Ion channels are fascinating biological structures that play a crucial role in various physiological processes. These tiny pores, found in the cell membrane of living organisms, are responsible for the passage of ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride in and out of cells. While they may seem small and unassuming, ion channels have unbelievable properties and functions that continue to astound scientists and researchers. From their diverse mechanisms of action to their involvement in the development of diseases, ion channels hold a wealth of secrets waiting to be unraveled. In this article, we will explore 14 unbelievable facts about ion channels that highlight their importance and uniqueness in the world of biology.
Key Takeaways:
- Ion channels are like gatekeepers in our bodies, controlling the flow of ions and playing a big role in nerve signals, muscle movement, and even our sense of taste and smell!
- Understanding ion channels can help scientists develop new medicines and treatments for diseases by targeting specific channels and regulating their activity.
Ion channels are protein molecules embedded in cell membranes.
Ion channels play a crucial role in facilitating the movement of ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride across cell membranes. They are highly selective and regulate various physiological processes in the body.
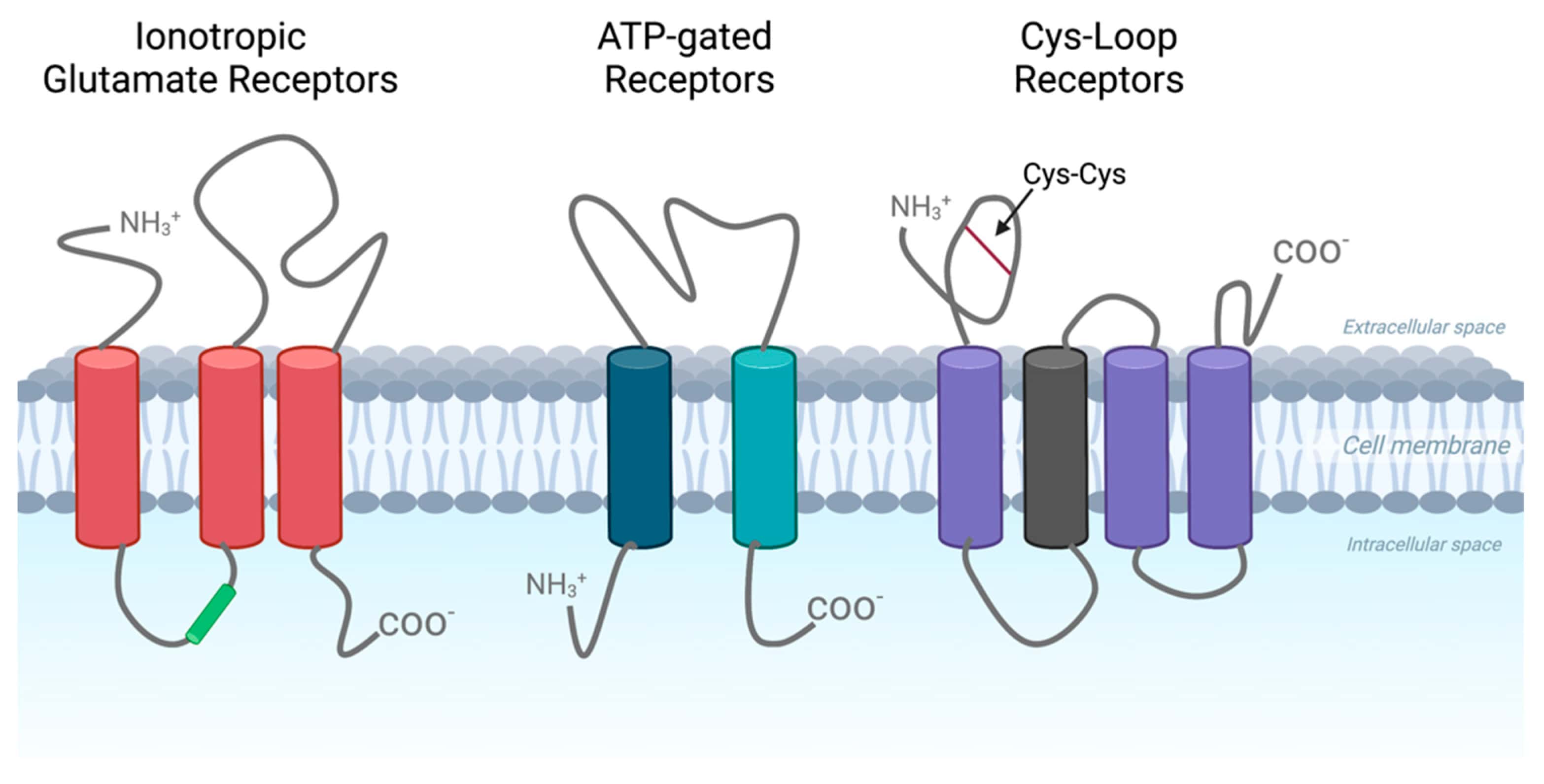
There are different types of ion channels.
Ion channels can be categorized into voltage-gated channels, ligand-gated channels, mechanically gated channels, and leak channels. Each type of ion channel opens or closes in response to different stimuli, allowing specific ions to flow in or out of cells.
Ion channels are essential for nerve impulse transmission.
Through the opening and closing of ion channels, nerve cells are able to generate and transmit electrical signals, known as action potentials. This enables communication between different parts of the nervous system and is crucial for motor functions, sensory perception, and cognitive processes.
Ion channels are involved in muscle contraction and relaxation.
Calcium ion channels play a vital role in muscle contraction, allowing calcium ions to enter muscle cells and initiate the contractile process. Potassium channels, on the other hand, help regulate the repolarization phase, ensuring proper relaxation of muscles.
Ion channels contribute to the regular heartbeat.
In the heart, ion channels help regulate the flow of ions necessary for cardiac muscle contraction and electrical conduction. Disruptions in ion channel function can lead to cardiac arrhythmias and other heart-related disorders.
Ion channels are involved in maintaining pH balance.
Proton-gated ion channels are responsible for the exchange of hydrogen ions, maintaining the pH balance of various body fluids. These channels are particularly important in the gastrointestinal tract and the kidney.
Ion channels have been linked to various diseases.
Defects or mutations in ion channels have been associated with numerous diseases, including cystic fibrosis, epilepsy, cardiac arrhythmias, and channelopathies. Understanding the role of ion channels in these conditions is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
Ion channels can be modulated by pharmaceutical drugs.
Pharmaceutical drugs can target specific ion channels, either by blocking or enhancing their function, to treat various medical conditions. For example, calcium channel blockers are used to manage hypertension, angina, and certain heart rhythm disorders.
Ion channels are responsible for the sense of taste and smell.
Ion channels located on taste buds and olfactory receptors enable us to perceive and distinguish different tastes and smells. They play a vital role in our enjoyment of food and the detection of potential dangers through odor perception.
Ion channels are present in plants as well.
Just like in animals, ion channels in plants regulate various processes such as nutrient uptake, signal transduction, and response to environmental stimuli. They are crucial for plant growth, development, and adaptation to changing conditions.
Some ion channels are sensitive to temperature.
Temperature-sensitive ion channels, known as thermoreceptors, allow us to perceive and respond to changes in temperature. They play a role in sensations like heat, cold, and pain.
Ion channels have potential applications in drug discovery.
Understanding the structure and function of ion channels has significant implications for drug discovery. By targeting specific ion channels, researchers can develop new drugs to treat various diseases and disorders.
Ion channels are involved in cell signaling.
Ion channels play a crucial role in transmitting signals between cells. They allow the passage of ions, which triggers a cascade of molecular events, leading to cellular responses such as secretion, contraction, and gene expression.
Ion channels are highly regulated.
Ion channels are subject to tight regulation to maintain proper ion balance and cellular function. Their activity can be modulated by various factors, including pH, temperature, hormones, neurotransmitters, and second messengers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ion channels are truly fascinating and essential components of biological systems. The 14 unbelievable facts about ion channels highlighted in this article demonstrate their critical role in cellular function.From their diverse structural variations to their involvement in various physiological processes, ion channels are key players in maintaining homeostasis and enabling cellular communication. The ability of ion channels to selectively allow the passage of specific ions is crucial for nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and many other biological functions.Furthermore, the regulation of ion channels by factors such as voltage, ligands, and post-translational modifications underscores their dynamic nature and adaptability to different cellular conditions.Understanding the intricacies of ion channels is vital not only for advancing our knowledge of fundamental biology but also for developing potential therapeutic interventions for numerous diseases that arise from ion channel dysfunctions.In summary, ion channels continue to captivate researchers and scientists alike, and their study will undoubtedly contribute to future discoveries and advancements in the field of biology and medicine.
FAQs
1. What are ion channels?
Ion channels are proteins present in cell membranes that allow the passage of specific ions in and out of cells, thus regulating various cellular processes.
2. What is the significance of ion channels?
Ion channels play a crucial role in maintaining cell homeostasis, transmitting nerve impulses, regulating muscle contraction, and facilitating numerous other physiological processes.
3. How do ion channels work?
Ion channels possess a selective pore that opens and closes in response to various signals, such as voltage changes, ligand binding, or mechanical stimulation, allowing the passage of specific ions.
4. How many types of ion channels are there?
There are several types of ion channels, including voltage-gated channels, ligand-gated channels, mechanically gated channels, and leak channels, each with specific properties and functions.
5. How are ion channels regulated?
Ion channels can be regulated through various mechanisms, including changes in voltage, binding of specific molecules (ligands), and post-translational modifications.
6. Can malfunctioning ion channels lead to diseases?
Yes, mutations or dysfunctions in ion channels can lead to various disorders, known as channelopathies, including cardiac arrhythmias, cystic fibrosis, epilepsy, and many others.
7. Are there drugs that target ion channels?
Yes, many drugs have been developed to modulate the activity of specific ion channels, either by enhancing or inhibiting their function, for therapeutic purposes.
8. Are ion channels only found in humans?
No, ion channels are present in virtually all living organisms, from bacteria to plants and animals, highlighting their evolutionary significance.
9. Can ion channels be studied in the lab?
Yes, scientists use various techniques, such as patch-clamp electrophysiology and fluorescence imaging, to study the properties and functions of ion channels in the laboratory setting.
10. Are there any ongoing research areas related to ion channels?
Yes, ongoing research focuses on understanding the role of ion channels in diseases, developing new drugs targeting ion channels, and uncovering their involvement in complex physiological processes.
Intrigued by the incredible world of ion channels? Keep exploring! Delve into the specifics of ligand-gated ion channels, which play crucial roles in neurotransmission and pharmacology. Ion channels hold countless secrets waiting to be uncovered, so continue your journey through the fascinating realm of cellular communication.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
