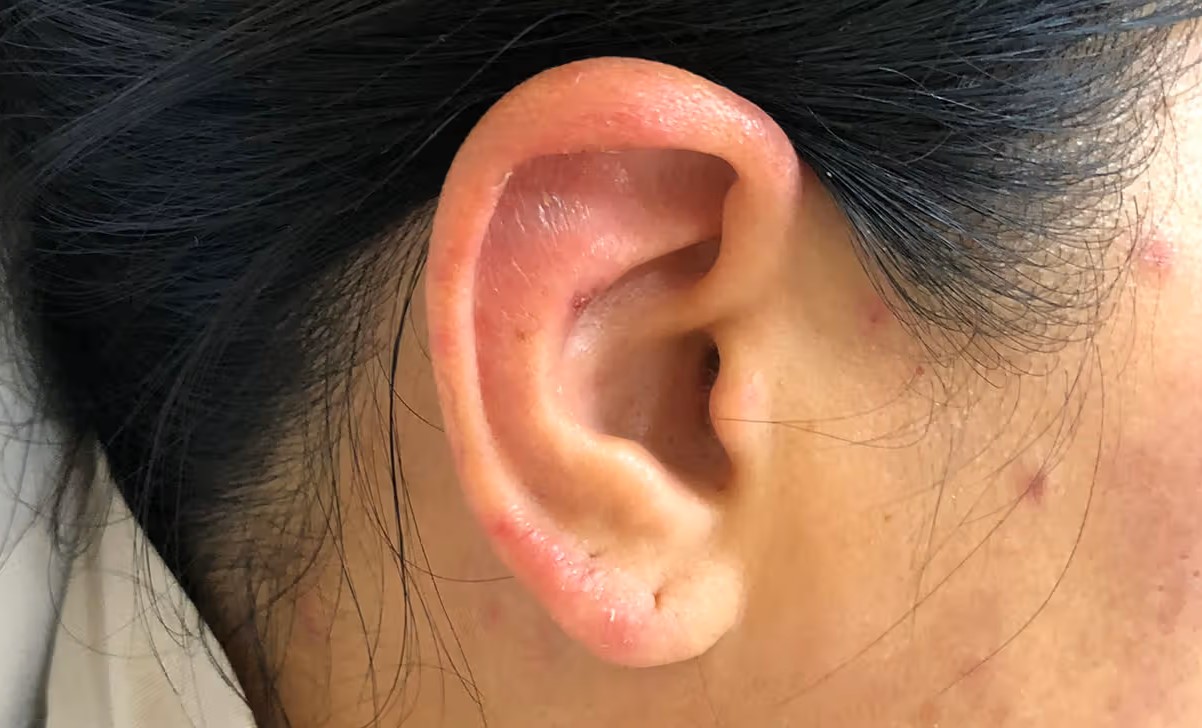
Polychondritis is a rare, chronic disorder that affects cartilage throughout the body. This condition can cause inflammation in areas like the ears, nose, joints, and even the respiratory tract. What causes polychondritis? The exact cause remains unknown, but it's believed to be an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cartilage. Symptoms can vary widely, making it tricky to diagnose. Common signs include painful, swollen ears, a saddle nose deformity, and joint pain. Treatment often involves medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. Understanding polychondritis is crucial for managing its symptoms and improving quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Polychondritis is a rare condition where the body's immune system attacks its own cartilage, causing pain and swelling in areas like the ears, nose, and joints.
- While there is no cure for Polychondritis, treatments like medication, physical therapy, and support from healthcare providers and patient organizations can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
What is Polychondritis?
Polychondritis is a rare, chronic disorder characterized by recurrent inflammation of cartilage and other tissues throughout the body. This condition can affect various parts, including the ears, nose, joints, and respiratory tract.
- Polychondritis primarily affects cartilage, the flexible tissue found in many parts of the body.
- The condition is also known as Relapsing Polychondritis (RP).
- Symptoms often include pain, redness, and swelling in affected areas.
- The exact cause of Polychondritis remains unknown.
- It is considered an autoimmune disorder, where the body's immune system attacks its own cartilage.
Symptoms of Polychondritis
Understanding the symptoms can help in early diagnosis and management. These symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
- Ear inflammation is one of the most common symptoms.
- Nose cartilage can also become inflamed, leading to a saddle-nose deformity.
- Joint pain and swelling are frequent complaints.
- Eye inflammation, known as uveitis, can occur.
- Respiratory tract involvement can lead to breathing difficulties.
Diagnosis of Polychondritis
Diagnosing Polychondritis can be challenging due to its rarity and the variability of symptoms. Medical professionals use a combination of clinical evaluation and tests.
- Diagnosis often involves a thorough physical examination.
- Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation.
- Imaging studies like X-rays or MRIs may be used.
- Biopsies of affected cartilage can confirm the diagnosis.
- Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for Polychondritis, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used.
- Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and immune response.
- Immunosuppressive drugs may be prescribed.
- Biologic agents targeting specific immune pathways are sometimes used.
- Physical therapy can help maintain joint function.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with Polychondritis can be challenging, but understanding its impact can help individuals manage their condition better.
- Chronic pain can affect daily activities.
- Fatigue is a common issue among patients.
- Hearing loss may occur due to ear involvement.
- Vision problems can result from eye inflammation.
- Respiratory issues can limit physical activity.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Polychondritis and develop more effective treatments.
- Genetic studies are exploring potential hereditary factors.
- New biologic therapies are being tested in clinical trials.
- Research is focusing on identifying specific immune system targets.
- Patient registries are being established to collect data.
- Increased awareness and funding are needed for further research.
Support and Resources
Support from healthcare providers, family, and patient organizations can make a significant difference.
- Patient support groups offer emotional and practical assistance.
- Online forums provide a platform for sharing experiences.
- Educational resources can help patients and families understand the condition.
- Advocacy organizations work to raise awareness and funding.
- Mental health support is crucial for coping with chronic illness.
Interesting Facts About Polychondritis
Here are some lesser-known facts that highlight the uniqueness of this condition.
- Polychondritis can affect people of any age, but it most commonly appears in middle age.
- Both men and women are equally affected.
- The condition can sometimes be triggered by infections or trauma.
- Polychondritis is often associated with other autoimmune disorders.
- The name "Polychondritis" comes from Greek words meaning "many" and "cartilage."
Famous Cases and Awareness
Raising awareness through notable cases can help bring attention to Polychondritis.
- Some celebrities have publicly shared their experiences with Polychondritis.
- Awareness campaigns often feature personal stories to highlight the impact of the condition.
- World Polychondritis Day is observed to raise awareness.
- Social media plays a significant role in spreading information.
- Increased public awareness can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Polychondritis
Understanding Polychondritis is crucial for managing this complex condition. Here are a few more facts to consider.
- Polychondritis can sometimes go into remission, where symptoms temporarily improve.
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential.
- Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help manage symptoms.
- Stress management techniques can improve overall well-being.
- Ongoing research offers hope for better treatments and a potential cure in the future.
Final Thoughts on Polychondritis
Polychondritis is a rare, chronic disorder that affects cartilage throughout the body. Knowing the symptoms and treatment options can make a big difference in managing this condition. Early diagnosis is key to preventing severe complications. Treatments often include steroids and immunosuppressive drugs to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers ensure that the condition is monitored closely.
Support groups and online communities can offer emotional support and practical advice. Staying informed and proactive in your healthcare can lead to better outcomes. Remember, while polychondritis is challenging, many people lead fulfilling lives with proper management. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Knowledge and early intervention are your best tools in dealing with this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
