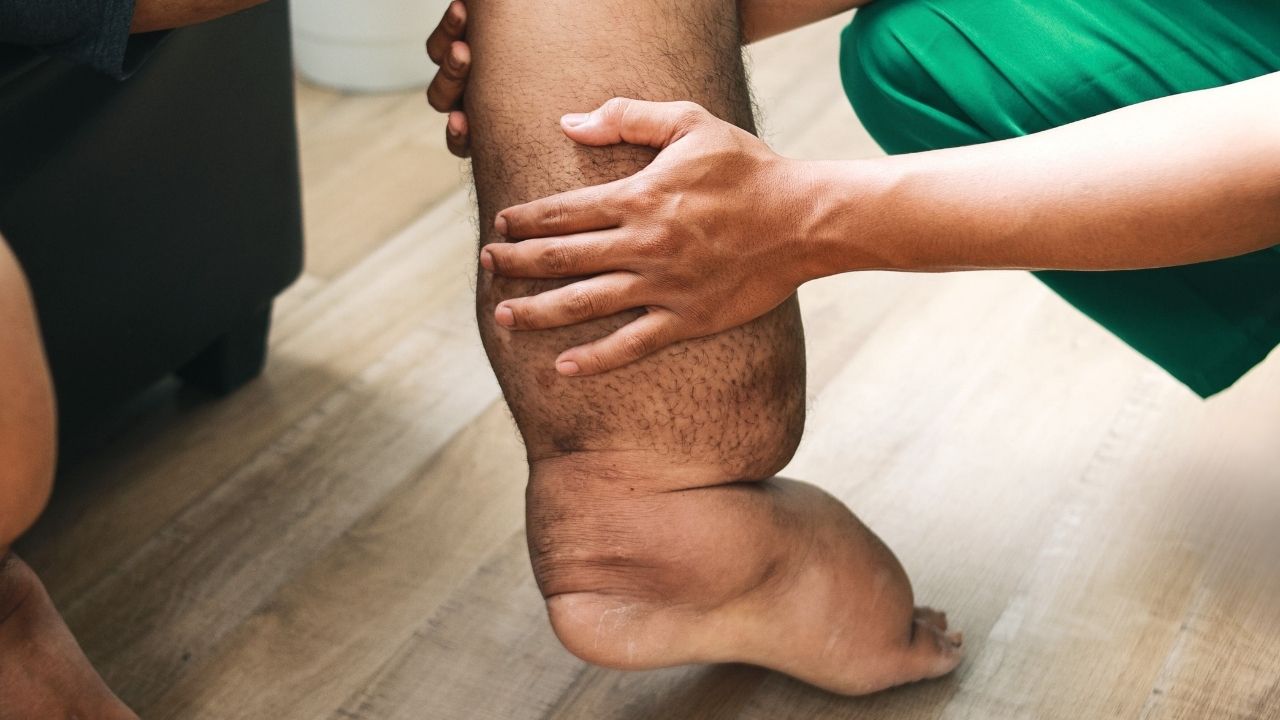
Lymphatic Filariasis, often called elephantiasis, is a parasitic disease caused by microscopic worms. These worms invade the lymphatic system, leading to severe swelling in the limbs and other body parts. Did you know that over 120 million people worldwide suffer from this condition? The disease spreads through mosquito bites, making it prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions. Symptoms can take years to appear, often starting with fever and progressing to extreme swelling. Treatment includes medication to kill the worms and alleviate symptoms, but prevention through mosquito control remains crucial. Understanding this disease is vital for global health efforts.
Key Takeaways:
- Lymphatic Filariasis, also known as elephantiasis, is a parasitic disease affecting over 120 million people worldwide. It causes severe swelling and disability, impacting communities and individuals.
- Early diagnosis, effective treatment, and global efforts are crucial in combating Lymphatic Filariasis. Support for affected individuals, research funding, and hope for the future drive the fight against this disease.
What is Lymphatic Filariasis?
Lymphatic Filariasis, also known as elephantiasis, is a parasitic disease caused by microscopic, thread-like worms. These worms affect the lymphatic system, leading to severe swelling and disability. Here are some intriguing facts about this disease.
- Lymphatic Filariasis is caused by three types of worms: Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and Brugia timori.
- The disease is transmitted through mosquito bites. Mosquitoes become infected when they bite a person already carrying the parasite.
- Over 120 million people worldwide are affected by Lymphatic Filariasis. The majority of cases occur in tropical and subtropical regions.
- The disease can lead to severe disability. Chronic infection can cause lymphoedema (tissue swelling) and elephantiasis (skin/tissue thickening).
- Lymphatic Filariasis is one of the leading causes of permanent disability worldwide. It significantly impacts the quality of life of those affected.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how to diagnose Lymphatic Filariasis is crucial for early treatment and management. Here are some key points.
- Early symptoms include fever, chills, and skin infections. These symptoms often go unnoticed or are mistaken for other illnesses.
- Lymphoedema is a common symptom. This swelling usually affects the legs but can also occur in the arms, breasts, and genitalia.
- Hydrocele is another symptom in men. This condition causes swelling of the scrotum.
- Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests. The presence of microfilariae (larval stage of the parasite) in the blood confirms the infection.
- Ultrasound can detect adult worms in the lymphatic system. This imaging technique helps visualize the movement of the worms.
Treatment and Prevention
Effective treatment and preventive measures can help control the spread of Lymphatic Filariasis. Here are some important facts.
- Antiparasitic medications are used to treat the infection. Drugs like diethylcarbamazine (DEC), ivermectin, and albendazole are commonly prescribed.
- Mass drug administration (MDA) programs help prevent the spread. These programs involve giving the entire at-risk population antiparasitic drugs.
- Good hygiene practices can reduce the risk of infection. Regular washing and proper wound care are essential.
- Mosquito control is crucial for prevention. Using insecticide-treated nets and eliminating standing water can help reduce mosquito populations.
- There is no vaccine for Lymphatic Filariasis. Research is ongoing to develop an effective vaccine.
Impact on Communities
Lymphatic Filariasis not only affects individuals but also has a significant impact on communities. Here are some insights.
- The disease can lead to social stigma. Visible symptoms like elephantiasis can cause affected individuals to be ostracized.
- Economic impact is substantial. Those affected may be unable to work, leading to loss of income and increased poverty.
- Healthcare costs can be high. Treatment and management of the disease require significant resources.
- Community-based care programs are essential. These programs provide support and education to affected individuals and their families.
- Global efforts are underway to eliminate the disease. Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) are working towards eradicating Lymphatic Filariasis.
Historical and Scientific Background
The history and science behind Lymphatic Filariasis provide a deeper understanding of the disease. Here are some fascinating facts.
- The disease has been known since ancient times. Historical texts from Egypt and India describe symptoms consistent with Lymphatic Filariasis.
- The parasite was first identified in the 19th century. Sir Patrick Manson discovered the link between mosquitoes and the transmission of the parasite.
- Lymphatic Filariasis is part of the Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs). These diseases affect over a billion people worldwide.
- Research is ongoing to understand the parasite's life cycle. Scientists are studying how the worms evade the immune system and cause disease.
- Genetic studies are being conducted to develop new treatments. Understanding the parasite's genetics can lead to targeted therapies.
Global Efforts and Future Prospects
Efforts to combat Lymphatic Filariasis are ongoing, with a focus on future prospects for eradication. Here are some key points.
- The Global Program to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (GPELF) was launched in 2000. This initiative aims to eliminate the disease as a public health problem.
- Over 7 billion treatments have been delivered through MDA programs. These efforts have significantly reduced the prevalence of the disease.
- Innovative diagnostic tools are being developed. New tests can detect the parasite more accurately and quickly.
- Community engagement is crucial for success. Educating and involving local communities helps ensure the effectiveness of prevention and treatment programs.
- The goal is to eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis by 2030. With continued efforts, this target is within reach.
Personal Stories and Experiences
Hearing personal stories and experiences can provide a human perspective on Lymphatic Filariasis. Here are some touching accounts.
- Many affected individuals face daily challenges. Simple tasks like walking or working can become difficult due to swelling and pain.
- Support groups offer a sense of community. These groups provide emotional and practical support to those affected.
- Healthcare workers play a vital role. They provide treatment, education, and support to affected individuals and their families.
- Stories of resilience and hope are common. Many individuals find ways to adapt and lead fulfilling lives despite the disease.
- Raising awareness is essential. Sharing personal stories helps educate others and reduce stigma.
Interesting Facts and Trivia
Here are some additional interesting facts and trivia about Lymphatic Filariasis that you might find surprising.
- The worms can live in the human body for up to 8 years. During this time, they produce millions of microfilariae.
- The disease is most common in rural areas. Limited access to healthcare and mosquito control measures contribute to higher prevalence.
- Elephantiasis is named after the swollen limbs resembling an elephant's leg. This term highlights the severe swelling caused by the disease.
- The worms are nocturnal. They are most active at night, which is why blood tests are often done during this time.
- Lymphatic Filariasis can affect animals too. Dogs and cats can also be infected by similar parasites.
Research and Innovations
Ongoing research and innovations are crucial for combating Lymphatic Filariasis. Here are some exciting developments.
- New drug combinations are being tested. Researchers are exploring more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
- Genetic engineering is being used to study the parasite. This technology helps scientists understand how the worms function and interact with the host.
- Vaccines are in development. Although there is no vaccine yet, promising candidates are being tested in clinical trials.
- Mobile health technology is being utilized. Apps and mobile devices help track and manage the disease in remote areas.
- Collaborative efforts are increasing. Partnerships between governments, NGOs, and researchers are essential for progress.
Final Thoughts
Lymphatic Filariasis is a complex disease with far-reaching impacts. Understanding its causes, symptoms, treatment, and global efforts can help in the fight against it. Here are a few more facts to consider.
- Public health education is vital. Educating communities about prevention and treatment can reduce the spread of the disease.
- Early diagnosis improves outcomes. Prompt treatment can prevent severe complications and disability.
- Support for affected individuals is crucial. Providing medical, emotional, and financial support can improve their quality of life.
- Research funding is essential. Continued investment in research is needed to develop new treatments and prevention strategies.
- Hope for the future is strong. With ongoing efforts and advancements, the goal of eliminating Lymphatic Filariasis is within reach.
Final Thoughts on Lymphatic Filariasis
Lymphatic filariasis, often called elephantiasis, affects millions worldwide. This disease, caused by parasitic worms, leads to severe swelling and disability. Understanding its transmission through mosquito bites is crucial for prevention. Efforts to combat it include mass drug administration, which has shown promising results in reducing infection rates. However, challenges remain, especially in remote areas with limited healthcare access.
Raising awareness and improving sanitation can help control the spread. Continued research and funding are essential to develop better treatments and vaccines. By working together, communities and health organizations can make strides toward eliminating this debilitating disease. Remember, every small effort counts in the fight against lymphatic filariasis. Stay informed, support initiatives, and contribute to a healthier future for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
