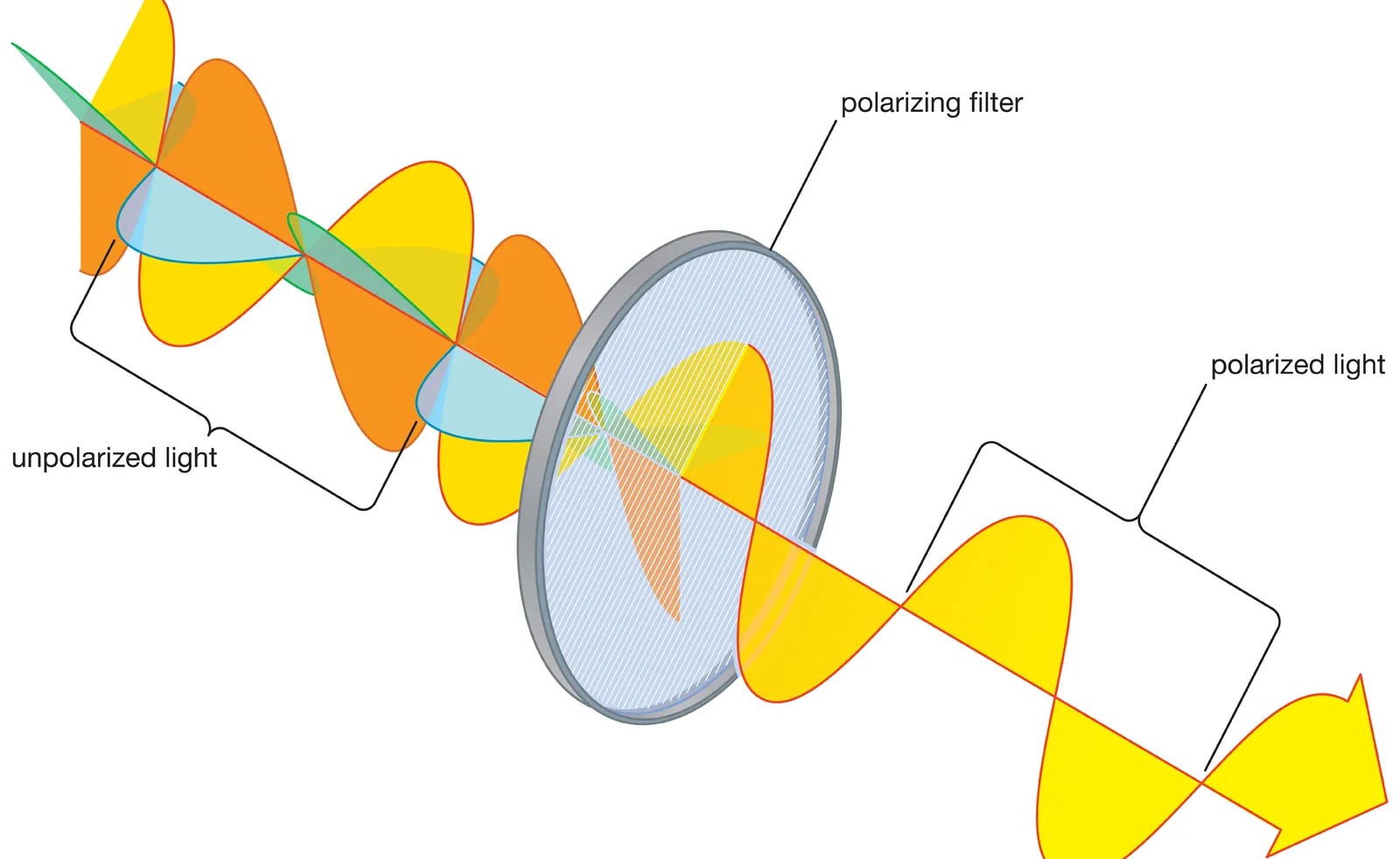
Polarization, a fundamental concept in physics, is much more than just a political term. It refers to the phenomenon where the oscillation of waves is confined to a single plane. While polarization may seem complex, it plays a crucial role in various aspects of our daily lives, from the creation of 3D glasses to the functioning of satellite communication systems.
In this article, we will explore twelve mind-blowing facts about polarization that will not only fascinate you but also deepen your understanding of this fascinating natural phenomenon. Whether you’re a science enthusiast or simply curious about the world around you, get ready to embark on a journey that will shed light on the wonders of polarization and its intriguing applications. So, let’s dive right in and unravel the secrets of polarization!
Key Takeaways:
- Polarization is everywhere! It’s in your sunglasses, 3D movies, and even in your phone’s screen. It helps us see better, communicate, and explore the universe.
- Polarization isn’t just about light. It’s in radio waves, sound waves, and even in virtual reality. Understanding it helps us create amazing technologies and discover hidden secrets.
Polarization is the division of a wave into two distinct vibrations.
When a wave undergoes polarization, it splits into two perpendicular vibrations along a specific axis. This phenomenon occurs when certain types of waves, such as light or electromagnetic waves, interact with certain materials or pass through specific filters.
Polarization is responsible for the glare on water and glass surfaces.
When light reflects off a smooth surface like water or glass, it often becomes polarized horizontally. This polarized light creates an inconvenient glare that can be reduced by wearing polarized sunglasses, which filter out horizontally polarized light waves.
Polarization can be used in 3D movies to create depth perception.
In 3D movies, special glasses with polarized lenses are used. The movie projector projects two slightly different images onto the screen, each with a different polarization direction. The glasses then filter out one image for the left eye and the other image for the right eye, creating the illusion of depth perception.
Polarization plays a crucial role in optical instruments like cameras and microscopes.
By using polarizing filters, photographers and scientists can selectively block or allow specific polarizations of light, enhancing contrast and reducing glare. This technique is widely used in various fields, such as wildlife photography, forensic analysis, and biological research.
Polarization is used in telecommunications to transmit and receive signals.
In fiber optic communication systems, polarized light is used to carry information over long distances. The polarization of the light can be manipulated to encode data, which is then transmitted through the fiber optic cables. Similarly, receivers can distinguish and process polarized signals to retrieve the transmitted information.
Polarization is used in LCD screens to control the light passing through.
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) utilize the properties of polarization to control the amount of light passing through each pixel. By manipulating the polarization states of liquid crystals, specific pixels can be turned on or off, resulting in the display of different colors and images.
Polarization is crucial in studying the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation.
Scientists studying the remnants of the Big Bang, known as the Cosmic Microwave Background, analyze the polarization patterns in the radiation to gain insights into the early universe. These polarization patterns provide valuable information about the universe’s age, composition, and evolution.
Polarization can be observed in everyday objects like sunglasses and 3D glasses.
Sunglasses with polarized lenses are widely used to reduce glare and improve visibility, especially in outdoor activities. 3D glasses, as mentioned earlier, utilize polarized lenses to create the illusion of depth in movies and other visual media.
Polarization affects the behavior of radio waves.
Radio waves can also undergo polarization, which influences how they propagate and interact with objects and antennas. Understanding polarization is essential for optimizing wireless communication systems and mitigating interference.
Polarized light can reveal hidden details in certain materials.
When polarized light interacts with transparent or reflective materials, it can unveil hidden details that are not visible under normal illumination. This technique is often used in gemology, material inspection, and art restoration to detect imperfections or authenticate valuable objects.
Polarization is not limited to electromagnetic waves.
While polarization is most commonly associated with light and other electromagnetic waves, it can also occur in other types of waves, such as sound waves or water waves. In these cases, the vibration direction of the wave corresponds to the polarization direction.
Polarization is used in modern-day virtual reality (VR) technology.
Virtual reality headsets incorporate polarized lenses to enhance the immersive experience. These lenses help filter out specific wavelengths of light and improve the perception of depth and realism in virtual environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, polarization is a fascinating and complex phenomenon that plays a significant role in various aspects of our lives. From physics and light polarization to social and political polarization, there are countless mind-blowing facts to explore.Understanding polarization can help us comprehend how light behaves and how it can be utilized in various applications such as sunglasses, 3D movies, and optical communication. Additionally, exploring the concept of social and political polarization can shed light on the dynamics of society and the challenges we face in fostering dialogue and understanding.By delving into the world of polarization, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of our universe and the intricacies of human interaction. Whether it’s contemplating the behavior of light waves or examining the divisions within society, polarization is truly a captivating topic that continues to pique our curiosity.
FAQs
Q: What is polarization?
A: Polarization refers to the orientation of waves in physical systems. In the context of light, it describes the direction in which the electromagnetic waves oscillate.
Q: How does polarization work?
A: Polarization occurs when light waves are filtered or constrained in a specific direction, allowing only waves oscillating in that orientation to pass through.
Q: What are some applications of polarization?
A: Polarization has numerous practical applications, such as reducing glare with polarized sunglasses, creating 3D effects in movies, and improving the efficiency of optical communication systems.
Q: Can polarization be observed in other fields besides physics?
A: Yes, polarization is not limited to physics. It can also be observed in social and political contexts, where it refers to the increasing divergence of people’s beliefs, opinions, and ideologies.
Q: How does social and political polarization impact society?
A: Social and political polarization can lead to increased division, reduced cooperation, and difficulties in reaching consensus. It can hinder progress, compromise, and understanding among diverse groups of people.
Q: Is it possible to mitigate social and political polarization?
A: While polarization is a complex issue, efforts can be made to foster dialogue, promote empathy, and encourage open-mindedness. Building bridges between different perspectives and promoting understanding can help bridge gaps and reduce polarization.
Polarization's mind-blowing effects extend far beyond what we've covered here. From the frigid polar climates to the barren polar deserts, there's still so much to learn about this fascinating phenomenon. If you're curious to explore more captivating facts about polarization and its impact on our world, keep reading to satisfy your craving for knowledge. Uncover the secrets of polar regions and delve deeper into the mysteries of polarization – you won't be disappointed!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
