Are you ready to explore the fascinating world of latitude? Latitude, a fundamental concept in geography, plays a crucial role in understanding the Earth’s geography and climate patterns. In this article, we will uncover 18 mind-blowing facts about latitude that will leave you in awe of the incredible complexity and diversity of our planet. From the equator to the polar regions, latitude not only determines the temperature and climate of a location but also has significant implications for navigation, seasons, and even cultural practices. Join us on this journey around the globe as we delve into the intriguing world of latitude and discover the fascinating facts that will broaden your understanding of our planet’s geography. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready for an adventure like no other!
Key Takeaways:
- Latitude measures how far a place is from the equator and affects climate, daylight, and wildlife. It’s like a horizontal ruler for the Earth, guiding everything from weather to navigation.
- The Arctic Circle, Tropic of Cancer, and Tropic of Capricorn are all defined by latitude and have unique effects on sunlight and seasons. Latitude isn’t just a line on a map—it shapes the world around us!
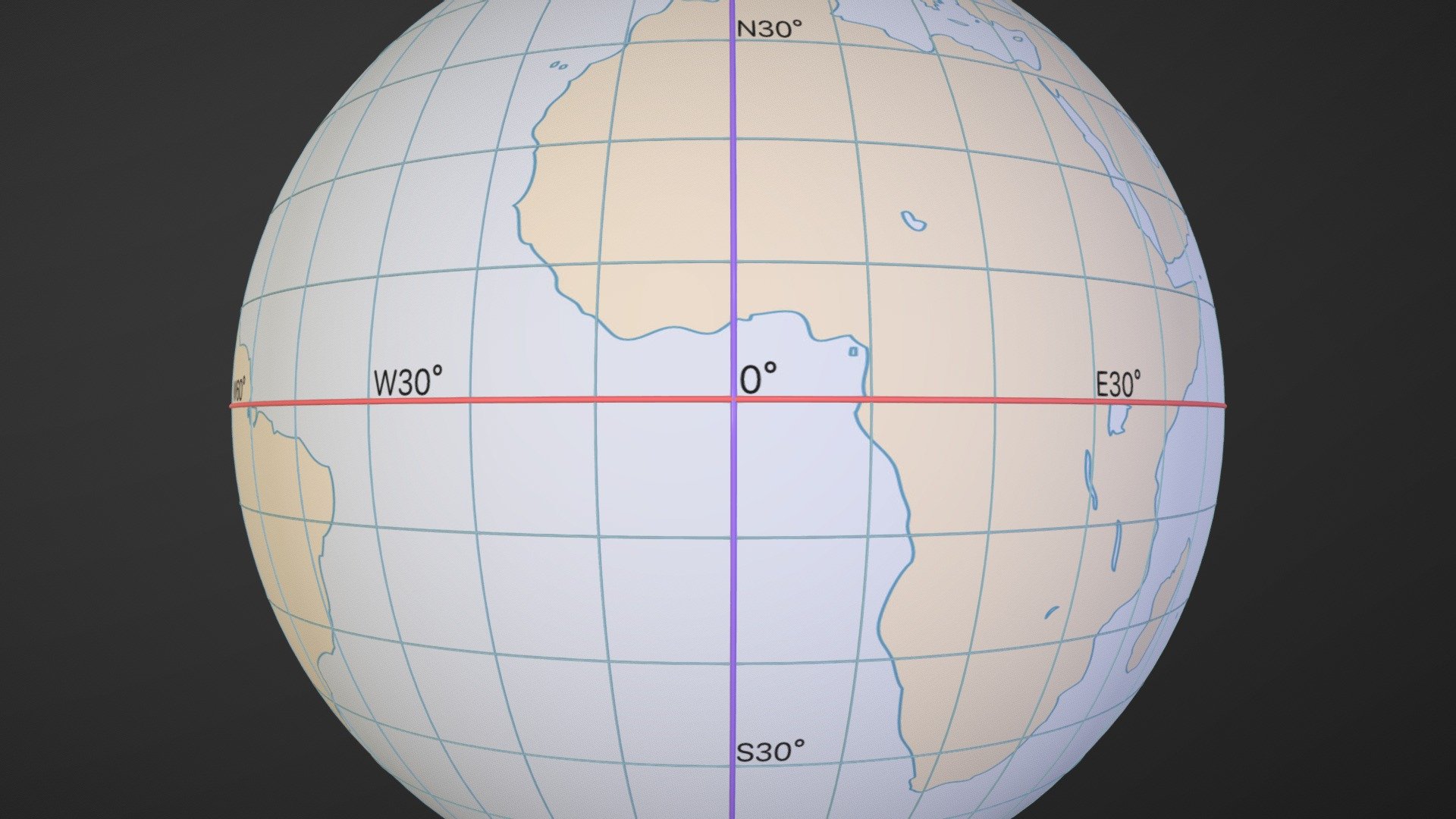
Latitude defines the angular distance of a location from the equator.
Latitude is a fundamental concept in geography that measures how far north or south a place is from the equator. It is expressed in degrees and ranges from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles. The equator itself has a latitude of 0°.
The Arctic Circle is located at approximately 66.5° north latitude.
The Arctic Circle is an imaginary line of latitude that marks the southernmost point where the sun remains visible for a full 24 hours during the summer solstice. It is a significant milestone for regions in the Northern Hemisphere.
The Antarctic Circle is located at approximately 66.5° south latitude.
Similar to the Arctic Circle, the Antarctic Circle is an imaginary line of latitude that marks the northernmost point where the sun remains visible for a full 24 hours during the summer solstice. It is an important landmark for areas in the Southern Hemisphere.
The Tropic of Cancer is located at approximately 23.5° north latitude.
The Tropic of Cancer is an important circle of latitude that corresponds to the farthest point north where the sun can be directly overhead. It marks the beginning of summer in the Northern Hemisphere during the June solstice.
The Tropic of Capricorn is located at approximately 23.5° south latitude.
Opposite to the Tropic of Cancer, the Tropic of Capricorn represents the farthest point south where the sun can be directly overhead. It marks the beginning of summer in the Southern Hemisphere during the December solstice.
The equator is the only line of latitude that divides the Earth into equal halves.
As the line of latitude with a latitude of 0°, the equator acts as the dividing point between the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. It is the longest line of latitude on Earth.
The Prime Meridian and the International Date Line are not lines of latitude.
While latitude measures the north-south position on Earth, the Prime Meridian and the International Date Line are lines of longitude that define the east-west position. The Prime Meridian passes through Greenwich, London, and has a longitude of 0°.
The Antarctic region experiences 6 months of continuous daylight and 6 months of continuous darkness.
Due to its extreme latitude, the Antarctic region goes through periods of extended daylight and darkness. During the summer solstice, the sun remains above the horizon for 24 hours, while during the winter solstice, it remains below the horizon for the same duration.
The Arctic region experiences the phenomenon of the Midnight Sun.
Similarly, the Arctic region also experiences periods of continuous daylight during the summer months. This natural phenomenon is known as the Midnight Sun and occurs because of the region’s high latitude.
The latitude of a location affects its climate and weather patterns.
The latitude of a place plays a significant role in determining its climate and weather conditions. Generally, regions closer to the equator experience warmer temperatures and tropical climates, while those closer to the poles have colder temperatures and polar climates.
Latitude lines are parallel to each other and never intersect.
Unlike lines of longitude, which converge at the poles, lines of latitude run parallel to each other and never intersect. This parallel nature allows for easy measurement of distance between latitudes.
The concept of latitude was first developed by Greek astronomer Hipparchus.
Hipparchus, a renowned Greek astronomer from the 2nd century BCE, is credited with introducing the concept of latitude to map the Earth’s surface. His work laid the foundation for our modern understanding of latitude.
The equator experiences the most consistent day length throughout the year.
Unlike other latitudes, the equator experiences a relatively consistent length of daylight throughout the year. This absence of significant seasonal variations in day length contributes to the region’s tropical climate.
Latitude affects the length of the growing season for plants.
The length of the growing season for plants is influenced by the latitude of a location. Areas with shorter growing seasons, such as those closer to the poles, have limited time for plant growth and cultivation.
The latitude of a location affects the angle at which sunlight reaches the Earth’s surface.
The angle at which sunlight reaches the Earth’s surface is determined by the latitude of a place. Higher latitudes experience lower angles of sunlight, resulting in less heat and shorter days.
The latitude of a location influences the types of wildlife and ecosystems found there.
Different latitudes support different types of wildlife and ecosystems. Tropical latitudes near the equator are home to diverse rainforests, while polar latitudes near the poles feature unique Arctic and Antarctic habitats.
The distance covered in one degree of latitude is constant.
One degree of latitude, regardless of location, always represents the same distance on Earth’s surface. This consistency makes latitude a valuable tool for measuring distances and navigation.
The rectangular grid system used in mapping is based on latitude and longitude.
The latitude and longitude system forms the basis of the rectangular grid system used to map the Earth’s surface. This system allows for accurate location plotting and navigation on various maps and GPS devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring the concept of latitude can open our minds to the amazing intricacies of our planet Earth. Latitude not only determines our climate and weather patterns but also plays a crucial role in navigation and timekeeping. From the fascinating facts about the equator to the significance of the Arctic and Antarctic circles, understanding latitude allows us to appreciate the diversity and beauty of our planet.By studying latitude, we gain valuable insights into the Earth’s tilt, the changing lengths of day and night, and the path of the sun across different regions. Latitude also influences the distribution of ecosystems and the variations in cultural practices across the globe. It is truly mind-blowing how this simple numerical measurement can have such profound implications.So, next time you look at a world map or embark on a journey, take a moment to marvel at the wonder of latitude and its impact on our world.
FAQs
1. What is latitude?
Latitude is the measurement of distance north or south of the Equator, expressed in degrees. It helps determine a location’s position on the Earth’s surface.
2. How do latitude lines affect climate?
Latitude plays a significant role in determining climate by influencing factors such as the angle of the sun’s rays, temperature, and the length of daylight hours.
3. What is the relation between latitude and seasons?
The angle of the Earth’s tilt in relation to the sun, as influenced by latitude, determines the changing seasons. Higher latitudes experience more pronounced seasonal variations.
4. How is latitude used in navigation?
Latitude is an essential component in navigation as it helps determine a ship or plane’s position relative to the Equator, enabling accurate course calculations and mapping.
5. Can latitude affect cultural practices?
Absolutely! Latitude affects the availability of sunlight, temperature, and natural resources, which in turn influence cultural practices, traditions, and even agricultural practices.
6. Are the latitudes fixed or do they change over time?
The latitudes are generally fixed as they are based on the Earth’s axial tilt. However, due to natural geological processes and continental drift, latitudes can shift slightly over geological timescales.
Latitude's influence on our world is truly remarkable, from shaping climate patterns to defining geographical boundaries. But there's more to explore! Dive into the vibrant world of music and arts at Latitude Festival, where creativity knows no bounds. Uncover the secrets of the Earth's latitude zones and how they impact life on our planet. And for a deeper understanding of our world's geography, delve into the fascinating interplay between latitude and longitude.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


