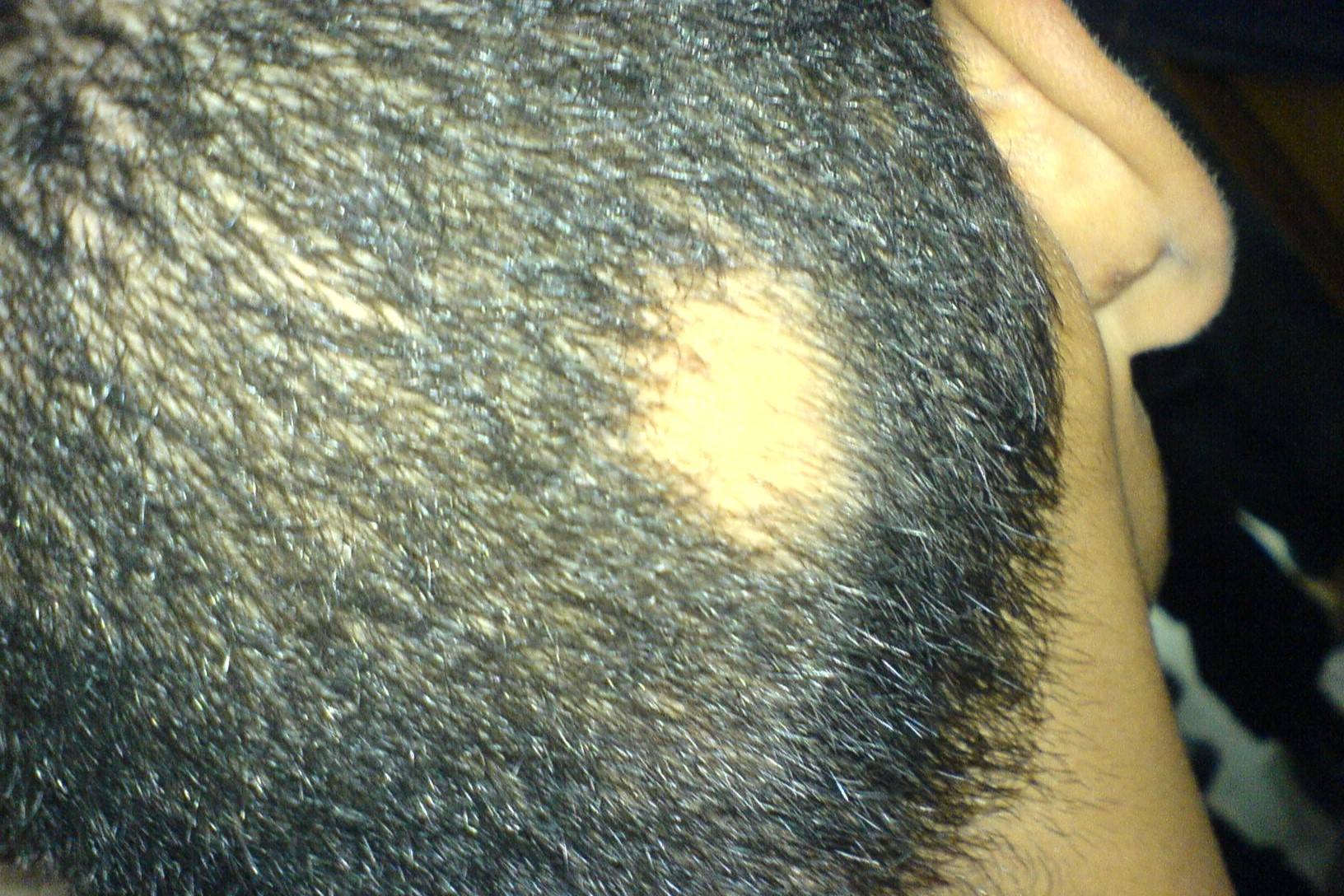
What is Johnson–McMillin Syndrome? Johnson–McMillin Syndrome, also known as Johnson neuroectodermal syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder. It affects fewer than 30 people worldwide. This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning one copy of the mutated gene can cause the syndrome. Symptoms usually appear in childhood and include alopecia (hair loss), anosmia or hyposmia (loss of smell), conductive hearing loss, microtia (small or malformed ears), and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (affecting the reproductive system). Additional features may include congenital heart defects, facial asymmetry, intellectual deficits, cleft palate, and dental issues. Diagnosis relies on clinical presentation and family history.
What is Johnson–McMillin Syndrome?
Johnson–McMillin syndrome, also known as Johnson neuroectodermal syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder. It affects various parts of the body, especially those derived from the neuroectoderm. This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning a single copy of the mutated gene can cause the syndrome. Here are 20 key facts about this rare condition.
Prevalence and Inheritance
Understanding how common this syndrome is and how it is passed down can help families and doctors manage expectations.
- Prevalence: Fewer than 30 cases of Johnson–McMillin syndrome have been described in medical literature, making it extremely rare.
- Inheritance Pattern: The syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. A single copy of the mutated gene is enough to cause the condition.
Symptoms and Features
The symptoms of Johnson–McMillin syndrome can vary but generally affect the hair, smell, hearing, ears, and reproductive system.
- Age of Onset: Symptoms typically become apparent during childhood.
- Alopecia: Hair loss, either complete or patchy, is a significant feature.
- Anosmia or Hyposmia: Loss or reduction of the sense of smell can significantly impact quality of life.
- Conductive Hearing Loss: This type of hearing loss occurs due to problems in the middle ear.
- Microtia: Small or malformed ears are common in individuals with this syndrome.
- Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: A condition affecting the reproductive system, leading to reduced production of sex hormones.
Additional Features and Complications
Beyond the primary symptoms, there are other variable features that can affect individuals with Johnson–McMillin syndrome.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Some individuals may have heart defects present from birth.
- Facial Asymmetry: Uneven facial features can be part of the syndrome.
- Intellectual Deficit: Some individuals may experience cognitive challenges.
- Cleft Palate: A split or opening in the roof of the mouth can occur.
- Choanal Stenosis: Narrowing of the nasal passages can cause breathing difficulties.
- Dental Caries: An increased tendency for cavities is often observed.
Genetic and Embryological Basis
Understanding the genetic and embryological aspects can provide insights into the syndrome's origins.
- Embryological Defect: The combination of developmental anomalies suggests a defect in the formation of neuroectodermal derivatives of the cephalic neural crest.
- Genetic Basis: While the exact genetic mutation is unknown, it likely involves genes affecting neural crest cell development.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing and managing Johnson–McMillin syndrome requires a multidisciplinary approach.
- Diagnostic Criteria: Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation and family history. Genetic testing may confirm the diagnosis but isn't always necessary.
- Treatment and Management: No specific treatment exists. Management focuses on addressing symptoms through a team of specialists like otolaryngologists, dermatologists, and endocrinologists.
Support and Research
Support resources and ongoing research are crucial for individuals and families affected by this syndrome.
- Patient-Centered Resources: Support groups and educational materials can help families understand and manage the condition.
- Research Activities: Limited research is ongoing to understand the genetic and embryological mechanisms, aiming to improve diagnostic tools and management strategies.
Understanding Johnson–McMillin Syndrome
Johnson–McMillin syndrome is a rare genetic disorder with a mix of developmental anomalies. Affecting fewer than 30 known individuals, this condition presents with symptoms like alopecia, anosmia, conductive hearing loss, microtia, and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. It's inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning one copy of the mutated gene can cause the syndrome. Diagnosis relies on clinical presentation and family history, with genetic testing sometimes confirming it. No specific treatment exists, so management focuses on symptom relief through a multidisciplinary approach. Research is limited but ongoing, aiming to uncover the genetic mechanisms behind the syndrome. Genetic counseling is crucial for affected families to understand the risks and make informed decisions. While challenging, a comprehensive management plan can significantly improve the quality of life for those with Johnson–McMillin syndrome.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


