Benzene is a fascinating chemical compound with a rich history and significant impact on various industries. Did you know benzene is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet odor? It’s found in crude oil and is a major part of gasoline. Benzene is also used to make plastics, resins, synthetic fibers, rubber lubricants, dyes, detergents, drugs, and pesticides. However, exposure to benzene can be harmful, causing serious health issues like leukemia. Understanding benzene's properties, uses, and risks is crucial for anyone interested in chemistry or industrial applications. Here are 38 facts about benzene that will give you a comprehensive overview of this important compound.
What is Benzene?
Benzene is a fascinating and essential chemical compound. It's a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet odor. Used in various industries, benzene is both beneficial and hazardous. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about benzene.
-
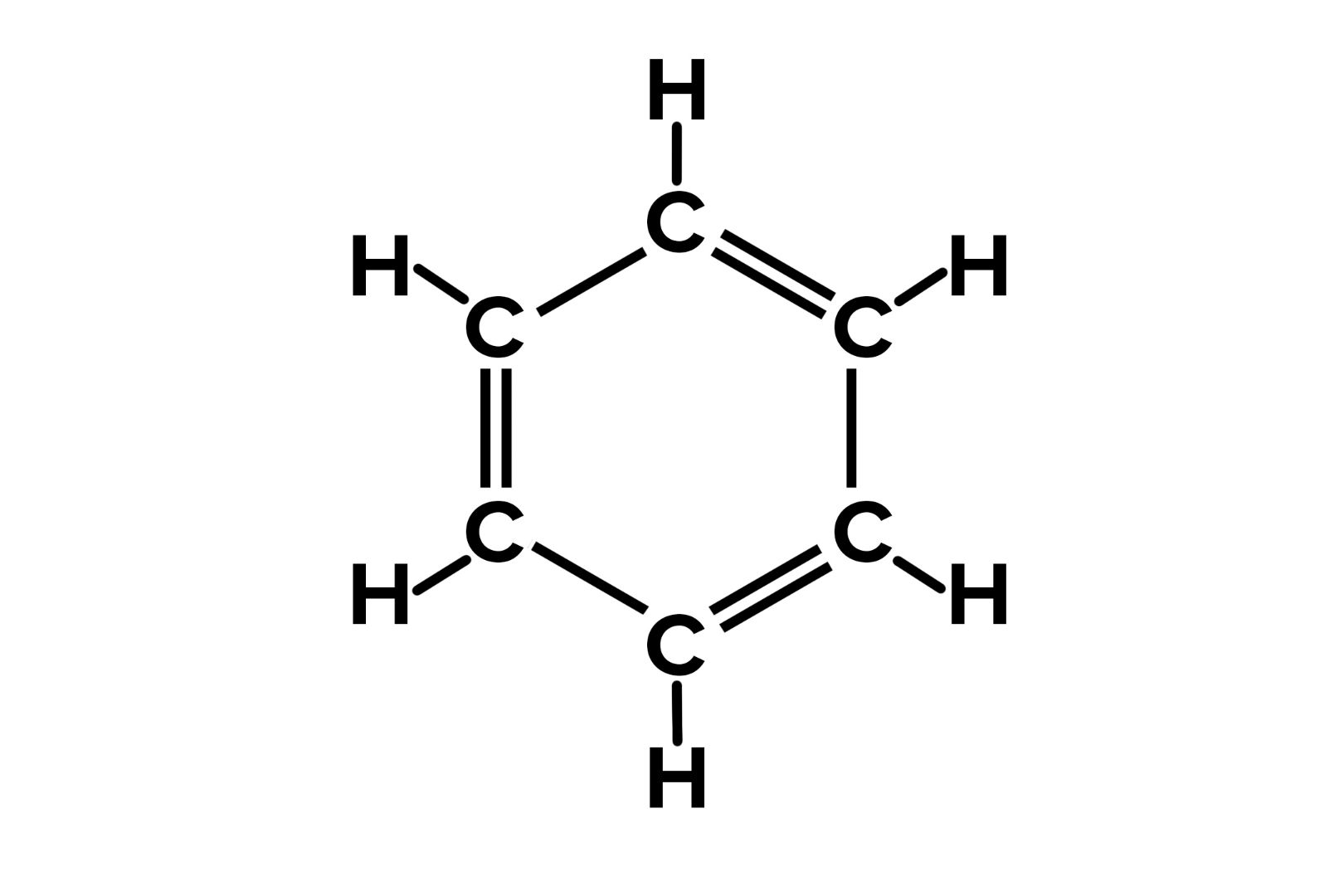
Chemical Formula: Benzene's chemical formula is C6H6. This means it contains six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms.
-
Structure: The structure of benzene is a ring of six carbon atoms, with alternating double bonds. This unique arrangement is called an aromatic ring.
-
Discovery: Benzene was discovered by Michael Faraday in 1825. He isolated it from an oily residue left by illuminating gas.
-
Name Origin: The name "benzene" comes from "gum benzoin," a resin known for its pleasant smell.
-
Natural Occurrence: Benzene is found naturally in crude oil, volcanoes, and forest fires. It's also a component of cigarette smoke.
-
Industrial Production: Most benzene is produced from petroleum sources. It's a byproduct of refining processes like catalytic reforming.
-
Uses: Benzene is used to make plastics, resins, synthetic fibers, rubber lubricants, dyes, detergents, drugs, and pesticides.
-
Solvent: Benzene is an excellent solvent for fats, waxes, resins, and rubber.
-
Toxicity: Benzene is highly toxic. Long-term exposure can cause serious health issues, including leukemia.
-
Regulations: Due to its toxicity, benzene use is heavily regulated. Many countries have strict guidelines to limit exposure.
Benzene in Everyday Life
Benzene might seem like a distant chemical, but it has a surprising presence in everyday products and activities.
-
Gasoline: Benzene is a component of gasoline. It helps improve the octane rating, which enhances engine performance.
-
Plastics: Many plastics, including polystyrene and nylon, are made using benzene.
-
Household Products: Benzene is found in some household products like glues, paints, furniture wax, and detergents.
-
Cigarette Smoke: Smoking cigarettes exposes individuals to benzene. It's one of the many harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke.
-
Soft Drinks: Some soft drinks contain benzene, formed from benzoate salts and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) under certain conditions.
-
Perfumes: Benzene derivatives are used in the fragrance industry to create perfumes and scents.
Health Impacts of Benzene
Understanding the health impacts of benzene is crucial due to its widespread use and presence.
-
Carcinogen: Benzene is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
-
Acute Exposure: Short-term exposure to high levels of benzene can cause dizziness, headaches, tremors, confusion, and unconsciousness.
-
Chronic Exposure: Long-term exposure can lead to bone marrow damage, resulting in blood disorders like anemia and leukemia.
-
Immune System: Benzene can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
-
Reproductive Health: Benzene exposure can affect reproductive health, potentially causing menstrual irregularities and decreased fertility.
-
Skin Contact: Direct skin contact with benzene can cause redness, blisters, and dermatitis.
Environmental Impact of Benzene
Benzene's impact isn't limited to human health; it also affects the environment.
-
Air Pollution: Benzene is a significant air pollutant. It's released from vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, and cigarette smoke.
-
Water Contamination: Benzene can contaminate water sources through industrial discharge and leaking underground storage tanks.
-
Soil Pollution: Spills and leaks can lead to soil contamination, affecting plant and animal life.
-
Biodegradation: Benzene can be broken down by microorganisms in soil and water, but this process is slow and depends on environmental conditions.
-
Regulations: Environmental agencies worldwide have set limits on benzene emissions to protect air and water quality.
Historical and Scientific Significance
Benzene has played a pivotal role in the development of organic chemistry and industrial processes.
-
Kekulé's Dream: The structure of benzene was famously proposed by August Kekulé in 1865. He claimed to have envisioned the ring structure in a dream.
-
Aromatic Compounds: Benzene is the simplest aromatic compound. Its discovery led to the identification of many other aromatic compounds.
-
Nobel Prize: The study of benzene and its derivatives has contributed to several Nobel Prizes in Chemistry.
-
Spectroscopy: Benzene's unique structure makes it an important molecule in spectroscopy studies.
-
Chemical Reactions: Benzene undergoes substitution reactions rather than addition reactions, preserving its aromatic ring.
Fun and Quirky Facts
Benzene has some fun and quirky aspects that make it even more interesting.
-
Sweet Smell: Benzene has a sweet, aromatic smell, which is why it was once used in aftershaves and perfumes.
-
Fireworks: Benzene derivatives are used to create the vibrant colors in fireworks.
-
Historical Uses: In the past, benzene was used as an aftershave and in decaffeinating coffee.
-
Benzene Rings in Nature: Many natural compounds, like caffeine and aspirin, contain benzene rings.
-
Space: Benzene has been detected in the atmosphere of Saturn and in interstellar space.
-
Pop Culture: Benzene has made appearances in literature and movies, often highlighting its dangerous properties.
Benzene: A Chemical Marvel
Benzene's impact on science and industry is undeniable. This simple yet powerful molecule has shaped everything from fuel production to pharmaceuticals. Its unique structure, a ring of six carbon atoms, makes it a cornerstone in organic chemistry. Despite its usefulness, benzene poses health risks. Long-term exposure can lead to serious conditions like leukemia. This dual nature—both beneficial and hazardous—makes understanding benzene crucial.
Regulations now limit benzene exposure to protect public health. Industries have adapted by finding safer alternatives and improving safety protocols. Yet, benzene remains a key player in many chemical processes. Its versatility and effectiveness ensure it won't disappear anytime soon.
So, next time you encounter benzene in your studies or work, remember its complex legacy. It's a chemical marvel that continues to challenge and inspire scientists worldwide.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
