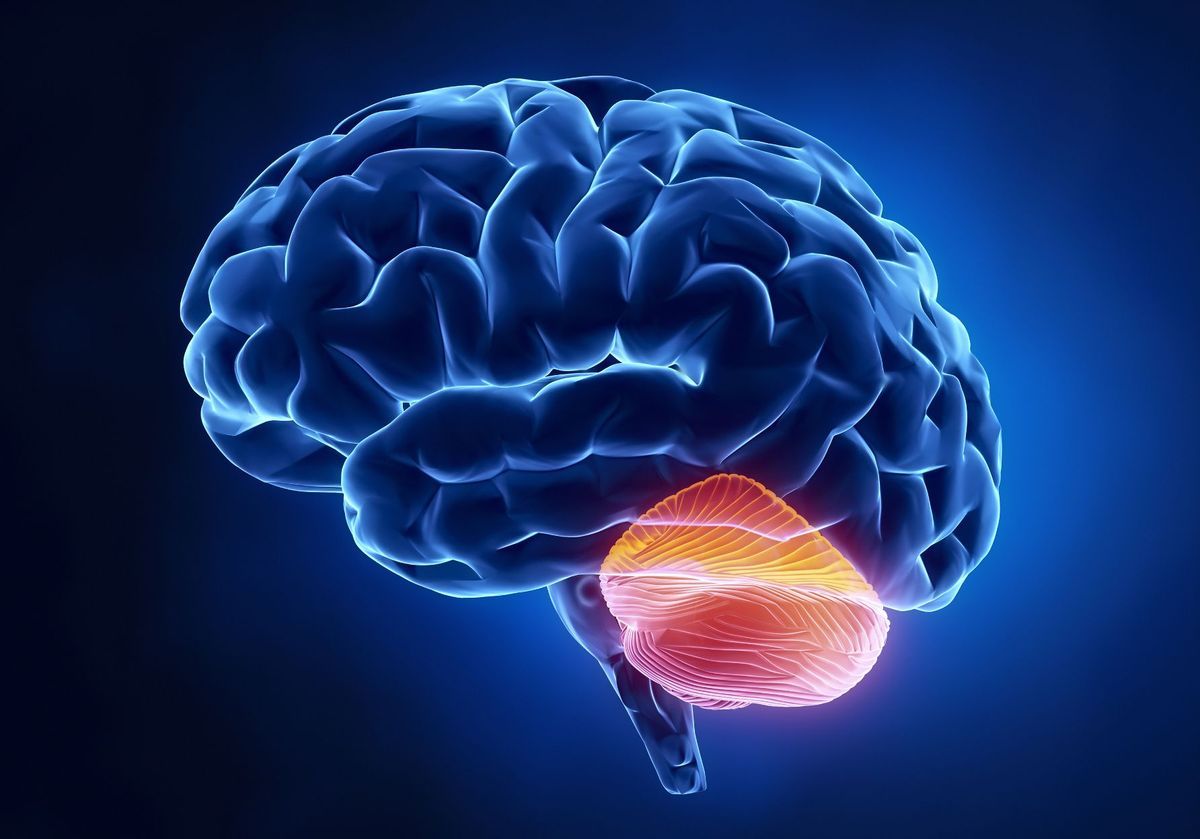
The cerebellum, often referred to as the “little brain,” may be small in size compared to the rest of the brain, but its importance cannot be overstated. This remarkable structure, located at the back of the brain, is responsible for a variety of crucial functions that allow us to move, balance, and coordinate our actions. While the cerebellum may not be as well-known as its counterparts like the cerebral cortex, it plays a vital role in our everyday lives.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the cerebellum and explore 18 captivating facts about this incredible organ. From its intricate structure to its indispensable role in motor control and beyond, we will uncover the wonders of the cerebellum and gain a deeper understanding of its significance. So, let’s dive in and discover the amazing secrets of the cerebellum!
Key Takeaways:
- The cerebellum, or “little brain,” is a powerhouse of the nervous system, coordinating movements and even contributing to cognitive functions. Its 18 captivating facts reveal its profound impact on our daily lives.
- With more neurons than the rest of the brain combined, the cerebellum’s timing and precision in motor control are unmatched. Its role in motor learning and memory makes it a fascinating and vital brain structure.
The Cerebellum: A Marvel of Structure and Function
The cerebellum, often referred to as the “little brain,” is a remarkable structure nestled at the back of the brain, beneath the cerebral cortex. Its role in coordinating voluntary movements, maintaining balance, and fine-tuning motor skills cannot be overstated. This powerhouse of the nervous system contains approximately half of the brain’s neurons, despite being only 10% of its total volume!
Smooth Operators: The Purkinje Cells
One of the most distinctive features of the cerebellum is its large and exceptionally arranged cells called Purkinje cells. Named after the Czech anatomist Jan Evangelista Purkyn?, these neurons play a crucial role in integrating sensory information and coordinating muscle movements.
The Cerebellum Has More Neurons than the Rest of the Brain Combined
Surprisingly, the cerebellum contains approximately 69 billion neurons, which is more than the combined total of neurons in all other parts of the brain. This abundance of neurons reflects the cerebellum’s importance in fine motor control and motor learning.
A Smooth Operator: The Vermis
The vermiform appendix-like structure that runs along the midline of the cerebellum is aptly named the “vermis,” which means “worm” in Latin. The vermis plays a significant role in balance and coordination, and its damage can lead to severe motor deficits.
The Cerebellum is Responsible for Cognitive Functions Too!
While the cerebellum is primarily associated with motor control, it also contributes to various cognitive functions. Recent research has uncovered its involvement in language processing, attention, working memory, and even emotional regulation.
A Symphony of Connections: The Cerebellum’s Communication Network
The cerebellum communicates with other parts of the brain through an extensive network of connections known as the cerebellothalamocortical pathway. This intricate system allows for the integration of sensory information and precise motor coordination.
A Gateway to Movement: The Cerebellar Peduncles
Three pairs of fiber bundles, known as cerebellar peduncles, act as the main highways connecting the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. These peduncles facilitate the transmission of information to and from the cerebellum, ensuring smooth motor performance.
Timing is Everything: The Precision of the Cerebellum
The cerebellum is known for its exceptional timing capabilities. It fine-tunes movements by precisely coordinating the timing and duration of muscle contractions, resulting in smooth and accurate motor control.
Alcohol and the Cerebellum: A Rocky Relationship
Excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on the cerebellum. Alcohol impairs the functioning of Purkinje cells, leading to difficulties with coordination, balance, and motor skills associated with intoxication.
Cerebellar Disorders: Affecting the Symphony of Movement
Disorders that affect the cerebellum, such as cerebellar ataxia and cerebellar hypoplasia, can result in significant motor impairments. These conditions may cause difficulties in balance, coordination, and voluntary muscle control.
Precision Medicine: Advancements in Cerebellar Research
The study of the cerebellum has gained considerable momentum in recent years. Advances in neuroimaging techniques have allowed researchers to deepen their understanding of the cerebellum’s role in various neurological conditions, paving the way for targeted therapies and interventions.
Cerebellar Circuits: Orchestrating Movement
The intricate neuronal circuits within the cerebellum work together to ensure the seamless execution of movements. These circuits receive input from sensory systems, integrate it with motor information, and send output to motor centers, fine-tuning movement coordination.
A Lifelong Learner: The Cerebellum’s Role in Motor Memory
The cerebellum plays a crucial role in motor learning and memory consolidation. Through a process called long-term depression, it refines motor skills, allowing for faster and more accurate movements with repetition and practice.
The Cerebellum in Evolution: A Symbol of Progress
The cerebellum has evolved along with vertebrates, becoming increasingly complex and specialized. Its expansion has paralleled the development of motor skills, suggesting its vital role in shaping movement and behavior.
Cerebellar Development: Fine-Tuning Motor Skills
The development of the cerebellum undergoes a complex and precisely orchestrated process. Genetic and environmental factors interact to shape its structure and function, ensuring the refinement of motor skills as we grow and learn.
Don’t Forget the Lobes: The Organization of the Cerebellum
The cerebellum is organized into three main lobes: the anterior lobe, the posterior lobe, and the flocculonodular lobe. Each lobe has unique functional contributions and connects with specific regions of the brain.
The Cerebellum: An Architect of Timing and Rhythm
The cerebellum’s involvement in timing extends beyond motor control. It also plays a crucial role in temporal processing, aiding in our ability to perceive and reproduce rhythmic patterns and sequences, such as in music and language.
Unlocking the Mysteries: Future Frontiers of Cerebellar Research
As our understanding of the cerebellum continues to evolve, exciting avenues of research emerge. Scientists are exploring the connections between the cerebellum and cognitive disorders, neurodevelopmental conditions, and the potential for therapies targeting this fascinating brain structure.
The 18 captivating facts about the cerebellum showcase its profound influence on our movements, coordination, and cognitive functions. This “little brain” has a big impact on our everyday lives and continues to captivate researchers and medical professionals alike.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cerebellum is an incredibly fascinating and important part of the human anatomy. It plays a crucial role in coordinating movement, maintaining posture and balance, and even influencing cognitive functions. With its intricate structure and functionalities, the cerebellum continues to intrigue scientists and researchers worldwide.Understanding the complexities of the cerebellum can help us gain insights into various neurological disorders and pave the way for innovative treatments and therapies. From its role in motor skills to its involvement in cognition and emotions, the cerebellum proves to be an essential component of our overall brain function.As we continue to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cerebellum, we unravel more captivating facts and pave the way for further understanding of this remarkable organ.
FAQs
1. What is the primary function of the cerebellum?
The primary function of the cerebellum is to coordinate voluntary movements, maintain balance, and control posture.
2. Can damage to the cerebellum cause problems with balance and coordination?
Yes, damage to the cerebellum can lead to significant problems with balance and coordination, resulting in issues with motor control and coordination.
3. Is the cerebellum responsible for cognitive functions?
While the cerebellum is primarily associated with motor functions, recent research indicates that it also plays a role in certain cognitive functions, such as attention, language, and emotional regulation.
4. Are there any specific exercises or activities that can help improve cerebellum function?
Engaging in activities that require balance, coordination, and precision movements, such as dancing, yoga, or playing a musical instrument, can help improve cerebellum function.
5. Can the cerebellum regenerate if it is damaged?
Although the cerebellum has limited regenerative capabilities compared to other parts of the brain, it does have some ability to repair and reorganize neural connections to a certain extent.
6. Can alcohol consumption affect the cerebellum?
Yes, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to damage to the cerebellum, resulting in poor balance, coordination, and difficulties with motor skills.
Cerebellum's captivating facts leave you yearning for more brain-teasing knowledge. Unbelievable truths about this neurological marvel await your discovery. Satisfy your cerebral curiosity by exploring additional articles packed with astonishing revelations. Prepare to have your mind blown as you unravel the cerebellum's best-kept secrets!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
