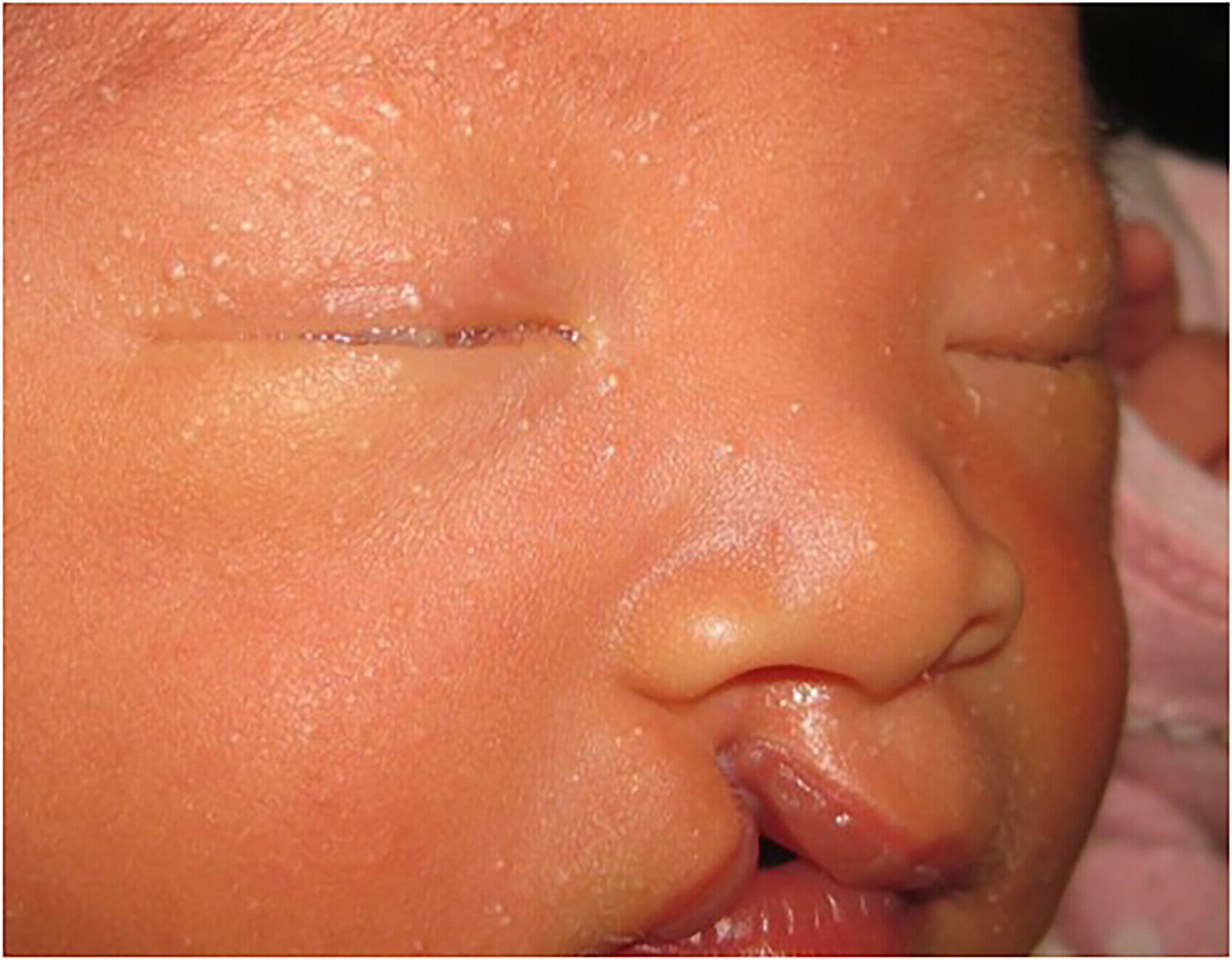
Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia is a rare blood disorder that affects the body's ability to produce platelets. Platelets are crucial for blood clotting, and without enough of them, individuals can experience excessive bleeding and bruising. This condition often stems from a problem in the bone marrow, where megakaryocytes (the cells responsible for producing platelets) are either absent or not functioning properly. Symptoms may include frequent nosebleeds, prolonged bleeding from cuts, and unexplained bruises. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests and bone marrow biopsies. Treatment options vary but may include medications, blood transfusions, or even bone marrow transplants. Understanding this condition is vital for managing its impact on daily life.
What is Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia?
Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia (AMT) is a rare blood disorder. It affects the body's ability to produce platelets, which are crucial for blood clotting. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
AMT is a congenital disorder. This means it is present at birth and often detected early in life.
-
The disorder is characterized by a lack of megakaryocytes. Megakaryocytes are large bone marrow cells responsible for producing platelets.
-
Platelet counts in AMT patients are extremely low. Normal platelet counts range from 150,000 to 450,000 per microliter of blood, but AMT patients have significantly fewer.
-
AMT can lead to severe bleeding. Due to the low platelet count, individuals with AMT are at a higher risk of bruising and bleeding.
Causes and Genetics of AMT
Understanding the causes and genetic factors behind AMT can help in managing and treating the condition.
-
AMT is often linked to genetic mutations. Mutations in the MPL gene are a common cause.
-
The MPL gene provides instructions for making a protein called thrombopoietin receptor. This protein plays a key role in the production of platelets.
-
AMT can be inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. This means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations.
-
Some cases of AMT are sporadic. These cases occur in individuals with no family history of the disorder.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of AMT
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for early intervention.
-
Common symptoms include easy bruising and frequent nosebleeds. These symptoms result from the low platelet count.
-
Petechiae are a common sign. These are small red or purple spots on the skin caused by bleeding underneath.
-
Severe cases may involve internal bleeding. This can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
-
Bone marrow biopsy is a key diagnostic tool. This test helps to identify the absence of megakaryocytes.
Treatment and Management of AMT
Managing AMT involves a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments.
-
Platelet transfusions are a common treatment. They help to temporarily increase platelet counts.
-
Bone marrow transplant can be a curative option. This procedure replaces the defective bone marrow with healthy marrow from a donor.
-
Medications like thrombopoietin receptor agonists may be used. These drugs stimulate platelet production.
-
Regular monitoring is essential. Frequent blood tests help to track platelet levels and adjust treatments as needed.
Living with Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia
Living with AMT requires careful management and support.
-
Patients should avoid activities that increase bleeding risk. Contact sports and certain medications like aspirin should be avoided.
-
A healthy diet is important. Nutrients that support bone marrow health, like iron and folate, can be beneficial.
-
Emotional support is crucial. Living with a chronic condition can be challenging, so psychological support and counseling can help.
-
Patient education is key. Understanding the condition and its management empowers patients and their families to make informed decisions.
Key Takeaways on Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia
Amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia is a rare blood disorder where the body doesn't produce enough platelets due to a lack of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. This condition can lead to excessive bleeding and bruising. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Treatments may include medications, blood transfusions, or bone marrow transplants. Genetic factors often play a role, so family history can be important. Regular monitoring and consultations with a hematologist are essential for those affected. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options can help patients and families navigate this challenging condition. Stay informed and proactive in seeking medical advice to manage amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia effectively.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.