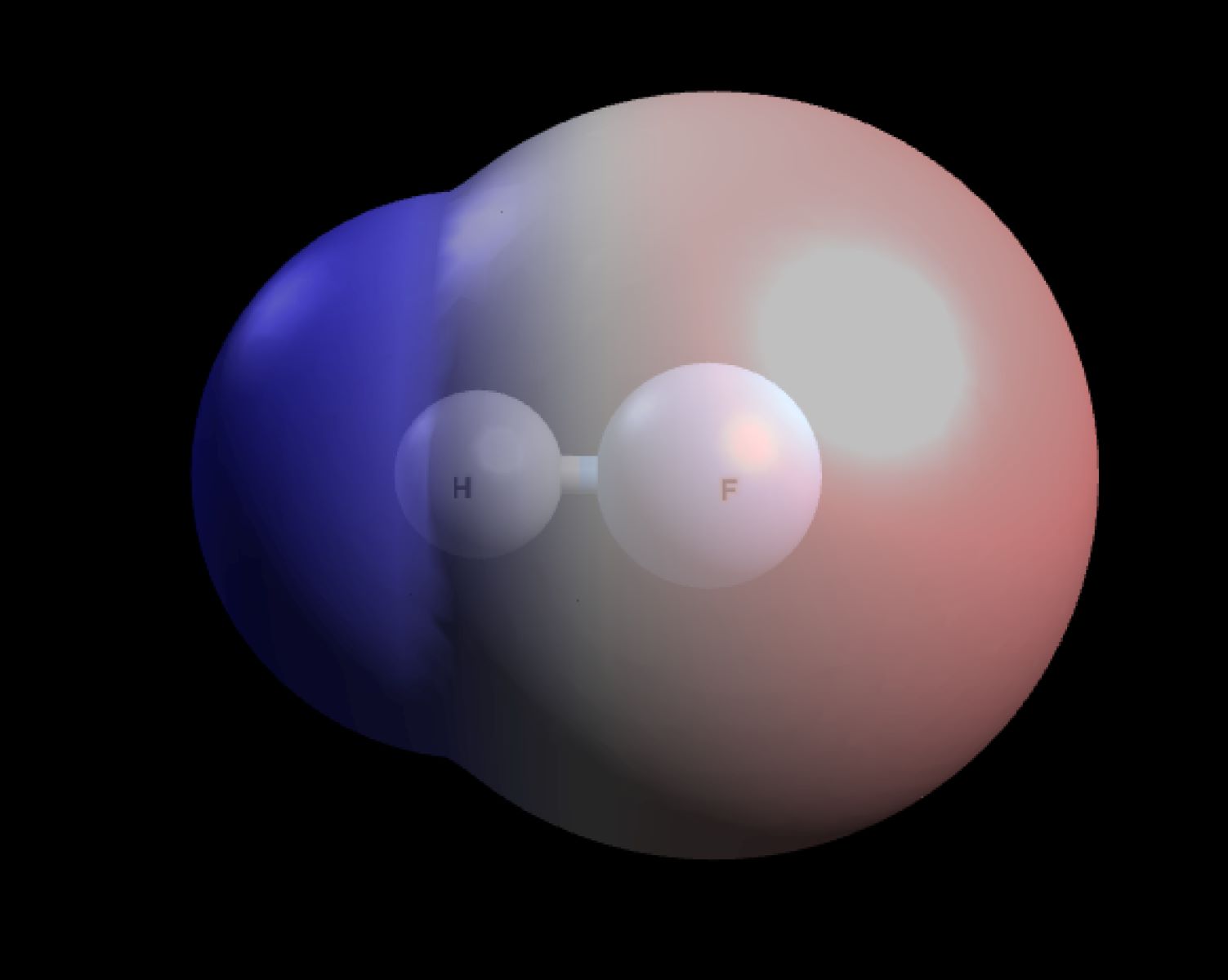
Polarizability is a property of molecules that describes how easily their electron cloud can be distorted by an external electric field. This distortion creates a temporary dipole moment, which can affect how molecules interact with each other. Why is polarizability important? It plays a crucial role in determining the physical properties of substances, such as boiling points, melting points, and solubility. Understanding polarizability helps in fields like chemistry, physics, and material science. For instance, it can explain why certain substances mix well while others don't. How does polarizability work? It depends on factors like the size of the molecule and the number of electrons. Larger molecules with more electrons are generally more polarizable. This introduction will delve into 18 fascinating facts about polarizability, shedding light on its significance and applications.
What is Polarizability?
Polarizability measures how easily an electron cloud in a molecule or atom can be distorted by an external electric field. This property plays a crucial role in many physical and chemical processes.
- Polarizability is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, influencing how molecules interact with each other.
- Electron clouds around atoms or molecules can be distorted, leading to temporary dipoles.
- External electric fields can induce these distortions, affecting molecular behavior.
Factors Affecting Polarizability
Several factors influence how easily an electron cloud can be distorted. Understanding these can help predict molecular interactions.
- Size of the atom or molecule: Larger atoms or molecules have more easily distorted electron clouds.
- Number of electrons: More electrons mean a higher chance of distortion.
- Shape of the molecule: Linear molecules are generally more polarizable than spherical ones.
Polarizability in Chemical Reactions
Polarizability affects how molecules interact during chemical reactions. It can influence reaction rates and product formation.
- Reaction rates: Higher polarizability can lead to faster reaction rates due to increased molecular interactions.
- Product formation: Polarizable molecules can stabilize transition states, affecting the products formed.
- Catalysis: Catalysts often work by enhancing polarizability, making reactions more efficient.
Polarizability and Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals forces, are significantly influenced by polarizability. These forces play a key role in determining the physical properties of substances.
- Van der Waals forces: These weak forces depend on polarizability for their strength.
- Boiling and melting points: Substances with higher polarizability generally have higher boiling and melting points.
- Solubility: Polarizable molecules are often more soluble in polar solvents.
Polarizability in Materials Science
In materials science, polarizability is crucial for designing materials with specific electrical and optical properties.
- Dielectric materials: High polarizability leads to better dielectric properties, useful in capacitors and insulators.
- Optical properties: Materials with high polarizability can have unique optical properties, such as high refractive indices.
- Semiconductors: Polarizability affects the behavior of semiconductors, crucial for electronic devices.
Measuring Polarizability
Scientists use various techniques to measure polarizability, providing insights into molecular and material properties.
- Spectroscopy: Techniques like Raman and infrared spectroscopy can measure polarizability.
- Computational methods: Quantum mechanical calculations help predict polarizability.
- Experimental setups: Specialized equipment can apply electric fields to measure how electron clouds distort.
Understanding polarizability helps in fields ranging from chemistry to materials science, influencing everything from reaction mechanisms to the design of new materials.
Final Thoughts on Polarizability
Understanding polarizability helps us grasp how molecules interact with electric fields. It plays a crucial role in chemical reactions, material properties, and biological processes. Knowing these 18 facts gives you a solid foundation in this fascinating topic. From how polarizability affects molecular behavior to its impact on everyday materials, this knowledge is both practical and intriguing.
Remember, polarizability isn't just a dry scientific term. It’s a key player in the world around us. Whether you're a student, a science enthusiast, or just curious, these insights can deepen your appreciation for the complexity and beauty of chemistry. Keep exploring, stay curious, and let your newfound understanding of polarizability enhance your view of the natural world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


