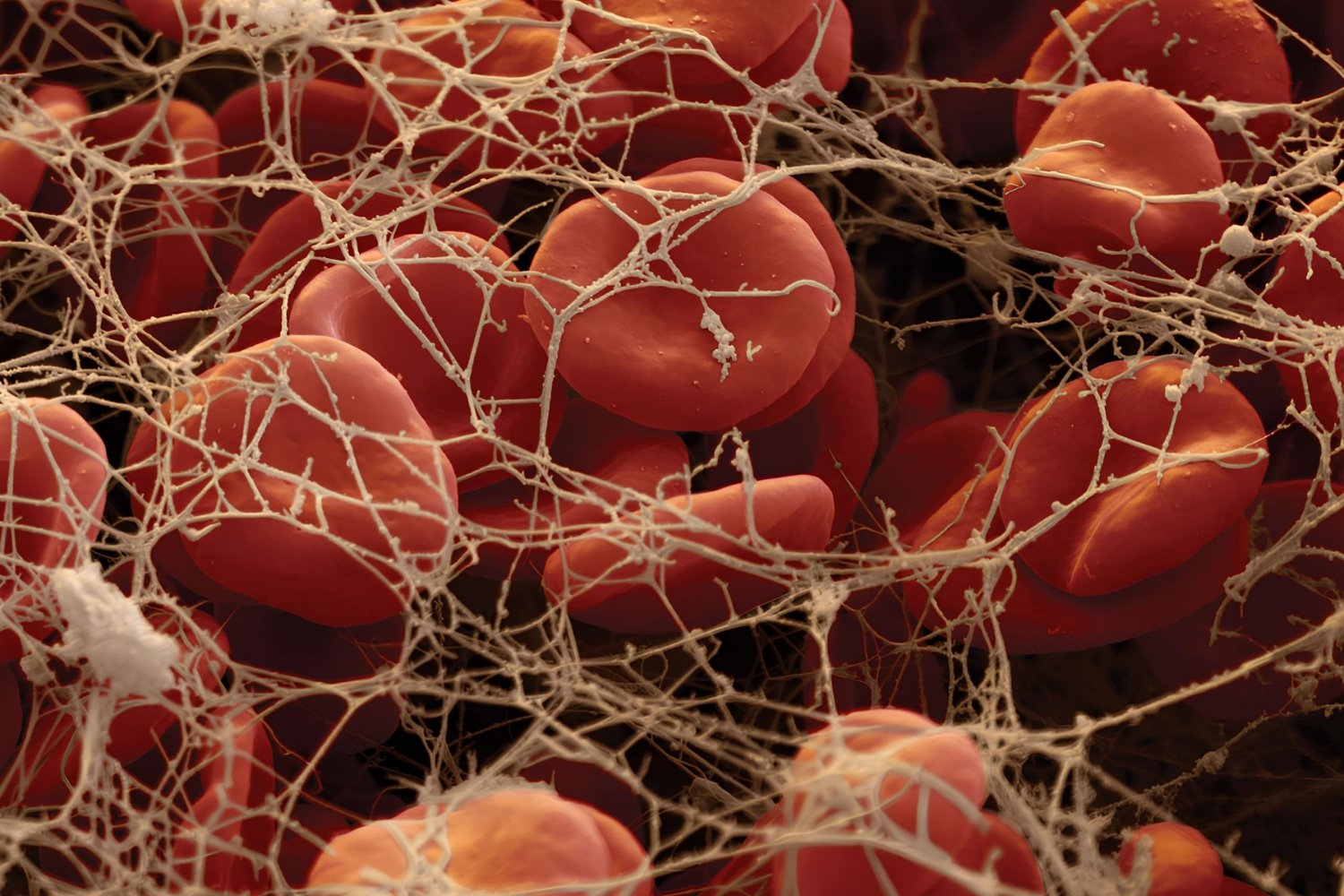
Fibrinogen might sound like a complex term, but it's a crucial protein in your blood. Ever wondered how your body stops bleeding when you get a cut? That's fibrinogen at work! This protein helps form blood clots, preventing excessive bleeding. Without it, even minor injuries could become serious. Fibrinogen levels can tell doctors a lot about your health. High levels might indicate inflammation or other conditions, while low levels could signal bleeding disorders. Understanding fibrinogen can help you grasp how your body heals and stays healthy. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 29 fascinating facts about this essential protein!
What is Fibrinogen?
Fibrinogen, a protein produced by the liver, plays a crucial role in blood clotting. When an injury occurs, fibrinogen transforms into fibrin, forming a clot to stop bleeding. This process is vital for wound healing and maintaining overall health.
- Fibrinogen is a glycoprotein that circulates in the blood plasma.
- It is one of 13 coagulation factors responsible for normal blood clotting.
- The liver produces fibrinogen, releasing it into the bloodstream.
- Normal fibrinogen levels range between 200-400 mg/dL in adults.
- Low fibrinogen levels can lead to excessive bleeding, while high levels may increase the risk of thrombosis.
The Role of Fibrinogen in Blood Clotting
Understanding fibrinogen's role in blood clotting helps appreciate its importance in the human body. This protein is essential for forming a stable blood clot, preventing excessive blood loss during injuries.
- Fibrinogen converts to fibrin through the action of thrombin.
- Fibrin strands weave together to form a mesh that stabilizes the blood clot.
- Platelets adhere to the fibrin mesh, reinforcing the clot.
- The clotting process involves a cascade of reactions, with fibrinogen playing a central role.
- Deficiencies in fibrinogen can lead to bleeding disorders like afibrinogenemia.
Fibrinogen and Health Conditions
Fibrinogen levels can indicate various health conditions. Monitoring these levels helps diagnose and manage diseases related to blood clotting and cardiovascular health.
- Elevated fibrinogen levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
- High fibrinogen levels can indicate inflammation or infection.
- Chronic inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can raise fibrinogen levels.
- Fibrinogen levels may increase during pregnancy as a natural response to prevent bleeding.
- Liver disease can lead to decreased fibrinogen production, affecting clotting ability.
Measuring Fibrinogen Levels
Healthcare professionals measure fibrinogen levels to assess clotting function and diagnose related disorders. Various tests help determine fibrinogen concentration in the blood.
- The Clauss method is a common test for measuring fibrinogen levels.
- A fibrinogen activity test evaluates how well fibrinogen functions in clot formation.
- Blood samples are required for fibrinogen testing, typically drawn from a vein.
- Fibrinogen levels can be affected by medications like anticoagulants.
- Regular monitoring of fibrinogen levels is crucial for patients with clotting disorders.
Factors Affecting Fibrinogen Levels
Several factors influence fibrinogen levels in the body. Understanding these factors helps manage conditions related to abnormal fibrinogen levels.
- Smoking can increase fibrinogen levels, raising the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Obesity is linked to higher fibrinogen levels, contributing to clotting risks.
- Physical activity can help lower fibrinogen levels, promoting cardiovascular health.
- Diet plays a role in fibrinogen levels; foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids may reduce levels.
- Stress and anxiety can elevate fibrinogen levels, impacting overall health.
Fibrinogen in Medical Treatments
Fibrinogen's role in blood clotting makes it a target for various medical treatments. These treatments aim to manage clotting disorders and improve patient outcomes.
- Fibrinogen concentrate is used to treat patients with fibrinogen deficiencies.
- Cryoprecipitate, a blood product, contains fibrinogen and is used in bleeding emergencies.
- Fibrin sealants, derived from fibrinogen, are used in surgeries to promote clotting and healing.
- Research is ongoing to develop new therapies targeting fibrinogen for clotting disorders.
Fibrinogen Facts: The Final Word
Fibrinogen, a vital protein in blood clotting, plays a crucial role in our health. Understanding its functions and importance can help us appreciate how our bodies heal and protect us. From its discovery to its role in medical diagnostics, fibrinogen has proven to be a fascinating subject. Knowing these 29 facts can enhance your knowledge about this essential protein and its impact on our well-being.
Whether you're a student, a medical professional, or just curious, these insights into fibrinogen offer valuable information. Keep these facts in mind, and you'll have a better grasp of how our bodies work to keep us safe and healthy. Remember, knowledge is power, and understanding fibrinogen is a step toward better health awareness. Stay curious and keep learning!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
