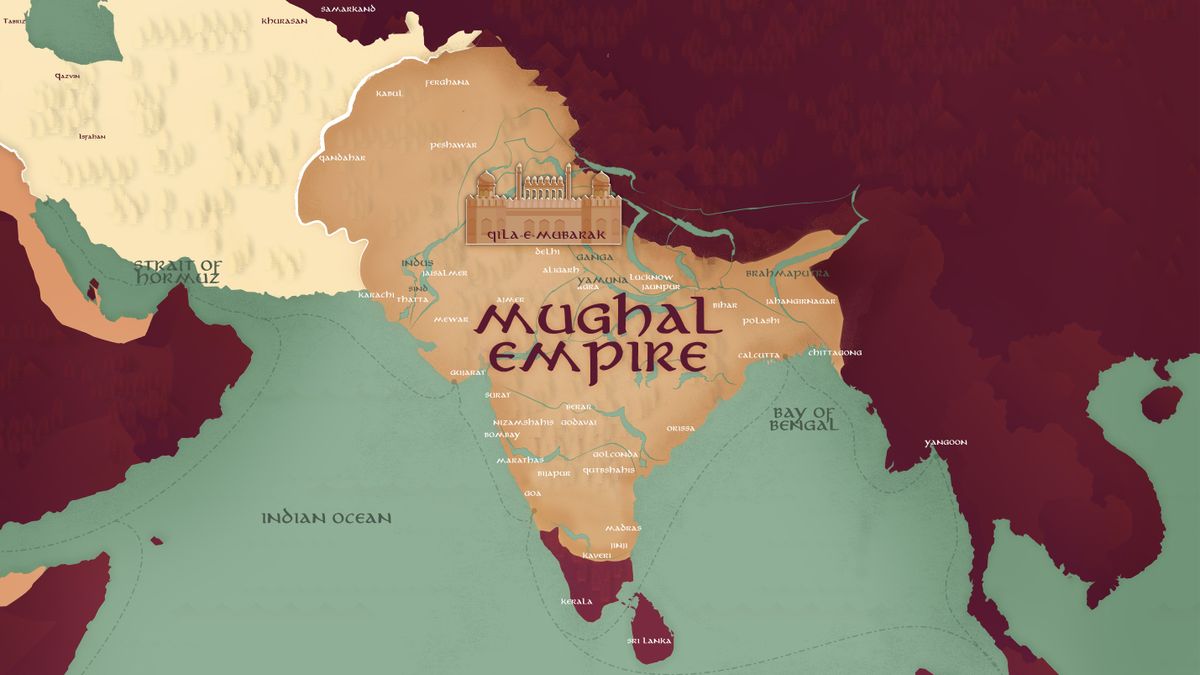
Ever wondered about the grandeur of the Mughal Empire, which once ruled vast swathes of the Indian subcontinent? Mughal Empire facts are not just historical tidbits; they're windows into a past world of intrigue, art, and architectural marvels. From the construction of the majestic Taj Mahal to the establishment of a unified administrative system, the Mughals left an indelible mark on the region's cultural and political landscape. But, how much do we really know about their contributions, their rulers, and the legacy they left behind? Let's peel back the layers of history and uncover some of the most fascinating facts about this empire that thrived from the 16th to the 19th century. Ready to get your mind blown by tales of opulence, conquest, and innovation?
Key Takeaways:
- The Mughal Empire, founded by Babur and reaching its peak under Akbar, blended cultures, promoted religious tolerance, and left a lasting legacy on India's art, cuisine, and architecture.
- Despite its decline, the Mughal Empire's influence on modern India remains strong, shaping architecture, festivals, and even fashion, while championing secularism and religious tolerance.
Origins of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire, a name synonymous with grandeur and sophistication, began its journey in the early 16th century. Babur, a descendant of Timur on his father's side and Genghis Khan on his mother's, founded this vast empire in 1526 after his victory over Ibrahim Lodi at the Battle of Panipat.
- Babur wasn't just a conqueror but also a lover of arts and literature, setting the tone for a dynasty that would value culture as much as conquest.
Expansion and Flourishing of the Empire
Under the leadership of Akbar the Great, the Mughal Empire reached its zenith, expanding its territories and embracing a diverse array of cultures. Akbar's policy of religious tolerance and his patronage of the arts led to a unique blending of cultures that is still celebrated today.
-
Akbar introduced a new religion, Din-i Ilahi, which attempted to merge elements of various religions, showcasing his commitment to unity and tolerance.
-
The empire's architecture, including the Taj Mahal and the Red Fort, remains iconic, blending Persian, Indian, and Islamic styles in a manner that has captivated visitors for centuries.
The Mughal Administration
The Mughal Empire was known for its structured administrative system, which allowed it to maintain control over vast territories. This system included the division of the empire into provinces or Subahs, each governed by a Subahdar.
-
The use of Persian as the administrative language promoted a cohesive cultural identity across the empire.
-
Zabt system of land revenue collection was another hallmark of their administration, ensuring efficient and fair tax collection methods.
Decline of the Mughal Empire
Despite its grandeur, the Mughal Empire began to decline in the 18th century, weakened by internal strife and external invasions. The invasion by Nadir Shah in 1739 and the subsequent battles with the Marathas drained the empire's resources.
-
The British East India Company's victory in the Battle of Plassey in 1757 marked a significant turning point, leading to British dominance in India.
-
By the mid-19th century, the last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar, was exiled, symbolizing the end of the empire.
Legacy of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire left behind a rich legacy that continues to influence the Indian subcontinent. From cuisine to language, the impacts of Mughal rule are evident in various aspects of life.
-
Mughlai cuisine, with its rich flavors and aromatic spices, reflects the culinary traditions of the Mughal era.
-
The use of Urdu and Persian in literature and poetry flourished under Mughal patronage, enriching the region's literary heritage.
-
The concept of gardens, with their emphasis on symmetry and the use of water, showcases the Mughal's love for nature and beauty.
Mughal Contributions to Art and Culture
The Mughals were great patrons of the arts, commissioning works that blended Persian, Indian, and Islamic traditions to create a unique Mughal style.
-
Miniature paintings, characterized by intricate details and vibrant colors, flourished during the Mughal era, telling stories of court life, nature, and mythology.
-
The construction of monuments like the Taj Mahal not only exemplifies Mughal architectural genius but also serves as a symbol of love and loss.
-
Music also saw significant advancements, with the Mughals introducing new instruments and ragas to the Indian musical landscape.
Mughal Influence on Modern India
The Mughal Empire's influence extends into modern India, shaping its culture, architecture, and society in profound ways.
-
Many Indian cities, including Delhi and Agra, still bear the architectural signatures of their Mughal past, attracting millions of tourists each year.
-
The concept of secularism and religious tolerance, championed by Akbar, remains a cornerstone of India's identity.
-
Festivals and traditions introduced or popularized during the Mughal era, such as Diwali celebrations in the Red Fort, continue to be celebrated with enthusiasm.
-
The Mughal Empire's emphasis on record-keeping has provided historians with valuable insights into the social, economic, and cultural aspects of life during their rule.
-
Lastly, the enduring popularity of Mughal-inspired fashion and jewelry designs underscores the lasting impact of Mughal aesthetics on contemporary style.
A Glimpse into Mughal Magnificence
Diving deep into the Mughal Empire reveals a rich tapestry of history, culture, and architectural marvels that continue to awe and inspire. From the grandeur of the Taj Mahal to the intricate policies of Akbar that promoted religious tolerance, these facts barely scratch the surface of Mughal splendor. Their contributions to art, architecture, and governance have left an indelible mark on the fabric of South Asian history. As we've journeyed through the 18 best facts, it's clear the Mughal Empire wasn't just about conquests and rule; it was about fostering a diverse and thriving society that valued knowledge, culture, and the arts. Their legacy, encapsulated in stone and stories, invites us to explore further and appreciate the depth of our shared past.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


