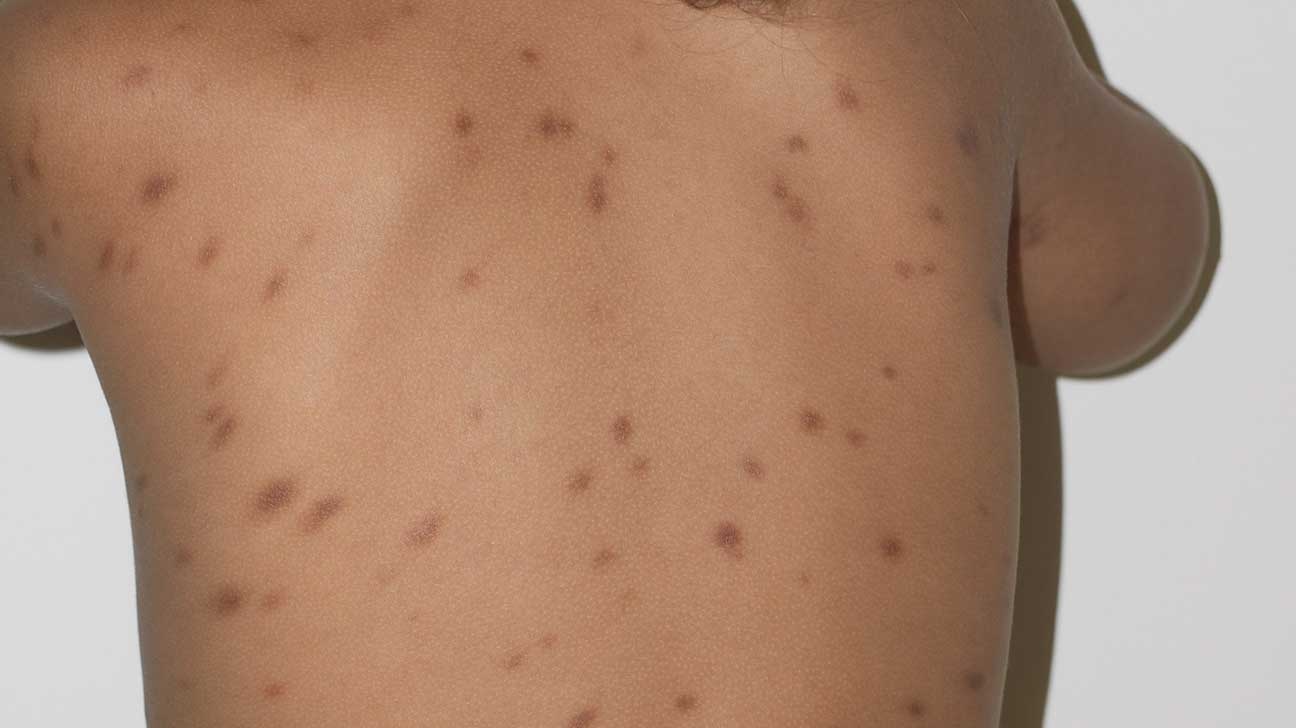
Urticaria Pigmentosa might sound like a spell from a wizard's book, but it's actually a skin condition. This rare disorder causes brownish spots and itchy bumps on the skin. Mast cells, which are part of the immune system, build up in the skin and release chemicals that cause itching and swelling. It's more common in children but can affect adults too. While it might look alarming, it's usually not dangerous. Symptoms can be managed with antihistamines and other treatments. Curious about what triggers it, how it's diagnosed, or what daily life is like for those with it? Keep reading to find out!
Key Takeaways:
- Urticaria Pigmentosa is a rare skin condition causing itchy brown lesions. Early diagnosis and avoiding triggers can help manage symptoms effectively, improving quality of life.
- While there is no cure for Urticaria Pigmentosa, treatments like antihistamines and lifestyle changes can help minimize symptoms and improve overall well-being.
What is Urticaria Pigmentosa?
Urticaria Pigmentosa is a rare skin condition that falls under the category of mastocytosis. It primarily affects the skin, causing brownish lesions and intense itching. Understanding this condition can help manage its symptoms better.
- Urticaria Pigmentosa is a form of cutaneous mastocytosis.
- It is characterized by the presence of brownish, itchy lesions on the skin.
- The condition is caused by an excess of mast cells in the skin.
- Mast cells release histamine, which leads to itching and swelling.
- Urticaria Pigmentosa can appear at any age but is most common in children.
- The condition often improves or resolves by adolescence in many cases.
- Adults with Urticaria Pigmentosa may experience a chronic form of the disease.
- The lesions can vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
- Scratching or rubbing the lesions can cause them to become red and swollen, known as Darier's sign.
- Urticaria Pigmentosa is not contagious.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis is crucial for managing Urticaria Pigmentosa. Here are some key points to consider.
- Common symptoms include itching, redness, and swelling of the skin.
- Lesions may appear on any part of the body but are often found on the trunk and limbs.
- Blisters may form, especially in infants and young children.
- A dermatologist can diagnose Urticaria Pigmentosa through a skin biopsy.
- Blood tests may be conducted to check for elevated levels of tryptase, an enzyme released by mast cells.
- In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy may be necessary to rule out systemic mastocytosis.
- Genetic testing can help identify mutations associated with the condition.
- Urticaria Pigmentosa can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis.
- Early diagnosis can help in managing symptoms more effectively.
- Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring the condition.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for Urticaria Pigmentosa, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Antihistamines are commonly prescribed to reduce itching and swelling.
- Topical corticosteroids can help alleviate inflammation and redness.
- Phototherapy, using ultraviolet light, may be beneficial for some patients.
- Oral corticosteroids are sometimes used for severe cases.
- Mast cell stabilizers can help prevent the release of histamine.
- Avoiding triggers like heat, stress, and certain medications can reduce flare-ups.
- Moisturizers and emollients can help soothe dry, itchy skin.
- Immunomodulatory drugs may be considered for severe or refractory cases.
- Epinephrine auto-injectors should be carried by patients at risk of anaphylaxis.
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet can improve overall well-being.
Living with Urticaria Pigmentosa
Managing daily life with Urticaria Pigmentosa involves understanding triggers and adopting lifestyle changes to minimize symptoms.
- Wearing loose, breathable clothing can reduce skin irritation.
- Using mild, fragrance-free soaps and detergents can prevent flare-ups.
- Staying cool and avoiding excessive heat can help manage symptoms.
- Stress management techniques like meditation and yoga can be beneficial.
- Keeping a symptom diary can help identify and avoid triggers.
- Educating family and friends about the condition can provide emotional support.
- Joining support groups can offer a sense of community and shared experiences.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring the condition.
- Sun protection is important, as UV exposure can worsen symptoms.
- Patients should inform healthcare providers about their condition before undergoing any medical procedures.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Urticaria Pigmentosa and develop more effective treatments.
- Scientists are studying the genetic mutations associated with the condition.
- New therapies targeting mast cells are being developed.
- Clinical trials are exploring the efficacy of various medications.
- Research is being conducted to understand the role of the immune system in Urticaria Pigmentosa.
- Advances in genetic testing may lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
- Patient registries are being created to collect data and improve understanding of the condition.
- Collaboration between researchers and patient advocacy groups is increasing.
- Awareness campaigns aim to educate the public and healthcare providers about Urticaria Pigmentosa.
- Future treatments may include targeted therapies based on individual genetic profiles.
- Ongoing research offers hope for better management and potential cures for Urticaria Pigmentosa.
Final Thoughts on Urticaria Pigmentosa
Urticaria Pigmentosa, a rare skin condition, affects both children and adults. It causes brownish lesions and itching, often triggered by heat, stress, or friction. While not life-threatening, it can impact quality of life. Treatments focus on managing symptoms, with antihistamines and topical steroids being common options.
Understanding this condition helps in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate care. Though there's no cure, many find relief through lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers can make a significant difference.
Remember, each case is unique. What works for one person might not work for another. Patience and persistence are key. With the right approach, those affected can lead comfortable, fulfilling lives. Stay proactive, stay informed, and don't hesitate to seek support when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
