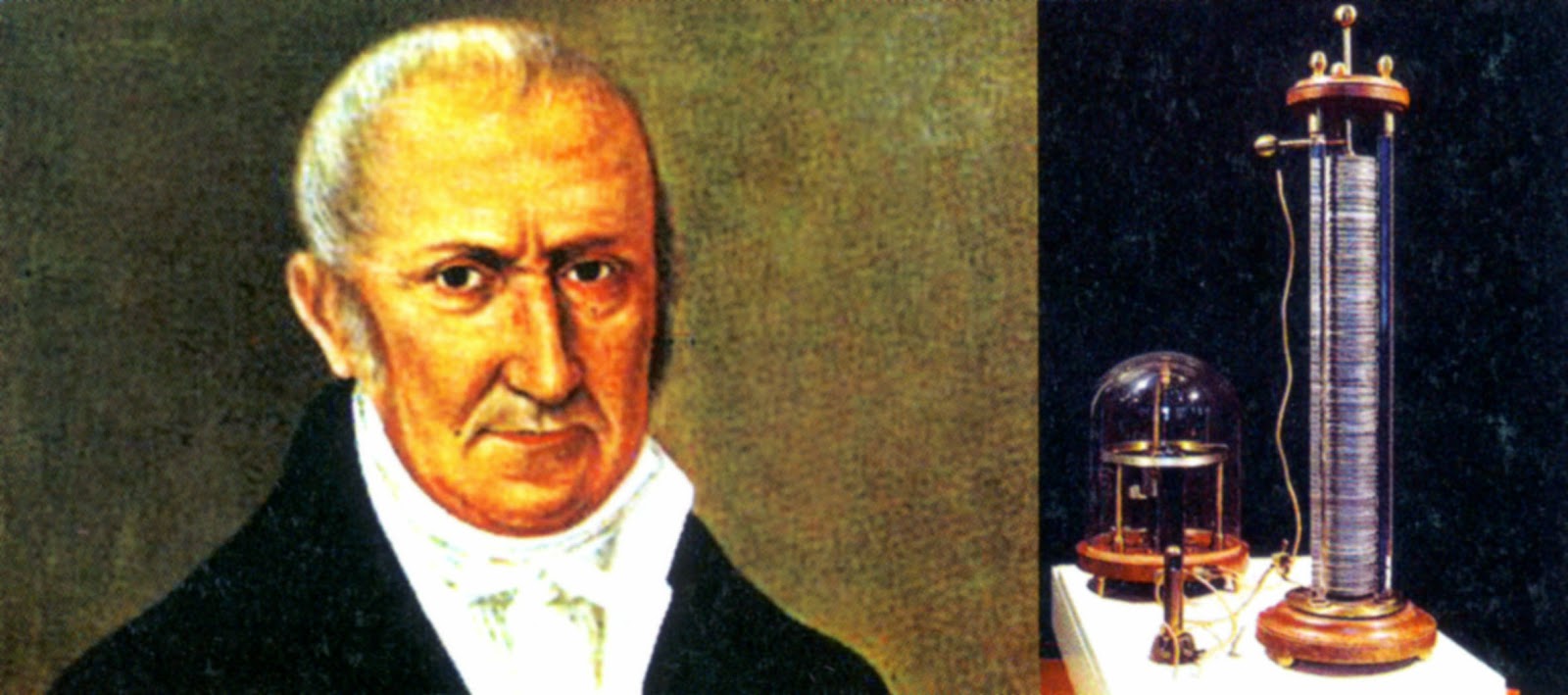
Alessandro Volta is a name that is synonymous with electricity and innovation. He was an Italian physicist and inventor who revolutionized the field of electrical science in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Volta is best known for his invention of the electric battery, a device that paved the way for the development of modern electrical systems. But there is so much more to know about this remarkable scientist.
In this article, we will delve into 17 fascinating facts about Alessandro Volta that will give you a deeper understanding of his life, achievements, and lasting impact on the world of science. From his early discoveries to his accolades and accomplishments, get ready to be amazed by the remarkable journey of this brilliant mind.
Key Takeaways:
- Alessandro Volta, an Italian physicist, invented the first true battery and inspired future scientists like Michael Faraday, leaving a lasting impact on the field of electricity and chemistry.
- Volta’s groundbreaking work in electricity led to practical applications, including the development of electric vehicles, and his legacy continues to influence scientific exploration and innovation.
Alessandro Volta was an Italian physicist born on February 18, 1745.
Alessandro Volta, born on February 18, 1745, was a renowned Italian physicist and pioneer in the field of electricity. His contributions to science have left an indelible mark on the world.
Volta invented the first true battery, known as the Voltaic Pile, in 1800.
In the year 1800, Alessandro Volta invented the Voltaic Pile, a device that produced a steady flow of electric current. This revolutionary invention laid the foundation for modern batteries.
The unit of measurement for electric potential, the volt, is named after Volta.
In recognition of his groundbreaking work in the field of electricity, the unit of measurement for electric potential, the volt, was named after Alessandro Volta. It serves as a testament to his contributions to the scientific community.
Volta’s invention of the battery led to numerous practical applications.
The invention of the battery by Alessandro Volta paved the way for various practical applications. It enabled advancements in fields such as telecommunication, transportation, and even medical devices.
Volta received numerous accolades for his scientific contributions.
Alessandro Volta’s significant contributions to the field of science did not go unnoticed. He received numerous accolades during his lifetime, including prestigious awards and honorary degrees from esteemed academic institutions.
Volta’s experiments debunked the theory of “animal electricity” proposed by Luigi Galvani.
Through his meticulous experiments, Alessandro Volta successfully refuted the theory of “animal electricity” put forward by Luigi Galvani. He demonstrated that the electric current produced in Galvani’s experiments was not generated by animal tissues but rather a chemical reaction.
Volta was the first to isolate and identify methane gas.
Alessandro Volta’s scientific curiosity extended beyond electricity. He also made significant contributions to the study of chemistry. Volta was the first to isolate and identify methane gas, a groundbreaking discovery that greatly impacted the field of chemistry.
Alessandro Volta was a professor at the University of Pavia.
Volta held the prestigious position of professor at the University of Pavia. He dedicated his career to teaching and conducting research, inspiring generations of aspiring scientists and nurturing intellectual curiosity.
Volta’s work inspired many future scientists, including Michael Faraday.
Alessandro Volta’s pioneering work in electricity had a profound influence on future scientists. One notable figure inspired by Volta was Michael Faraday, whose own contributions to the field of electromagnetism revolutionized science.
The Volta Prize was established to honor scientific achievements.
In recognition of Alessandro Volta’s impact on the scientific community, the Volta Prize was established. This prestigious award celebrates outstanding achievements in the field of electricity and related disciplines.
The Voltaic Pile consisted of alternating layers of zinc and copper discs.
The Voltaic Pile, Volta’s groundbreaking invention, comprised a series of alternating zinc and copper discs separated by cardboard soaked in saltwater. This arrangement created an electric current when metals with different potentials came into contact.
Volta’s discovery of the electric battery led to the development of electric vehicles.
Alessandro Volta’s invention of the electric battery played a crucial role in the development of electric vehicles. Today, his work continues to inspire advancements in battery technology and sustainable transportation.
Alessandro Volta was appointed a senator by Napoleon Bonaparte.
Recognizing Volta’s exceptional contributions to science, Napoleon Bonaparte appointed him as a senator of the Italian Kingdom. This prestigious position further highlighted Volta’s standing in society as a respected scientist and intellectual.
Volta performed extensive research on atmospheric electricity.
In addition to his contributions to other branches of science, Alessandro Volta conducted extensive research on atmospheric electricity. His studies contributed to a deeper understanding of natural phenomena like lightning and electrical discharges in the atmosphere.
A lunar crater is named after Alessandro Volta.
In honor of his significant contributions to the field of science, a lunar crater on the far side of the moon has been named after Alessandro Volta. This serves as a lasting tribute to his legacy and impact on the scientific community.
Volta’s experiments laid the groundwork for the development of the field of electrochemistry.
The experiments conducted by Alessandro Volta laid the groundwork for the field of electrochemistry. His discoveries and understanding of chemical reactions paved the way for further advancements in this scientific discipline.
Alessandro Volta passed away on March 5, 1827, in Como, Italy.
After a lifetime of groundbreaking discoveries and contributions to science, Alessandro Volta passed away on March 5, 1827, in his hometown of Como, Italy. His legacy lives on, and his impact will continue to be felt for generations to come.
These 17 fascinating facts about Alessandro Volta shed light on the life and remarkable achievements of one of history’s most influential scientists. From his invention of the first true battery to his extensive contributions to the fields of physics and chemistry, Volta’s legacy lives on as a testament to human ingenuity and scientific exploration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Alessandro Volta was a remarkable individual whose contributions to the field of electricity have had a lasting impact on our modern world. From his invention of the first battery, known as the Voltaic pile, to his investigations into the nature of electricity and how it could be harnessed, Volta paved the way for numerous scientific advancements. His ingenuity and dedication to his work made him a pioneer in the field and set the stage for future discoveries in electricity. Today, we continue to benefit from Volta’s discoveries and his name has become synonymous with electrical units of measurement. The legacy of Alessandro Volta serves as a reminder of the power of scientific curiosity and the potential for groundbreaking discoveries that can change the world.
FAQs
Q: What is Alessandro Volta best known for?
A: Alessandro Volta is best known for inventing the first battery, known as the Voltaic pile, in 1800.
Q: How did Volta’s battery work?
A: Volta’s battery consisted of alternating discs of zinc and copper, separated by pieces of cardboard soaked in saltwater. This arrangement generated an electric current when connected to a circuit.
Q: What is the unit of measurement named after Volta?
A: The unit of electrical potential difference, the volt, is named after Alessandro Volta to honor his contributions to the field of electricity.
Q: Did Volta discover anything else apart from the battery?
A: Yes, Volta also made significant contributions to the understanding of the nature of electricity, including groundbreaking experiments on electromagnetism and the development of the electrophorus, a device used to generate static electricity.
Q: What impact did Volta’s discoveries have on society?
A: Volta’s discoveries revolutionized the field of electricity and laid the foundation for advancements in various industries. His inventions and research paved the way for developments such as electric power generation, telecommunications, and modern electronic devices.
Alessandro Volta's groundbreaking work paved the way for modern technology. His invention of the voltaic pile, the first practical battery, revolutionized our understanding of electricity. Volta's contributions to physics laid the foundation for countless scientific advancements. His research also played a crucial role in the development of electrochemistry, a field that continues to shape our world today. Explore more fascinating facts about batteries, physics, and electrochemistry in our related articles.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


