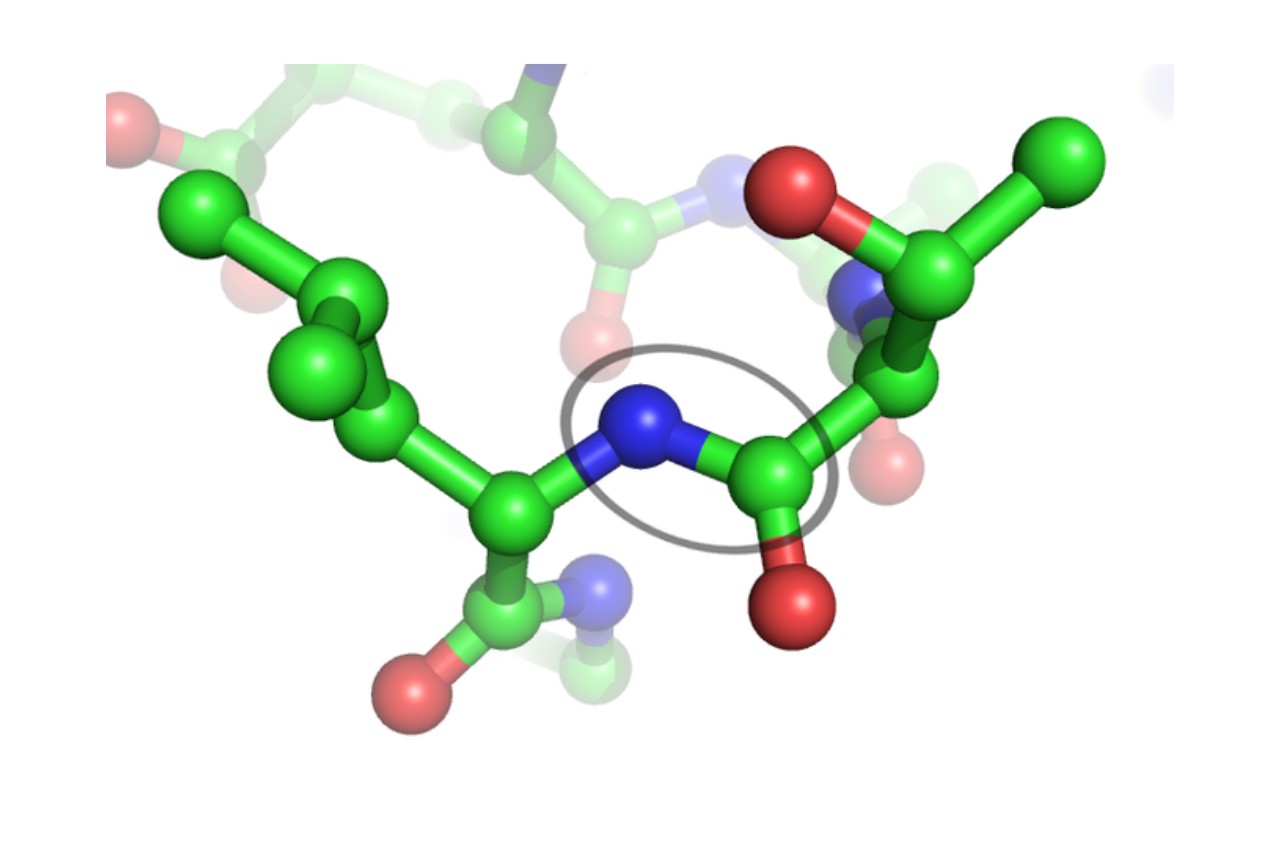
The peptide bond is a fundamental concept in chemistry that plays a vital role in our understanding of proteins and the formation of complex biological molecules. It is a bond that connects amino acids together, forming a protein chain. Peptide bonds are not only essential for the structure and function of proteins but also have significant implications in fields such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and biochemistry.
In this article, we will delve into 18 captivating facts about peptide bonds that will deepen your understanding of their importance and applications. From their chemical composition to their role in protein synthesis, we will explore the fascinating world of peptide bonds and shed light on the significance of these remarkable molecular connections.
Key Takeaways:
- Peptide bonds are like the glue that holds proteins together, making them strong and stable. They also determine the shape and function of proteins, which are essential for life.
- Peptide bonds are involved in protein synthesis, digestion, and even immune response. They are like the secret agents of the body, working behind the scenes to keep everything running smoothly.
The peptide bond is a crucial component of proteins.
The peptide bond is the chemical bond that connects amino acids together to form a protein chain. It is a covalent bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another. This bond is responsible for the structural integrity and stability of proteins.
Peptide bonds are formed through a process called condensation reaction.
In order for a peptide bond to form, a molecule of water is expelled as two amino acids react with each other. This condensation reaction, also known as dehydration synthesis, occurs when the carboxyl group of one amino acid combines with the amino group of another amino acid, resulting in the formation of a peptide bond.
Peptide bonds exhibit resonance characteristics.
Peptide bonds possess partial double bond character due to resonance between different electronic structures. This resonance leads to the rigidity of the peptide bond and restricts rotation around the bond, contributing to the stability and structure of proteins.
The peptide bond is planar.
The peptide bond has a rigid and planar structure, with the carbonyl carbon, the nitrogen, and the neighboring alpha carbon lying in the same plane. This planarity is important for the formation of secondary protein structures like alpha helices and beta sheets.
Peptide bonds are amide bonds.
Peptide bonds are a specific type of amide bond that forms between the carbonyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another. This amide bond is highly stable and resistant to hydrolysis under normal physiological conditions.
Peptide bonds contribute to the diversity of proteins.
The sequence and arrangement of amino acids connected by peptide bonds determine the unique structure and function of proteins. The variety of possible amino acid combinations and the length of the protein chain give rise to the incredible diversity of proteins found in living organisms.
Peptide bonds are essential for protein synthesis.
During protein synthesis, a ribosome facilitates the formation of peptide bonds between successive amino acids. This process, known as translation, is vital for the production of functional proteins in cells.
The strength of peptide bonds makes protein digestion challenging.
Peptide bonds are resistant to hydrolysis, making the breakdown of proteins into individual amino acids during digestion a complex process. Special enzymes called proteases are responsible for breaking these peptide bonds and releasing the amino acids for absorption by the body.
The rigidity of peptide bonds influences protein folding.
The planarity and rigidity of peptide bonds play a crucial role in determining the three-dimensional structure of proteins. Protein folding relies on the specific arrangement and interactions of amino acids connected by peptide bonds, which ultimately determine the protein’s shape and function.
Peptide bond formation is facilitated by ribosomes.
During protein synthesis, ribosomes provide the platform for the assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide chain. The ribosome catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids based on the instructions encoded in the mRNA molecule.
The length of a peptide chain is determined by the number of peptide bonds.
The number of peptide bonds in a protein chain determines its length. Proteins can range in size from small peptides consisting of a few amino acids to large proteins composed of hundreds or even thousands of amino acids connected by multiple peptide bonds.
Peptide bonds contribute to protein stability.
The presence of peptide bonds within a protein chain contributes to its overall stability. The rigidity and strength of peptide bonds help proteins maintain their specific shape and structure, allowing them to carry out their biological functions effectively.
Diverse properties of amino acids influence peptide bond strength.
Different amino acids possess distinct chemical properties that impact the strength of peptide bonds they form. Amino acids with bulky side chains or charged groups can influence the stability of the peptide bond, affecting the overall structure and function of the protein.
Peptide bonds can be chemically modified.
Chemical modifications, such as phosphorylation or glycosylation, can occur at specific amino acids within a protein chain. These modifications can affect the stability and function of the peptide bond, leading to alterations in protein structure and activity.
Peptide bonds play a role in immune response.
The peptide bonds within antigens, foreign substances that trigger immune responses, are recognized by immune cells. These bonds help in distinguishing self from non-self and play a crucial role in the body’s immune defense mechanisms.
The formation of peptide bonds requires energy.
The process of forming peptide bonds during protein synthesis requires the input of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This energy drives the condensation reaction that results in the formation of the peptide bond.
Peptide bonds contribute to the communication and signaling within cells.
Signaling peptides, such as hormones or neurotransmitters, contain specific peptide bonds that enable them to interact with receptors and transmit signals within the body. These peptide bonds are critical for cellular communication and the regulation of physiological processes.
Peptide bonds can be targeted by drugs and inhibitors.
Given the importance of peptide bonds in protein structure and function, they can be targeted by drugs and inhibitors in medical research and drug development. These compounds selectively bind to and disrupt peptide bonds, leading to suppression or modification of specific protein activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, peptides bonds are essential components of proteins and play a crucial role in various biological processes. Understanding the structure and properties of peptide bonds is vital for advancing our knowledge of biochemistry and drug development. We have explored 18 captivating facts about peptide bonds, shedding light on their significance and applications.Peptide bonds are formed through a condensation reaction between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. This process results in the formation of a peptide bond and the release of a water molecule.Peptide bonds are incredibly strong and resistant to hydrolysis due to the delocalization of electrons within the bond. This stability is crucial for maintaining protein structure and function.Peptide bonds are responsible for the primary structure of proteins, determining the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. This sequence ultimately governs a protein’s structure and function.Peptide bonds can undergo enzymatic cleavage, leading to the breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides or individual amino acids. This process is essential for protein metabolism and nutrient absorption.Research on peptide bonds has led to significant advancements in drug development, particularly in the field of peptide therapeutics. Peptides can be synthesized to mimic natural hormones, enzymes, or antimicrobial agents, offering great potential for targeted therapies.In summary, peptide bonds are not just the building blocks of proteins but also fascinating molecules with unique properties and applications. By delving deeper into the world of peptide bonds, we can unlock new insights and innovation in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals.
FAQs
Q: What is a peptide bond?
A: A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. It is a crucial component in the formation of proteins.
Q: How are peptide bonds formed?
A: Peptide bonds are formed through a condensation reaction between two amino acids. This reaction results in the release of water and the formation of a peptide bond between the two amino acids.
Q: What is the importance of peptide bonds in proteins?
A: Peptide bonds are responsible for the primary structure of proteins. They determine the sequence of amino acids in a protein, which in turn governs its overall structure and function.
Q: Are peptide bonds strong?
A: Yes, peptide bonds are incredibly strong and resistant to hydrolysis due to the delocalization of electrons within the bond. This stability is crucial for maintaining the integrity of proteins.
Q: Can peptide bonds be broken?
A: Yes, peptide bonds can be broken through enzymatic cleavage. This process is essential for protein metabolism and the breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides and individual amino acids.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
