How does the refrigeration cycle work? Imagine a hot summer day, and you reach for a cold drink from the fridge. Ever wondered how that drink stays cold? The refrigeration cycle is the magic behind it. It involves four main steps: evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion. First, a refrigerant absorbs heat inside the fridge, turning into a gas. Then, a compressor squeezes this gas, raising its temperature. Next, the hot gas releases heat outside the fridge, turning back into a liquid. Finally, the liquid refrigerant expands, cools down, and the cycle starts again. This continuous loop keeps your food fresh and drinks chilled.
The Basics of the Refrigeration Cycle
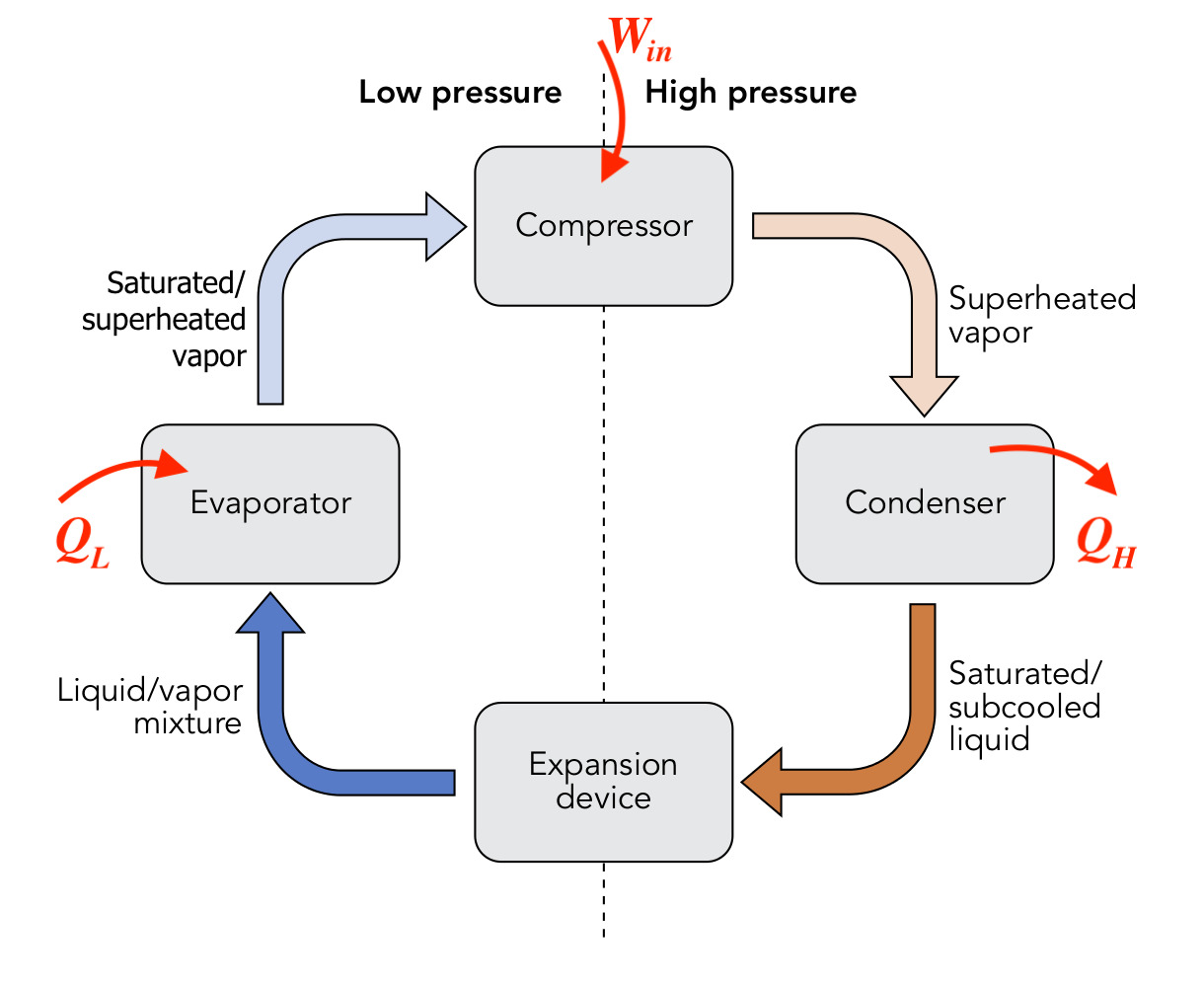
Understanding the refrigeration cycle is essential for grasping how cooling systems work. This cycle involves several key components and processes that work together to remove heat from an area.
-
Refrigeration Cycle: The refrigeration cycle is a process that removes heat from one area and transfers it to another, usually to cool a space or preserve food.
-
Four Main Components: The cycle consists of four main components: the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator.
-
Heat Transfer: The primary function of the refrigeration cycle is to transfer heat from a low-temperature area to a high-temperature area.
-
Refrigerant: A refrigerant is a substance used in the cycle that absorbs and releases heat as it changes states between liquid and gas.
The Role of the Compressor
The compressor is a vital part of the refrigeration cycle. It compresses the refrigerant, increasing its pressure and temperature.
-
Compressor Function: The compressor's main job is to compress the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature.
-
Types of Compressors: There are various types of compressors, including reciprocating, rotary, and centrifugal compressors.
-
Energy Consumption: Compressors are one of the most energy-consuming parts of the refrigeration cycle.
-
Lubrication: Compressors require proper lubrication to function efficiently and prevent wear and tear.
The Condenser's Job
The condenser plays a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle by releasing the heat absorbed by the refrigerant.
-
Heat Release: The condenser releases the heat absorbed by the refrigerant into the surrounding environment.
-
Location: Condensers are usually located outside the area being cooled to effectively release heat.
-
Air-Cooled vs. Water-Cooled: Condensers can be air-cooled or water-cooled, depending on the system design.
-
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the condenser is essential to ensure efficient heat transfer.
Expansion Valve and Its Importance
The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, playing a critical role in the refrigeration cycle.
-
Pressure Drop: The expansion valve causes a pressure drop in the refrigerant, allowing it to expand and cool.
-
Types of Expansion Valves: Common types include thermostatic expansion valves and capillary tubes.
-
Temperature Control: The expansion valve helps control the temperature within the refrigeration system.
-
Preventing Flooding: Proper functioning of the expansion valve prevents flooding of the evaporator with liquid refrigerant.
The Evaporator's Function
The evaporator is where the refrigerant absorbs heat, cooling the surrounding area.
-
Heat Absorption: The evaporator absorbs heat from the area to be cooled, causing the refrigerant to evaporate.
-
Location: Evaporators are typically located inside the area being cooled, such as a refrigerator or air conditioner.
-
Surface Area: A larger surface area of the evaporator allows for more efficient heat absorption.
-
Frost Build-Up: Frost can build up on the evaporator, reducing its efficiency and requiring periodic defrosting.
Refrigerant Properties
The refrigerant is the lifeblood of the refrigeration cycle, and its properties are crucial for the system's efficiency.
-
Boiling Point: Refrigerants have a low boiling point, allowing them to evaporate and absorb heat at low temperatures.
-
Environmental Impact: Some refrigerants have a high global warming potential, leading to the development of more eco-friendly alternatives.
-
Toxicity: The toxicity of refrigerants varies, with some being safe for use in residential systems and others requiring careful handling.
-
Leak Detection: Detecting refrigerant leaks is essential to maintain system efficiency and prevent environmental harm.
Efficiency and Performance
The efficiency and performance of the refrigeration cycle depend on various factors, including system design and maintenance.
-
Coefficient of Performance (COP): The COP measures the efficiency of a refrigeration system, with higher values indicating better performance.
-
Insulation: Proper insulation of the cooled area reduces the load on the refrigeration system, improving efficiency.
-
Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance of all components ensures optimal performance and extends the system's lifespan.
-
Energy Efficiency: Modern refrigeration systems are designed to be more energy-efficient, reducing operating costs and environmental impact.
Innovations in Refrigeration
Advancements in technology have led to significant improvements in refrigeration systems.
-
Smart Refrigeration: Smart refrigeration systems use sensors and IoT technology to optimize performance and energy use.
-
Magnetic Refrigeration: Magnetic refrigeration is an emerging technology that uses magnetic fields to cool, offering a more eco-friendly alternative.
-
Solar-Powered Refrigeration: Solar-powered refrigeration systems use solar energy to operate, reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
-
Cryogenic Refrigeration: Cryogenic refrigeration involves cooling to extremely low temperatures, used in specialized applications like medical and scientific research.
-
Variable Speed Compressors: Variable speed compressors adjust their speed based on cooling demand, improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
The Cool Truth
Refrigeration cycles are more than just a way to keep your drinks cold. They play a crucial role in food preservation, medical storage, and even air conditioning. Understanding the basics of how these cycles work can help you appreciate the technology that keeps our modern world running smoothly. From the compressor to the evaporator, each component has a specific job that contributes to the overall efficiency of the system.
Knowing these facts can also help you troubleshoot minor issues and make informed decisions when purchasing new appliances. So next time you open your refrigerator, take a moment to think about the fascinating process happening behind the scenes. It’s a marvel of engineering that we often take for granted but is essential for our daily lives. Stay cool and keep learning!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
