Urticarial Vasculitis is a rare condition that combines features of hives and inflammation of blood vessels. Unlike typical hives, the welts from urticarial vasculitis last longer than 24 hours and often leave a bruise. This condition can be linked to underlying health issues like lupus or infections. Symptoms may include joint pain, abdominal pain, and fever. Diagnosing urticarial vasculitis usually involves a skin biopsy and blood tests. Treatment varies based on severity but often includes antihistamines, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants. Understanding this condition is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Here are 50 facts to help you grasp the essentials of urticarial vasculitis.
Key Takeaways:
- Urticarial vasculitis is a rare condition combining hives and blood vessel inflammation, more common in adults. It can lead to serious complications, but proper management can improve quality of life.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for urticarial vasculitis. Symptoms include itchy welts, joint pain, and kidney complications. Support groups and healthcare providers play a vital role in managing the condition.
What is Urticarial Vasculitis?
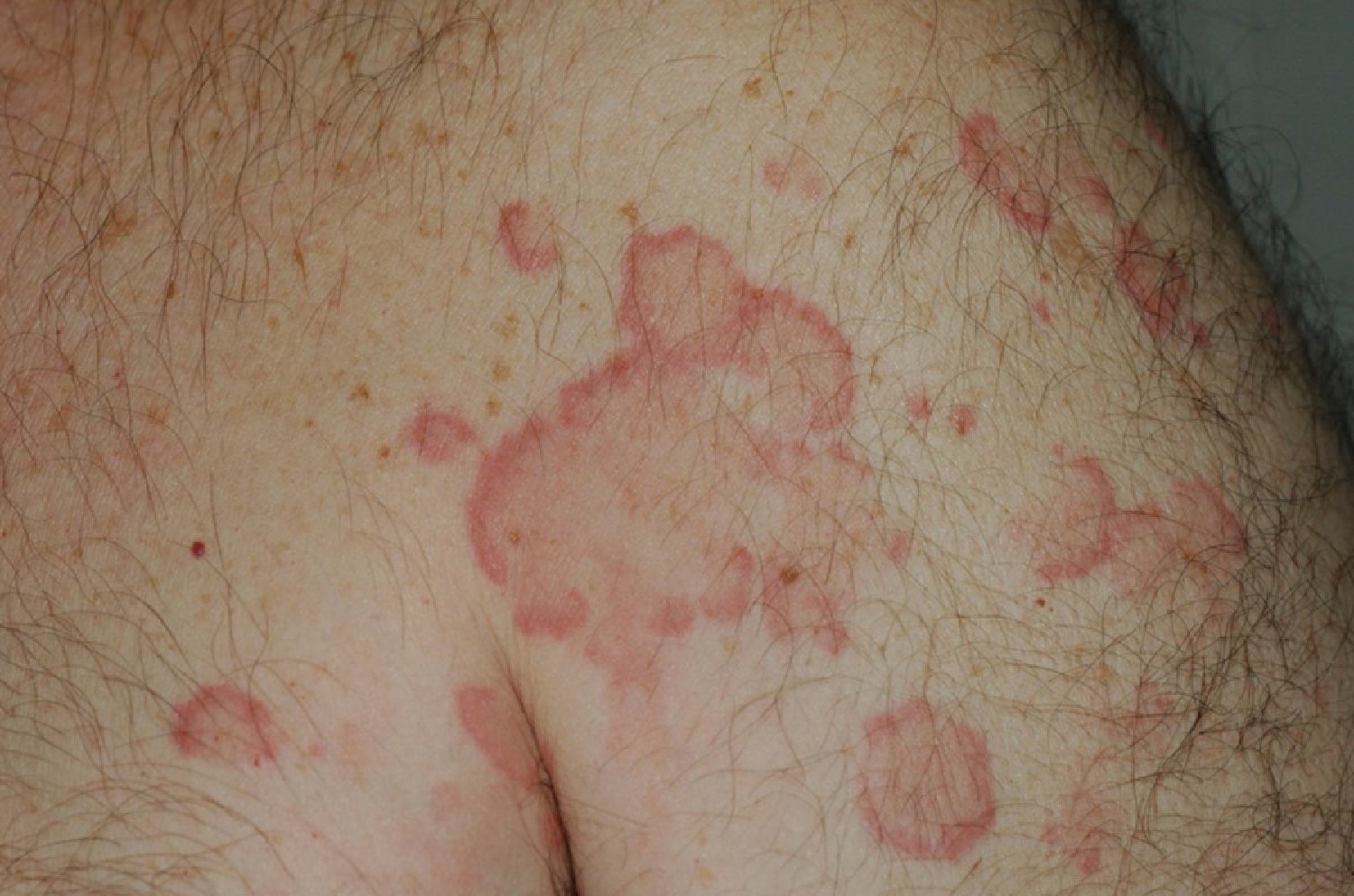
Urticarial vasculitis is a rare condition that combines features of urticaria (hives) and vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels). This condition can be challenging to diagnose and manage due to its complex nature. Here are some intriguing facts about urticarial vasculitis.
- Urticarial vasculitis is characterized by red, itchy welts that last longer than 24 hours.
- Unlike typical hives, the welts in urticarial vasculitis can be painful and may leave a bruise.
- This condition is more common in adults than in children.
- Women are more likely to develop urticarial vasculitis than men.
- The exact cause of urticarial vasculitis is unknown, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder.
Symptoms of Urticarial Vasculitis
Recognizing the symptoms of urticarial vasculitis is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
- Common symptoms include fever, joint pain, and abdominal pain.
- Some patients may experience swelling in the face, lips, or tongue.
- Fatigue and general malaise are also frequently reported.
- Eye inflammation, known as uveitis, can occur in some cases.
- Kidney involvement, leading to proteinuria or hematuria, is a serious complication.
Diagnosis of Urticarial Vasculitis
Diagnosing urticarial vasculitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and sometimes skin biopsies.
- A skin biopsy can reveal inflammation in the blood vessels, confirming the diagnosis.
- Blood tests may show elevated levels of inflammatory markers like ESR and CRP.
- Complement levels (C3 and C4) are often low in patients with urticarial vasculitis.
- Immunofluorescence studies can detect immune complex deposits in the skin.
- A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Urticarial Vasculitis
Treatment for urticarial vasculitis aims to control symptoms and prevent complications. The approach can vary depending on the severity of the condition.
- Antihistamines are commonly used to relieve itching and swelling.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids are often prescribed for more severe cases.
- Immunosuppressive agents like azathioprine or methotrexate may be necessary for refractory cases.
- Biologic therapies, such as rituximab, have shown promise in some patients.
Complications of Urticarial Vasculitis
Urticarial vasculitis can lead to several complications if not properly managed. Awareness of these potential issues is important for patients and healthcare providers.
- Chronic kidney disease can develop due to persistent inflammation.
- Lung involvement, leading to conditions like interstitial lung disease, is possible.
- Gastrointestinal complications, such as ulcers or bleeding, may occur.
- Cardiovascular issues, including heart inflammation, have been reported.
- Persistent skin lesions can lead to scarring and hyperpigmentation.
Living with Urticarial Vasculitis
Managing urticarial vasculitis involves not only medical treatment but also lifestyle adjustments. Here are some tips for living with this condition.
- Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential for monitoring the disease.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and staying hydrated can support overall health.
- Stress management techniques, like yoga or meditation, may help reduce flare-ups.
- Avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods or medications, can prevent symptoms.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and coping strategies.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for understanding urticarial vasculitis and developing new treatments. Here are some recent advancements and future directions in this field.
- Genetic studies are exploring the hereditary aspects of urticarial vasculitis.
- New biomarkers are being investigated for earlier and more accurate diagnosis.
- Advances in immunotherapy are offering new hope for treatment-resistant cases.
- Clinical trials are testing the efficacy of novel biologic agents.
- Collaborative research efforts are focusing on the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
Interesting Facts about Urticarial Vasculitis
Here are some lesser-known but fascinating facts about urticarial vasculitis that highlight the complexity and uniqueness of this condition.
- Urticarial vasculitis can sometimes be associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Environmental factors, like infections or exposure to certain chemicals, may trigger the condition.
- Some patients experience spontaneous remission, where symptoms disappear without treatment.
- The condition can mimic other skin disorders, making diagnosis challenging.
- Urticarial vasculitis is considered a type of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, characterized by the presence of fragmented white blood cells in the affected vessels.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths and misconceptions about urticarial vasculitis that can lead to confusion and misinformation. Here are some common ones debunked.
- Myth: Urticarial vasculitis is just a severe form of hives. Fact: It involves blood vessel inflammation, unlike typical hives.
- Myth: Only older adults get urticarial vasculitis. Fact: It can affect individuals of any age, though it is more common in adults.
- Myth: Urticarial vasculitis is contagious. Fact: It is an autoimmune condition and not contagious.
- Myth: There is no effective treatment for urticarial vasculitis. Fact: Various treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Myth: Urticarial vasculitis always leads to severe complications. Fact: With proper management, many patients lead normal lives.
Support and Resources
Finding support and reliable resources can make a significant difference for those living with urticarial vasculitis. Here are some options to consider.
- National and international vasculitis foundations offer information and support.
- Online forums and social media groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and advice.
- Patient advocacy organizations work to raise awareness and fund research.
- Educational materials, such as brochures and videos, can help patients and families understand the condition.
- Healthcare providers, including dermatologists and rheumatologists, are key resources for managing urticarial vasculitis.
Final Thoughts on Urticarial Vasculitis
Urticarial vasculitis, a rare condition, often gets mistaken for common hives. Unlike regular hives, it involves inflammation of blood vessels, causing pain and lasting longer than 24 hours. Symptoms include red patches, burning sensations, and sometimes fever or joint pain. Diagnosis usually requires a skin biopsy to confirm the presence of inflamed blood vessels. Treatment varies based on severity, ranging from antihistamines to corticosteroids or immunosuppressants.
Living with urticarial vasculitis can be challenging, but understanding the condition helps manage it better. Regular check-ups and following prescribed treatments are crucial. Awareness and education about this condition can lead to earlier diagnosis and improved quality of life for those affected. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Stay informed, stay proactive, and take control of your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
