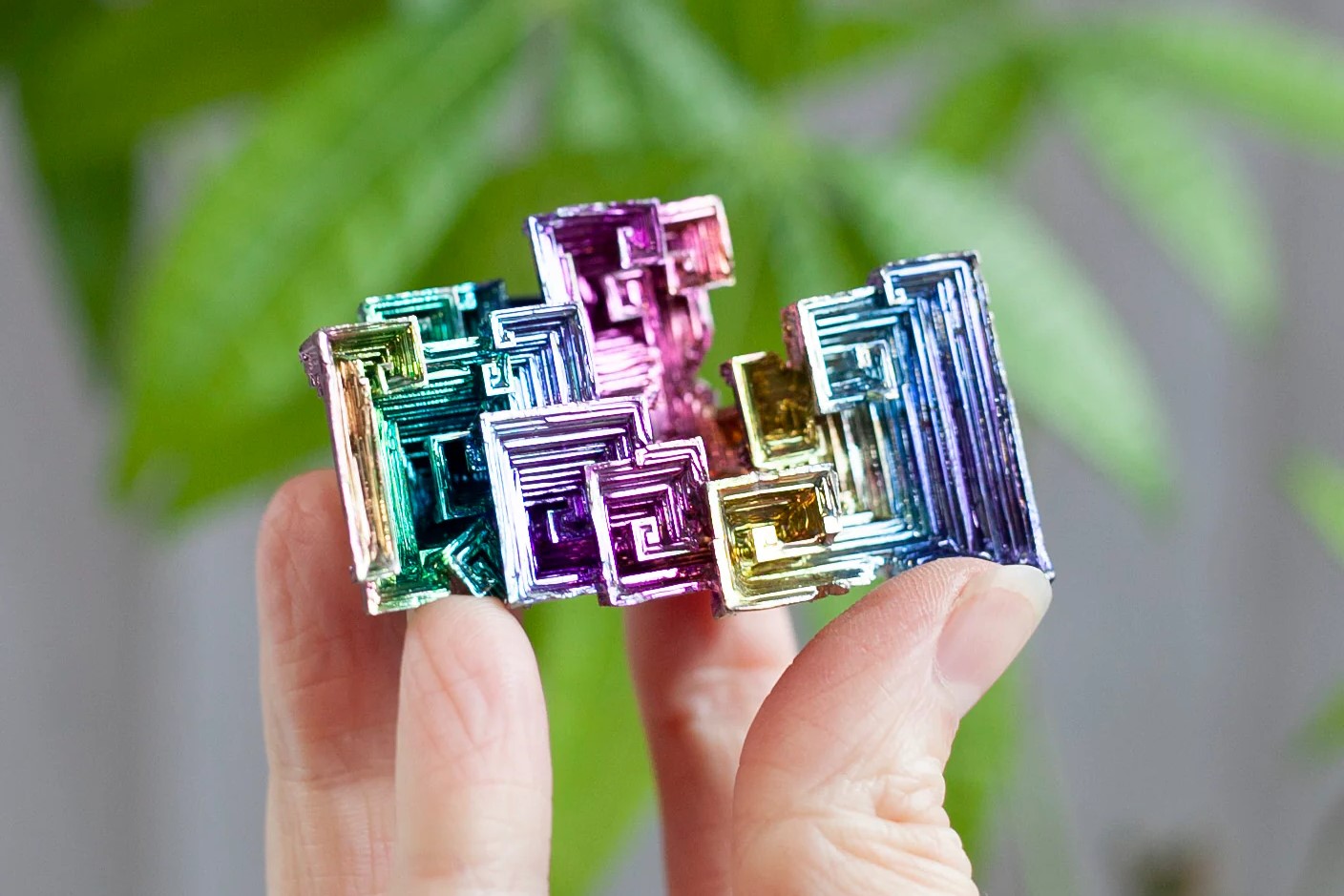
Bismuth is a fascinating element with a lot more to it than meets the eye. Ever wondered what makes this metal so unique? Bismuth stands out due to its rainbow-colored crystals, which are not only beautiful but also scientifically intriguing. This metal is heavier than lead yet non-toxic, making it a safer alternative in various applications. Did you know that bismuth has the highest atomic number of all stable elements? Its low thermal conductivity and high electrical resistance make it useful in many industries. From cosmetics to medical procedures, bismuth plays a crucial role in our daily lives. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 50 amazing facts about bismuth!
Key Takeaways:
- Bismuth, a unique and colorful metal, is used in art, medicine, and technology. Its low toxicity and stunning crystal formations make it a versatile and eco-friendly element.
- From treating gastrointestinal disorders to creating beautiful jewelry, bismuth's properties make it a valuable and fascinating element with a rich history and cultural significance.
What is Bismuth?
Bismuth is a fascinating element with unique properties and a rich history. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this metal.
- Bismuth is a brittle metal with a silvery-white hue, often tinged with a pinkish tint due to oxidation.
- It is the 83rd element on the periodic table, symbolized by "Bi."
- Bismuth has been known since ancient times, often confused with lead and tin.
- It is the most diamagnetic of all metals, meaning it repels magnetic fields.
- Bismuth expands when it solidifies, unlike most metals that contract.
Physical Properties of Bismuth
Bismuth's physical characteristics make it stand out among other elements.
- It has a melting point of 271.5°C (520.7°F), relatively low for a metal.
- Bismuth's boiling point is 1,564°C (2,847°F).
- The metal has a density of 9.78 grams per cubic centimeter.
- Bismuth crystals form intricate, stair-step structures due to its unique atomic arrangement.
- Its thermal conductivity is lower than any metal except mercury.
Chemical Properties of Bismuth
Bismuth's chemical behavior is equally intriguing.
- It is relatively stable and does not tarnish quickly in air.
- Bismuth reacts with halogens, such as chlorine and bromine, to form bismuth halides.
- It forms various compounds, including bismuth oxide, bismuth sulfide, and bismuth nitrate.
- Bismuth is less toxic than its periodic table neighbors, lead and polonium.
- It is often used as a non-toxic replacement for lead in various applications.
Uses of Bismuth
Bismuth's unique properties lend it to a variety of uses in different industries.
- It is used in cosmetics, particularly in eyeshadows and nail polishes, for its pearlescent effect.
- Bismuth subsalicylate is the active ingredient in Pepto-Bismol, a popular antacid.
- It is used in low-melting alloys for fire detection and suppression systems.
- Bismuth is employed in the production of free-machining steels and aluminum alloys.
- It is used in the manufacturing of shotgun pellets and fishing sinkers as a lead substitute.
Bismuth in Art and Jewelry
Bismuth's aesthetic appeal makes it a favorite in artistic and decorative applications.
- Bismuth crystals are often used in jewelry for their iridescent colors and geometric shapes.
- Artists use bismuth to create intricate sculptures and decorative pieces.
- The metal's unique crystal formations are popular among collectors.
- Bismuth's rainbow-like oxidation layer adds a stunning visual effect to art pieces.
- It is sometimes used in stained glass windows for its vibrant colors.
Bismuth in Science and Technology
Bismuth plays a crucial role in various scientific and technological fields.
- It is used in thermoelectric materials for converting heat into electricity.
- Bismuth-based compounds are being researched for their potential in superconductors.
- It is used in nuclear reactors as a coolant and in the production of nuclear fuels.
- Bismuth is employed in the semiconductor industry for its electronic properties.
- It is used in the development of new materials with unique magnetic and optical properties.
Environmental Impact of Bismuth
Bismuth's environmental footprint is relatively small compared to other heavy metals.
- It is considered environmentally friendly due to its low toxicity.
- Bismuth mining has a lower environmental impact than lead or mercury mining.
- It is often recycled from industrial waste and used in new applications.
- Bismuth compounds are used in eco-friendly pesticides and fungicides.
- The metal's non-toxic nature makes it a safer alternative in various industries.
Fun and Unusual Facts about Bismuth
Bismuth has some quirky and lesser-known aspects that make it even more interesting.
- It is the heaviest non-radioactive element, although it has a very long half-life.
- Bismuth crystals can be grown at home using simple methods and materials.
- The metal's name comes from the German word "Wismut," meaning "white mass."
- Bismuth was once believed to be a form of lead until the 18th century.
- It is used in some types of fire extinguishers due to its low melting point.
Bismuth in Medicine
Bismuth's medicinal properties have been known for centuries and continue to be valuable today.
- Bismuth compounds are used to treat gastrointestinal disorders.
- It is used in some ointments and creams for its antibacterial properties.
- Bismuth-based drugs are being researched for their potential in treating infections.
- The metal is used in radiology for shielding and imaging purposes.
- Bismuth subsalicylate helps reduce inflammation and irritation in the digestive tract.
Bismuth in History and Culture
Bismuth has a rich history and cultural significance that spans centuries.
- Alchemists in the Middle Ages believed bismuth had magical properties.
- It was used in ancient China for casting bronze and making coins.
- Bismuth's unique properties have inspired various myths and legends.
- The metal has been used in traditional medicine for centuries.
- Bismuth's vibrant colors and patterns have made it a symbol of beauty and creativity.
Bismuth: A Metal Like No Other
Bismuth stands out among metals for its unique properties and fascinating characteristics. From its iridescent crystals to its low toxicity, bismuth has captured the interest of scientists and hobbyists alike. Its high density and low melting point make it useful in various applications, including medical procedures and fire detection systems. Bismuth's environmental benefits also make it a preferred choice over more toxic metals like lead.
Whether you're interested in its crystal formations or its practical uses, bismuth offers something for everyone. Its colorful appearance and non-toxic nature make it a favorite for art projects and scientific experiments. So next time you come across this remarkable element, you'll know just how special it is. Dive into the world of bismuth and discover its many wonders for yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.