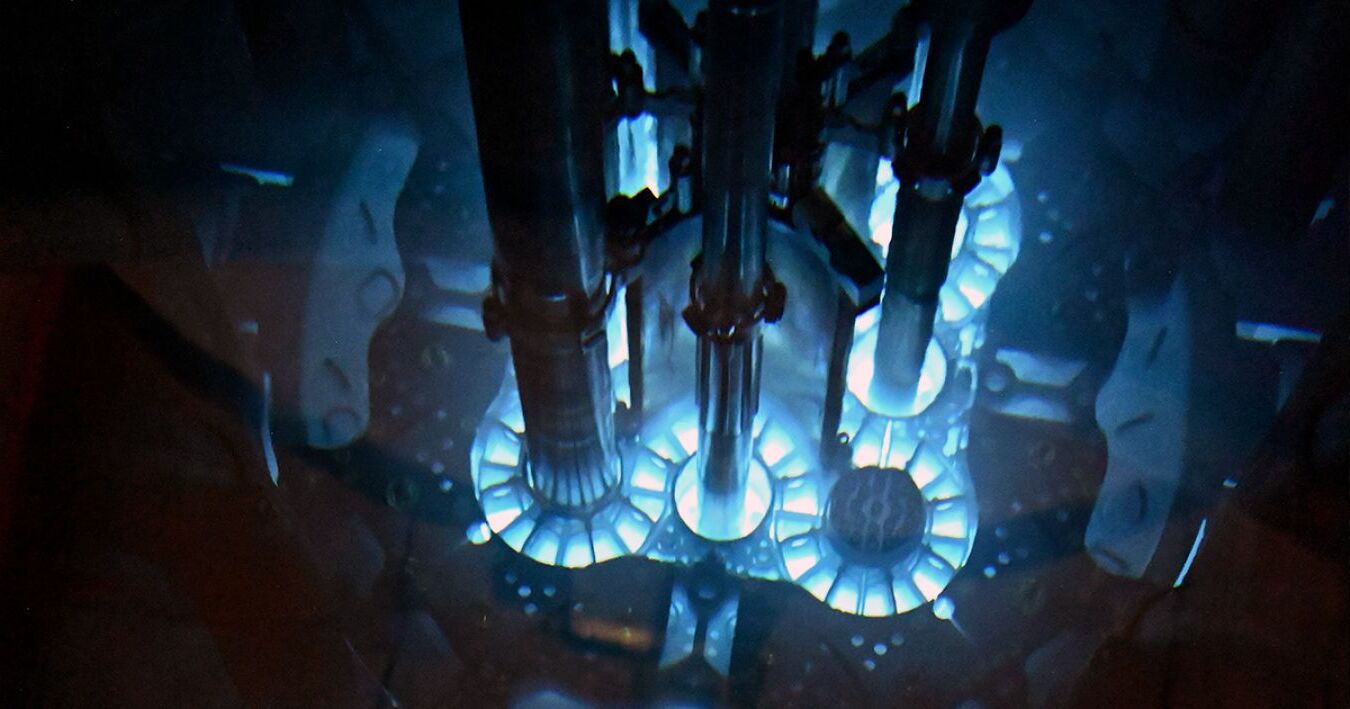
What is Cherenkov Radiation? Cherenkov radiation, often called the "blue glow," is a phenomenon where charged particles travel through a medium faster than light can in that medium. This creates a shockwave of light, similar to a sonic boom but with photons. Named after Soviet physicist Pavel Cherenkov, who first observed it in 1934, this radiation is commonly seen in nuclear reactors and particle detectors. The distinct blue hue is due to the specific wavelengths of light emitted. Why does Cherenkov Radiation occur? It happens when particles, like electrons, exceed the speed of light in water or another transparent substance. This fascinating effect not only looks cool but also helps scientists study high-energy particles and cosmic events.
Key Takeaways:
- Cherenkov radiation is a cool blue glow caused by particles moving faster than light in water or glass. It's used in nuclear reactors, medical imaging, and even in detecting cosmic rays!
- Despite its sci-fi vibes, Cherenkov radiation is not harmful or radioactive by itself. It's a fascinating phenomenon with practical applications in science, from detecting high-speed particles to potential use in water purification.
What is Cherenkov Radiation?
Cherenkov radiation is a fascinating phenomenon that occurs when a charged particle, such as an electron, travels through a dielectric medium (like water) at a speed greater than the speed of light in that medium. This results in a characteristic blue glow, often seen in nuclear reactors.
-
Named After Pavel Cherenkov: Cherenkov radiation is named after the Soviet physicist Pavel Cherenkov, who first observed it in 1934. He received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1958 for this discovery.
-
Faster Than Light: Although nothing can travel faster than light in a vacuum, particles can exceed the speed of light in a medium like water or glass. This is when Cherenkov radiation occurs.
-
Blue Glow: The blue glow associated with Cherenkov radiation is due to the emission of photons in the blue and ultraviolet spectrum. This is why nuclear reactors submerged in water often appear to glow blue.
How Does Cherenkov Radiation Occur?
Understanding the conditions under which Cherenkov radiation occurs helps in grasping its significance in various scientific fields.
-
Dielectric Medium: Cherenkov radiation only occurs in a dielectric medium, which is a non-conducting substance like water, glass, or plastic.
-
Charged Particles: Only charged particles, such as electrons or protons, can produce Cherenkov radiation. Neutral particles do not cause this effect.
-
Speed Threshold: The particle must travel faster than the phase velocity of light in the medium. This speed threshold is crucial for the radiation to occur.
Applications of Cherenkov Radiation
Cherenkov radiation is not just a scientific curiosity; it has practical applications in various fields.
-
Nuclear Reactors: Cherenkov radiation is used to monitor the activity of nuclear reactors. The blue glow indicates the presence of high-energy particles.
-
Particle Detectors: Cherenkov detectors are used in particle physics to identify high-speed particles. These detectors can differentiate between particles based on their speed.
-
Medical Imaging: In medical imaging, Cherenkov radiation can help visualize certain types of tumors. This is particularly useful in cancer research.
Interesting Facts About Cherenkov Radiation
There are many intriguing aspects of Cherenkov radiation that make it a subject of ongoing research and fascination.
-
Cosmic Rays: Cherenkov radiation can be observed in cosmic rays entering Earth's atmosphere. These high-energy particles produce a faint blue glow.
-
Neutrino Detection: Cherenkov radiation is used in neutrino detectors, such as the Super-Kamiokande in Japan. These detectors can observe the elusive neutrinos by detecting the Cherenkov light they produce.
-
Underwater Detection: Cherenkov radiation can be used to detect underwater nuclear explosions. The radiation produced by the explosion can be detected by specialized sensors.
Cherenkov Radiation in Popular Culture
Cherenkov radiation has also made its way into popular culture, often depicted in movies and TV shows.
-
Science Fiction: Cherenkov radiation is frequently featured in science fiction, often as a visual effect to indicate high-energy phenomena or advanced technology.
-
Movies: Films like "The Abyss" and "Chernobyl" have depicted Cherenkov radiation, adding a sense of realism to their portrayal of nuclear events.
-
Video Games: Some video games, especially those involving nuclear themes, include Cherenkov radiation as a visual element to enhance the gaming experience.
Misconceptions About Cherenkov Radiation
Despite its scientific basis, there are several misconceptions about Cherenkov radiation that need clarification.
-
Not Harmful: The blue glow of Cherenkov radiation is not harmful by itself. However, the high-energy particles that cause it can be dangerous.
-
Not Radioactive: Cherenkov radiation is not the same as radioactivity. It is a byproduct of high-speed particles moving through a medium, not a form of radiation like alpha or beta particles.
-
Not Always Visible: Cherenkov radiation is not always visible to the naked eye. It often requires special equipment to detect, especially in low-intensity scenarios.
Advanced Research on Cherenkov Radiation
Ongoing research continues to uncover new aspects and potential applications of Cherenkov radiation.
-
Astrophysics: Researchers are studying Cherenkov radiation to understand high-energy cosmic events, such as supernovae and black hole activity.
-
Quantum Mechanics: Some studies are exploring the quantum mechanical aspects of Cherenkov radiation, aiming to understand its behavior at the subatomic level.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Cherenkov radiation is being investigated for its potential in environmental monitoring, particularly in detecting radioactive contamination in water bodies.
Cherenkov Radiation in Everyday Life
While Cherenkov radiation might seem like a phenomenon confined to laboratories and nuclear reactors, it has some everyday implications.
-
Airport Security: Some advanced airport security systems use Cherenkov radiation to detect hidden radioactive materials in luggage.
-
Water Purification: Research is being conducted on using Cherenkov radiation for water purification, leveraging its ability to break down contaminants at the molecular level.
-
Educational Tools: Cherenkov radiation is used in educational settings to teach students about particle physics and the behavior of light.
Historical Milestones in Cherenkov Radiation Research
The history of Cherenkov radiation research is filled with significant milestones that have advanced our understanding of this phenomenon.
-
First Observation: Pavel Cherenkov first observed the radiation in 1934 while studying the effects of gamma radiation in liquids.
-
Nobel Prize: In 1958, Pavel Cherenkov, along with Igor Tamm and Ilya Frank, received the Nobel Prize in Physics for their theoretical and experimental work on Cherenkov radiation.
-
First Detector: The first Cherenkov detector was developed in the 1950s, revolutionizing particle physics by allowing scientists to identify high-speed particles more accurately.
-
Modern Applications: Today, Cherenkov radiation is used in various cutting-edge technologies, from medical imaging to astrophysical research, demonstrating its enduring relevance.
The Glow of Knowledge
Cherenkov radiation, with its distinct blue glow, isn't just a scientific curiosity. It plays a crucial role in nuclear reactors, particle physics, and even medical imaging. This phenomenon, discovered by Pavel Cherenkov, has helped scientists understand the behavior of particles moving faster than light in a medium. Its applications, from detecting cosmic rays to monitoring reactor cores, highlight its importance in both research and practical uses.
Understanding Cherenkov radiation not only deepens our grasp of physics but also showcases the interconnectedness of science and technology. Next time you see that eerie blue glow in a science documentary or research lab, you'll know the fascinating facts behind it. Keep exploring, stay curious, and let the light of knowledge guide your way.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
