against heavy metal poisoning. By binding to toxic metals, metallothionein can mitigate the harmful effects of heavy metal exposure.
-
Potential therapeutic target. Researchers are exploring ways to modulate metallothionein levels for therapeutic purposes, particularly in diseases related to metal ion imbalance.
-
Influences aging. Metallothionein levels tend to decrease with age, which may contribute to age-related decline in metal ion homeostasis and increased oxidative stress.
Interesting Facts About Metallothionein
Here are some lesser-known yet fascinating facts about metallothionein that highlight its unique properties and functions.
-
Highly conserved across species. The structure and function of metallothionein have remained remarkably consistent throughout evolution.
-
Exists in multiple isoforms. There are several different forms of metallothionein, each with slightly different functions and metal-binding affinities.
-
Can be induced by various stimuli. Factors like metal ion exposure, oxidative stress, and inflammation can increase metallothionein production.
-
Found in different tissues. While it is present in almost all tissues, metallothionein levels are particularly high in the liver, kidneys, and intestines.
-
Plays a role in embryonic development. Metallothionein is essential for proper development, particularly in the early stages of life.
-
Involved in taste perception. Zinc-bound metallothionein is crucial for the function of taste buds, influencing taste perception.
-
Can be measured in biological samples. Researchers can measure metallothionein levels in blood, urine, and tissue samples to assess metal ion status and exposure.
-
Used as a biomarker. Metallothionein levels can serve as a biomarker for metal exposure and certain diseases.
-
Has antioxidant properties. By binding to metal ions, metallothionein can prevent the formation of reactive oxygen species, acting as an antioxidant.
-
Involved in the metabolism of drugs. Metallothionein can influence the metabolism and detoxification of certain drugs, affecting their efficacy and toxicity.
-
Can be genetically modified. Scientists have developed genetically modified organisms with altered metallothionein levels to study its functions and potential therapeutic applications.
-
Interacts with other proteins. Metallothionein can interact with various other proteins, influencing their functions and stability.
-
Subject of ongoing research. Despite being discovered over 60 years ago, metallothionein continues to be a topic of active research, with new discoveries being made regularly.
The Final Word on Metallothionein
Metallothionein, a small but mighty protein, plays a crucial role in our bodies. It helps regulate essential metals like zinc and copper, while also protecting us from toxic heavy metals. This protein's ability to bind metals makes it a key player in detoxification processes. Research shows its involvement in immune response, cell growth, and repair mechanisms. Understanding metallothionein can lead to breakthroughs in treating metal toxicity and neurodegenerative diseases. Scientists continue to uncover its secrets, promising a future where we can better harness its potential. So, next time you hear about metallothionein, remember its vital contributions to health and well-being. This tiny protein packs a powerful punch, proving that sometimes, the smallest things make the biggest difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
