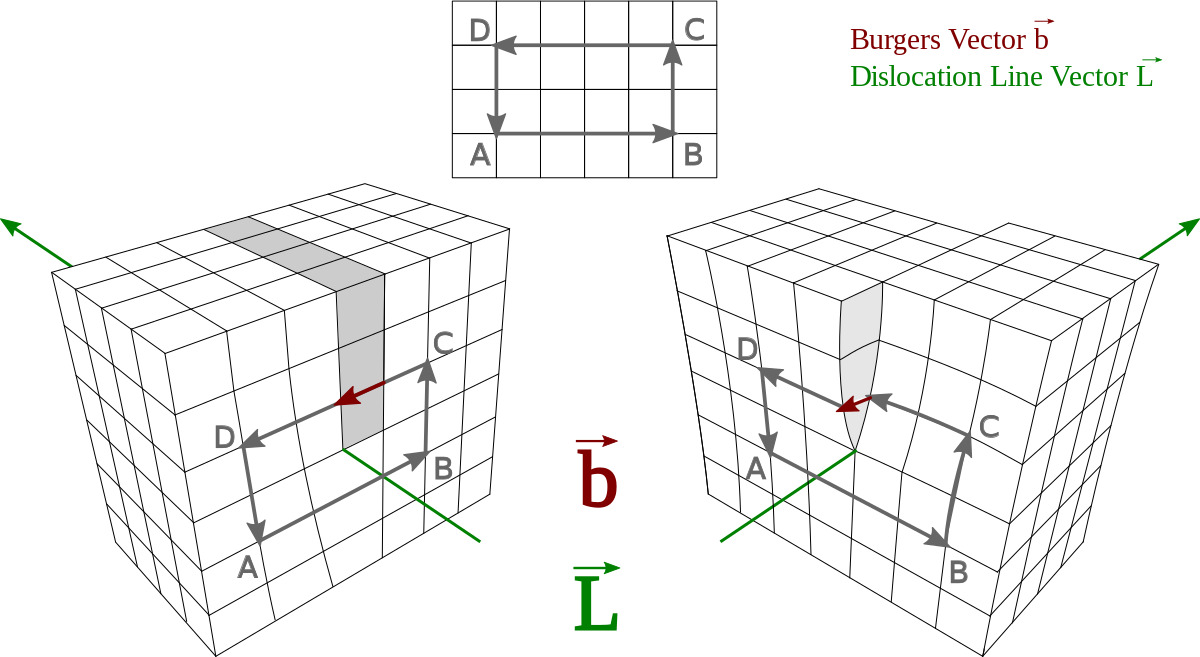
Dislocation is a fascinating phenomenon that occurs in various aspects of life, from the physical world to the world of chemistry. It involves the displacement of one or more components from their normal position or arrangement. This intriguing concept has captured the attention of scientists and researchers for centuries, leading to numerous discoveries and insights.
In this article, we will delve into the enigmatic world of dislocation and uncover 18 intriguing facts that will leave you astounded. From the strange behavior of dislocated atoms to the remarkable properties of dislocation loops, prepare to embark on a journey of discovery and wonder.
Whether you are a chemistry enthusiast, a curious learner, or simply someone intrigued by the mysteries of the universe, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of dislocation and its myriad manifestations. So, let’s dive in and unravel the secrets behind this perplexing phenomenon!
Key Takeaways:
- Dislocations are painful joint injuries caused by trauma or sudden force. Immediate medical attention and preventive measures can help manage and reduce the risk of dislocations.
- Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of dislocations can help prevent long-term complications and promote healthy, stable joints. Prompt medical attention is crucial for effective care.
Dislocation: A Painful Condition
Dislocation is a traumatic injury in which the bones of a joint are forced out of their normal position. It causes severe pain and immobility, requiring immediate medical attention.
Common Dislocated Joints
The most commonly dislocated joints are the shoulder, fingers, knees, and hips. These joints are highly mobile and susceptible to injuries.
Causes of Dislocation
Dislocations can occur due to falls, sports injuries, accidents, or sudden force applied to a joint. Ligament tears and weak joint structures can also increase the risk.
Signs and Symptoms
The common signs of a dislocated joint include swelling, bruising, deformity, intense pain, loss of movement, and a popping or tearing sensation at the time of injury.
Immediate First Aid
When a dislocation occurs, it is important to keep the injured person still and immobilize the joint. Applying ice packs and elevating the affected area can help reduce pain and swelling.
Diagnosis
A doctor will perform a physical examination and may order X-rays or other imaging tests to confirm a dislocation and assess any associated fractures or soft tissue damage.
Reduction Techniques
The process of returning a dislocated joint to its original position is called reduction. It can be done manually by a medical professional using gentle maneuvers or through surgical intervention in complex cases.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
After a joint is relocated, rehabilitation and physical therapy are crucial for restoring strength, mobility, and stability. Exercises and stretches help prevent recurrence and improve overall joint function.
Complications of Dislocation
Dislocation can lead to complications such as nerve or blood vessel damage, joint instability, recurrent dislocations, and early onset of osteoarthritis.
Preventive Measures
Engaging in proper warm-up exercises, using protective gear during sports activities, maintaining strong joint muscles through regular exercise, and avoiding situations that may lead to injury can help prevent dislocations.
Dislocation in Children
Children are more prone to dislocations due to their active lifestyles and growing bones. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent long-term complications.
Different Types of Dislocations
There are several types of dislocations, including anterior and posterior dislocations, complete and incomplete dislocations, and volar and dorsal dislocations, each requiring specific treatments.
Dislocation vs. Subluxation
A subluxation refers to a partial dislocation where the joint surfaces are not completely separated. It may cause similar symptoms but is less severe than a complete dislocation.
Age and Dislocation Risk
As we age, the risk of dislocation increases due to factors such as weakened bones, reduced muscle strength, and degenerative joint conditions like arthritis.
Joint Dislocation and Hypermobility
People with joint hypermobility syndrome have increased flexibility and are more prone to joint dislocations. They require careful management and strengthening exercises.
Dislocation in Sports
Contact sports, such as football, rugby, and basketball, have a higher risk of joint dislocations due to the intensity of physical contact and sudden movements involved.
Recurrent Dislocations
In some cases, individuals may experience recurrent dislocations, where a joint repeatedly slips out of place. Proper treatment and rehabilitation can help reduce the risk of recurrence.
Seeking Professional Help
If you or someone you know experiences a dislocation, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Only qualified healthcare professionals can provide the necessary care and treatment.
Dislocations are painful and often unexpected injuries that require immediate attention. By understanding these enigmatic facts about dislocation, you can better recognize, prevent, and manage this condition. Remember, taking proactive measures can help maintain healthy and stable joints, reducing the risk of dislocations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dislocation is a fascinating aspect of chemistry that showcases the dynamic and complex nature of atoms and molecules. By understanding the process of dislocation, scientists are able to gain deeper insights into the properties and behavior of materials. The 18 enigmatic facts presented in this article highlight the diverse range of phenomena associated with dislocation, from the formation of dislocation loops to the role of dislocations in strengthening materials.By delving into the world of dislocation, we can appreciate the intricacies of crystal structures, defects, and the interplay between dislocations and other atomic features. The study of dislocation has numerous practical applications, including in the development of stronger and more durable materials for various industries.So, the next time you encounter a material undergoing deformation, remember the secrets hidden within its dislocations. From the movement of atoms to the flow of electrons, dislocation is an integral part of the chemistry world, shaping the properties and performance of materials we encounter every day.
FAQs
1. What is a dislocation in chemistry?
A dislocation in chemistry refers to a line defect or irregularity in the arrangement of atoms within a crystal lattice. It is a critical mechanism responsible for the plastic deformation of materials.
2. How are dislocations formed?
Dislocations can be formed through various processes, including crystallization, mechanical deformation, and thermal effects. They can also arise from external factors such as stress, pressure, and temperature changes.
3. What are the effects of dislocations on material properties?
Dislocations can significantly affect the mechanical properties of materials. They can increase material strength, promote ductility, and influence the material’s response to external forces and conditions.
4. Why are dislocations important in materials science?
Dislocations play a crucial role in materials science as they influence the behavior of materials during deformation, processing, and failure. Understanding and controlling dislocations are essential for designing materials with desired properties.
5. How are dislocations studied in the laboratory?
Dislocations are studied using various techniques, including microscopy, diffraction, and computer simulations. These methods allow scientists to visualize and analyze the structure and behavior of dislocations at the atomic scale.
6. Can dislocations be eliminated or repaired?
Dislocations can be partially or fully eliminated through processes such as annealing or through the introduction of impurities. However, complete removal of all dislocations is often impractical or impossible.
7. Are all materials prone to dislocation?
Most crystalline materials are prone to dislocation, although the prevalence and behavior of dislocations can vary depending on factors such as crystal structure, composition, and external conditions.
8. Can dislocations occur in non-crystalline materials?
Dislocations are characteristic of crystalline materials, as they involve defects in the arrangement of atoms within ordered lattices. Non-crystalline materials, such as glasses, do not possess a well-defined crystal structure and hence do not exhibit dislocations.
9. Can dislocations be beneficial?
Yes, dislocations can be beneficial in some cases. They can enhance the strength and ductility of materials, making them more resistant to deformation and fracture.
10. Is dislocation a permanent defect in materials?
Dislocations are not necessarily permanent defects. They can move and rearrange within the crystal lattice, and under certain conditions, they can annihilate or interact with other dislocations, altering the material’s structure and properties.
11. Do dislocations occur only at the macroscopic level?
No, dislocations occur at the atomic level and can extend over significant distances within a crystal, even though they manifest as visible defects at the macroscopic level.
12. Are dislocations related to defects in materials?
Yes, dislocations are considered defects in the crystal structure of materials. However, they play a crucial role in the mechanical behavior and plastic deformation of materials.
13. Can dislocations be observed directly?
Dislocations cannot be observed directly with the naked eye or conventional optical microscopes due to their atomic-scale dimensions. Specialized microscopy techniques, such as transmission electron microscopy, are required to visualize dislocations.
14. How do dislocations impact the electrical properties of materials?
Dislocations can affect the electrical properties of materials by influencing the movement of charge carriers, altering conductivity, and generating localized electrical fields.
15. Can dislocations cause material failure?
Dislocations can contribute to material failure by initiating cracks and promoting the propagation of fractures. Understanding and managing dislocations is crucial for enhancing the durability and reliability of materials.
16. Are dislocations only relevant in metals?
Dislocations are commonly associated with metallic materials due to their crystalline nature and high plasticity. However, dislocations can also occur in other crystalline materials such as ceramics and semiconductors.
17. Are there different types of dislocations?
Yes, there are various types of dislocations, including screw dislocations, edge dislocations, and mixed dislocations. These different types have distinct geometries and movement characteristics.
18. Can dislocations be used to explain crystal defects?
Dislocations are closely related to crystal defects. In fact, dislocations are considered one of the primary types of crystal defects, along with point defects and line defects such as grain boundaries.Each question and answer pair is wrapped in a single
tag, and each question is enclosed within tags.
Dislocation facts provide valuable insights into this painful condition, but there's more to explore. Delve deeper into the world of crystal defects and learn about edge dislocation's astounding characteristics. Screw dislocation's fascinating properties will leave you intrigued and eager for more. For a comprehensive understanding, don't miss the extraordinary facts about line defects, which play a crucial role in material science. Expand your knowledge and satisfy your curiosity by reading these informative articles.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
