T-cell lymphoma is a type of cancer that starts in T-cells, which are part of the immune system. This disease can be tricky to understand, but knowing some key facts can help. T-cell lymphoma comes in various forms, each with its own symptoms and treatment options. Some types grow slowly, while others spread quickly. Early diagnosis is crucial for better outcomes. Treatments may include chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapies. It's important to recognize the signs, such as swollen lymph nodes, fever, or unexplained weight loss. By learning more about T-cell lymphoma, you can better understand this complex disease and its impact on health.
Key Takeaways:
- T-Cell Lymphoma is a rare cancer affecting the body's immune system. Early detection, proper treatment, and healthy lifestyle choices can improve outcomes and quality of life.
- Research and advancements in T-Cell Lymphoma treatment offer hope for better outcomes. Support groups and resources provide valuable assistance for patients and caregivers.
What is T-Cell Lymphoma?
T-Cell Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in T-cells, a kind of white blood cell crucial for the immune system. Understanding this disease involves knowing its causes, symptoms, treatments, and more.
- T-Cell Lymphoma is a rare form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- It accounts for about 15% of all non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases.
- T-cells help protect the body from infections and cancer.
- The disease can develop in lymphoid tissues like lymph nodes, spleen, and skin.
- Symptoms often include swollen lymph nodes, fever, and night sweats.
Types of T-Cell Lymphoma
There are several types of T-Cell Lymphoma, each with unique characteristics and treatment approaches.
- Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma (PTCL) is the most common type.
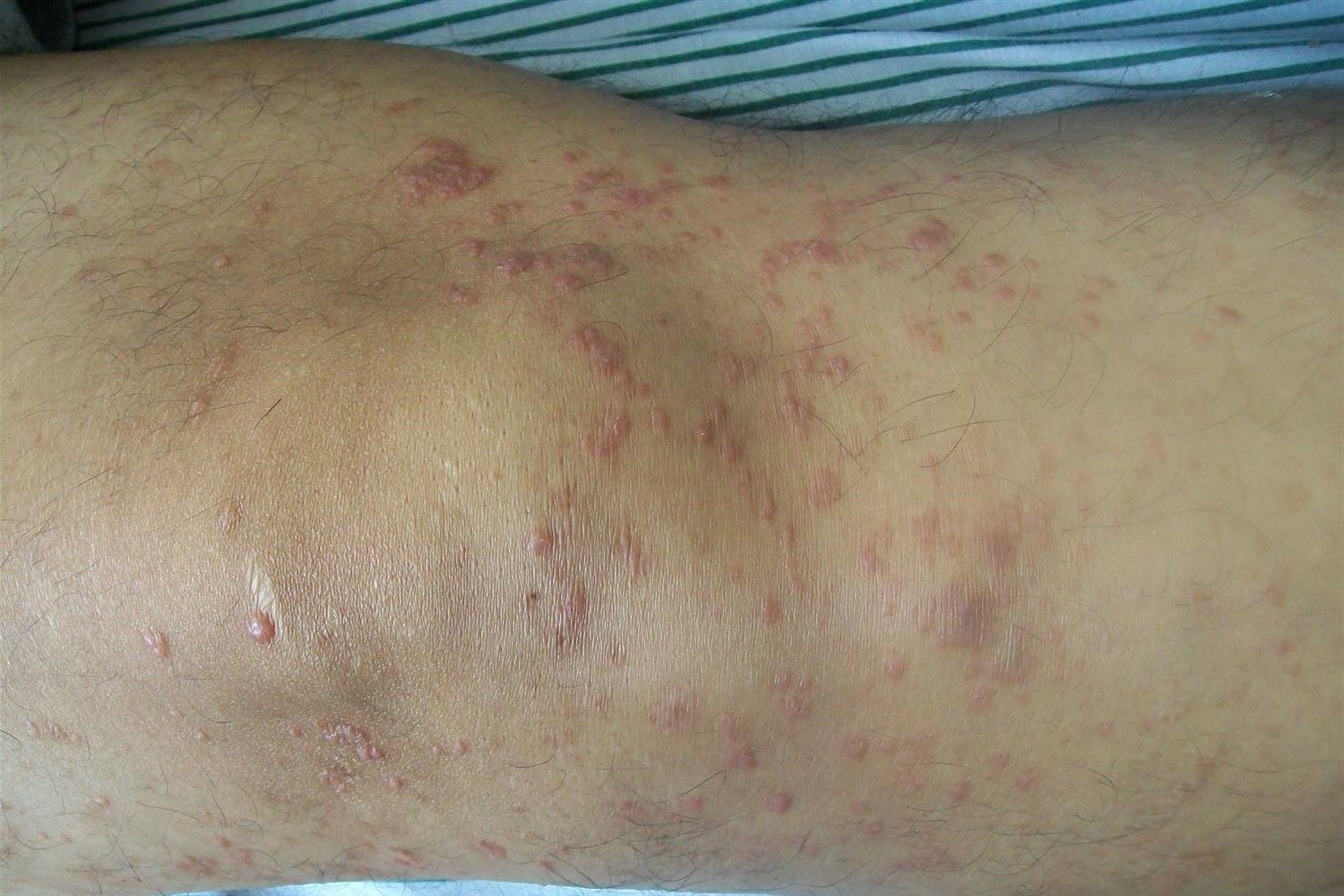
- Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma (CTCL) primarily affects the skin.
- Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) can be systemic or cutaneous.
- Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma (AITL) involves the lymph nodes and blood vessels.
- Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (ATLL) is linked to the HTLV-1 virus.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes T-Cell Lymphoma and the risk factors can help in early detection and prevention.
- The exact cause of T-Cell Lymphoma is unknown.
- Genetic mutations may play a role in its development.
- Exposure to certain chemicals and radiation increases risk.
- A weakened immune system can make one more susceptible.
- Infections like Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) are linked to some types.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and knowing how T-Cell Lymphoma is diagnosed is crucial for timely treatment.
- Common symptoms include unexplained weight loss and fatigue.
- Skin rashes and itching are signs of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma.
- Biopsies are often used to diagnose the disease.
- Blood tests can reveal abnormal T-cells.
- Imaging tests like CT scans help determine the extent of the disease.
Treatment Options
Various treatments are available for T-Cell Lymphoma, depending on the type and stage of the disease.
- Chemotherapy is a common treatment method.
- Radiation therapy targets specific areas affected by cancer.
- Stem cell transplants may be considered for advanced cases.
- Immunotherapy uses the body's immune system to fight cancer.
- Clinical trials offer access to new and experimental treatments.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Knowing the prognosis and survival rates can provide a clearer picture of what to expect.
- The prognosis varies depending on the type and stage.
- Early-stage T-Cell Lymphoma has a better prognosis.
- Advanced stages may have lower survival rates.
- Five-year survival rates range from 20% to 80%, depending on the type.
- Ongoing research aims to improve these rates.
Living with T-Cell Lymphoma
Managing life with T-Cell Lymphoma involves more than just medical treatments.
- Regular follow-up appointments are essential.
- Support groups can provide emotional and psychological help.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle is crucial.
- Physical activity can improve overall well-being.
- Mental health support is important for coping with the disease.
Research and Advances
Continuous research is leading to new discoveries and advancements in treating T-Cell Lymphoma.
- New drugs are being developed to target specific cancer cells.
- Genetic research is uncovering potential causes and treatments.
- Immunotherapy is showing promise in clinical trials.
- Personalized medicine tailors treatment to individual genetic profiles.
- Advances in imaging technology improve diagnosis accuracy.
Myths and Misconceptions
Clearing up myths and misconceptions can help in understanding T-Cell Lymphoma better.
- T-Cell Lymphoma is not contagious.
- It is not caused by poor hygiene or lifestyle choices.
- Not all lymphomas are the same; T-Cell Lymphoma is distinct.
- Alternative treatments should not replace conventional medical care.
- Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes.
Support and Resources
Various resources are available to help those affected by T-Cell Lymphoma.
- Organizations like the Lymphoma Research Foundation provide valuable information.
- Online forums offer a platform for sharing experiences and advice.
- Financial assistance programs can help with treatment costs.
- Educational materials are available for patients and caregivers.
- Healthcare teams can provide comprehensive support and guidance.
Final Thoughts on T-Cell Lymphoma
T-Cell Lymphoma, a complex and rare type of cancer, affects the body's immune system. Understanding its symptoms, types, and treatments can make a big difference in early detection and management. From skin rashes to swollen lymph nodes, recognizing the signs is crucial. Treatments vary from chemotherapy to stem cell transplants, offering hope to many patients.
Staying informed about the latest research and advancements is essential. Support groups and resources can provide much-needed emotional and practical help. Remember, early diagnosis improves outcomes significantly.
By spreading awareness and knowledge, we can support those affected and contribute to ongoing research efforts. Keep these facts in mind, share them with others, and stay proactive in health matters. Knowledge truly is power when battling diseases like T-Cell Lymphoma.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
